Application of micropeptide ASRPS in treating cancer
A micropeptide, cancer technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, to achieve the effect of inhibiting the formation of breast cancer blood vessels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] Example 1 ASRPS gene knockout promotes TNBC tumor growth
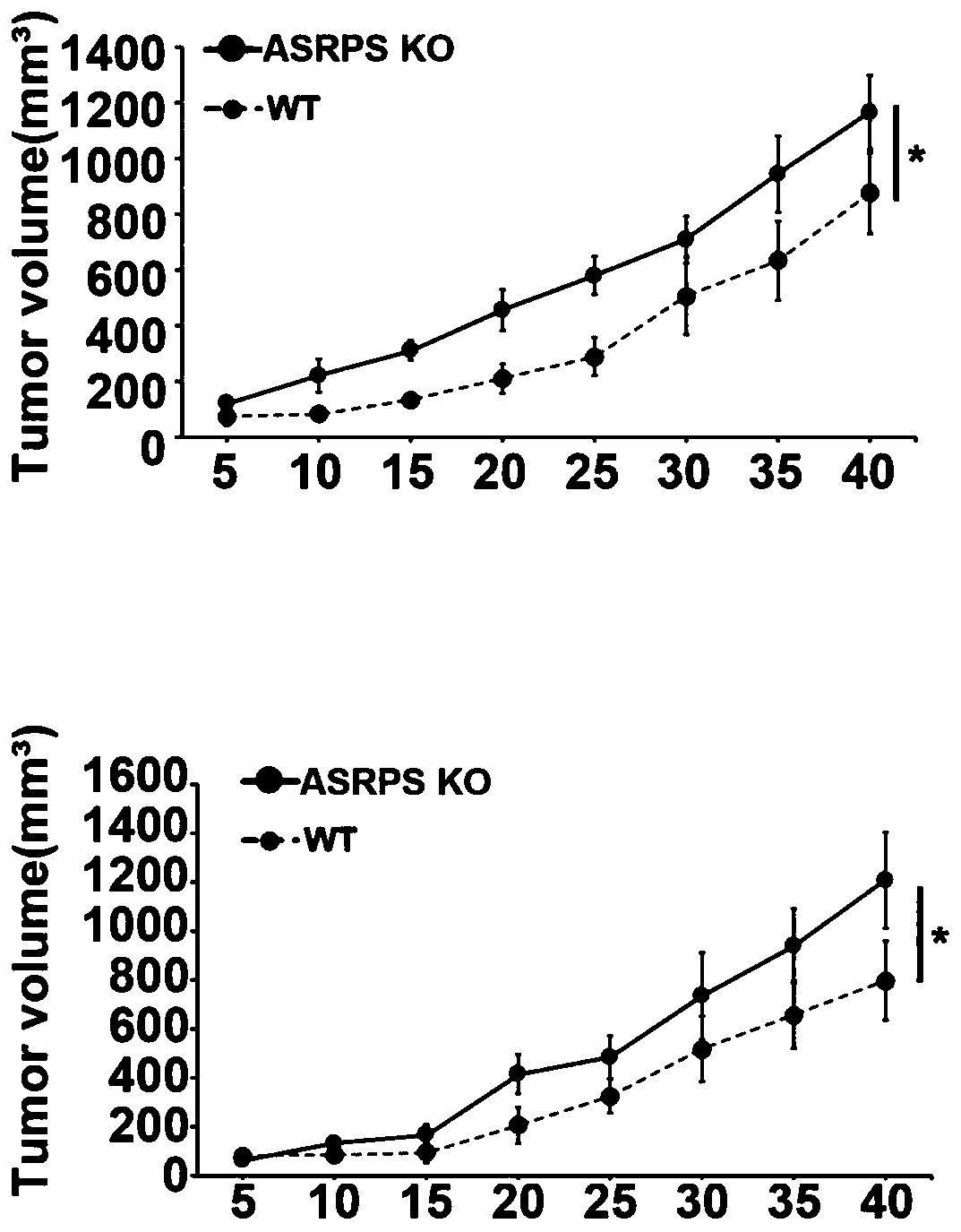
[0061] See Figure 1A to Figure 1D , experimentally determined the effect of ASRPS knockout on tumor growth using a mouse TNBC xenograft model.
