Method for in-situ no-damage determination of biomass of submerged plant
A technology for submerged plants and biomass, which is applied to measuring devices, processing response signals of detection, and analyzing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic waves, achieving the effects of simple operation, easy method and small estimation error.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