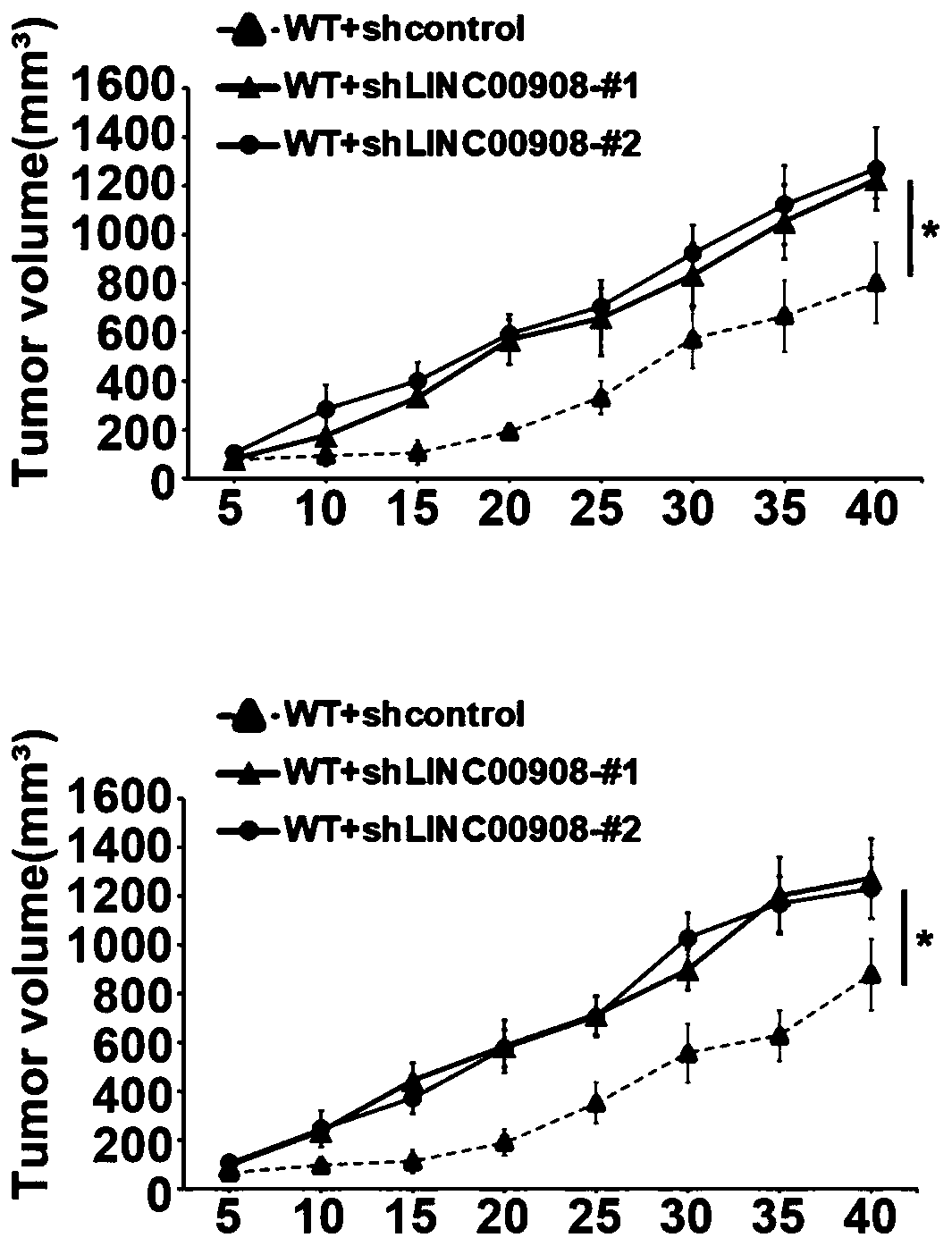
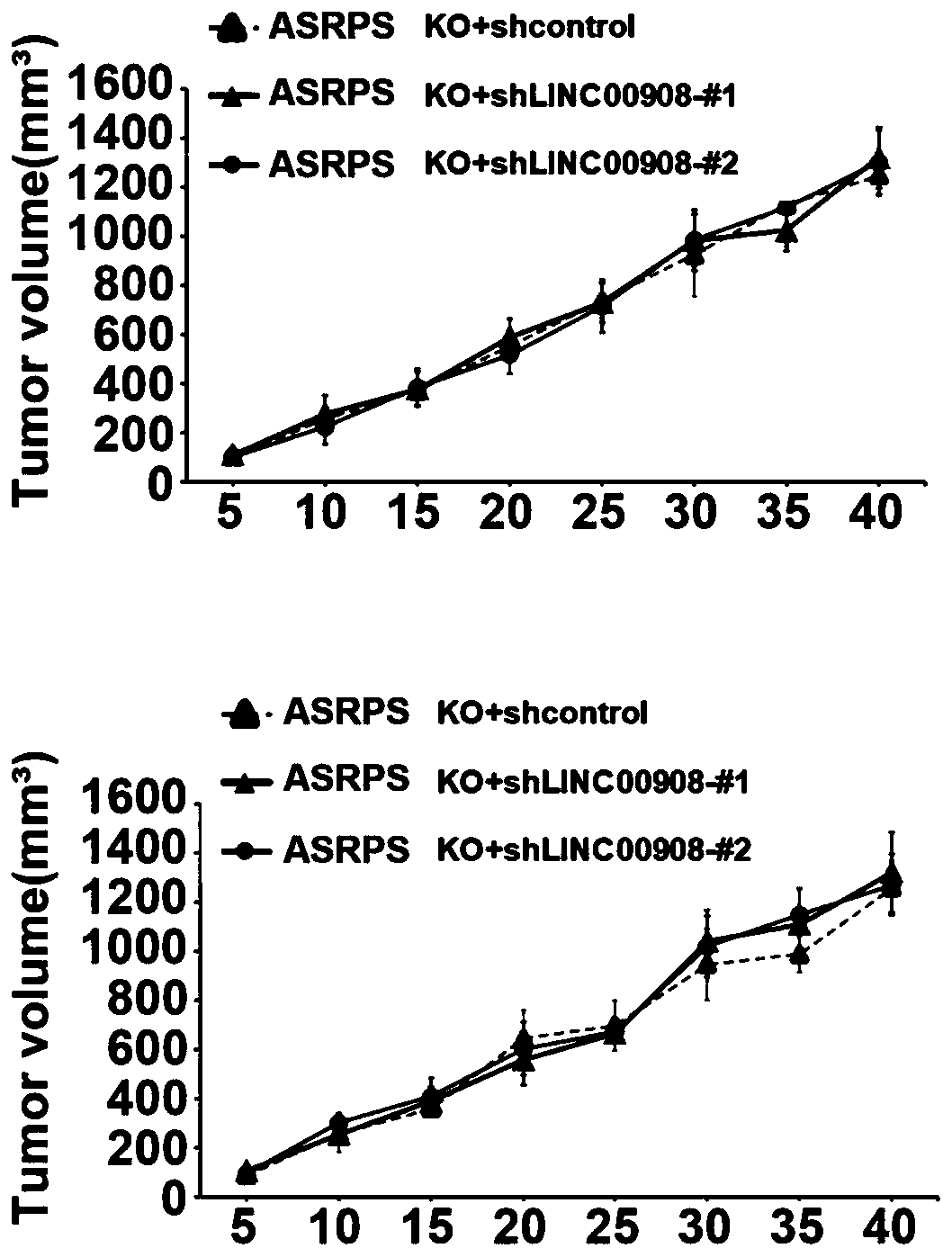
[0062] The inventors used a mouse TNBC xenograft model to study the effect of ASRPS gene knockout on tumor growth. The tumor volume line graph showed that the tumor growth of ASRPS knockout TNBC cells was significantly higher than that of wild-type TNBC cells ( Figure 1A ). To investigate the role of LINC00908 transcripts in TNBC tumor growth, we knocked out LINC00908 in wild-type and ASRPS knockout TNBC cells. We found that knockout of LINC00908 promoted the growth of wild-type TNBC cells but not ASRPS knockout TNBC cells ( Figure 1B and Figure 1C ).
[0063] Furthermore, we found that reintroduction of full-length LINC00908 or ASRPS in ASRPS knockout reversed tumor growth ( Figure 1D ). The results showed that ASRPS could significantly promote the growth o...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Example 2 Micropeptide ASRPS inhibits tumor angiogenesis
[0065] See Figure 2A to Figure 2D , the micropeptide ASRPS inhibits tumor angiogenesis.
[0066] The inventors cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) in conditioned medium prepared from MDA-MB-231 cells and Hs578T cells, and treated them with ASRPS overexpression and knockout. Using 3D spheroid-based in vitro angiogenesis assays, overexpressed ASRPS caused HUVECs to produce shorter shoots than controls, and knockdown of ASRPS strongly promoted shoot growth compared with WT ( Figure 2A ). Next, we performed the Matrigel plug angiogenesis assay in vivo. When Matrigel was mixed with ASRPS overexpression cell culture medium, the Matrigel plug was light white, while the ASRPS removal group was bright red, HE results showed that the more ASRPS, the more blood vessels ( Figure 2B ). Next, the inventors used a mouse xenograft model to determine the effect of ASRPS overexpression and gene knockou...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Example 3 Micropeptide ASRPS inhibits angiogenesis of breast cancer in MMTV-PyMT mice
[0068] See Figure 3A to Figure 3B , Effect of micropeptide ASRPS on angiogenesis of breast cancer in MMTV-PyMT mice.
[0069] To gain insight into the effect of ASRPS on breast cancer angiogenesis, the inventors applied ASRPS to 186B / 6 mice crossed with MMTV-PyMT mice to generate MMTV-PyMT;ASRPS+ / + mice. Anti-CD31 immunohistochemical staining showed that tumor vessel recruitment in MMTV-PyMT and ASRPS+ / + mice decreased ( Figure 3A ). Furthermore, to investigate the effect of exogenous ASRPS treatment on angiogenesis, we injected ASRPS into the mammary pads of MMTV-PyMT mice and demonstrated that ASRPS can significantly inhibit primary tumor angiogenesis ( Figure 3B ). In conclusion, the micropeptide ASRPS has an important anti-angiogenic effect in the MMTV-PyMT mouse model.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com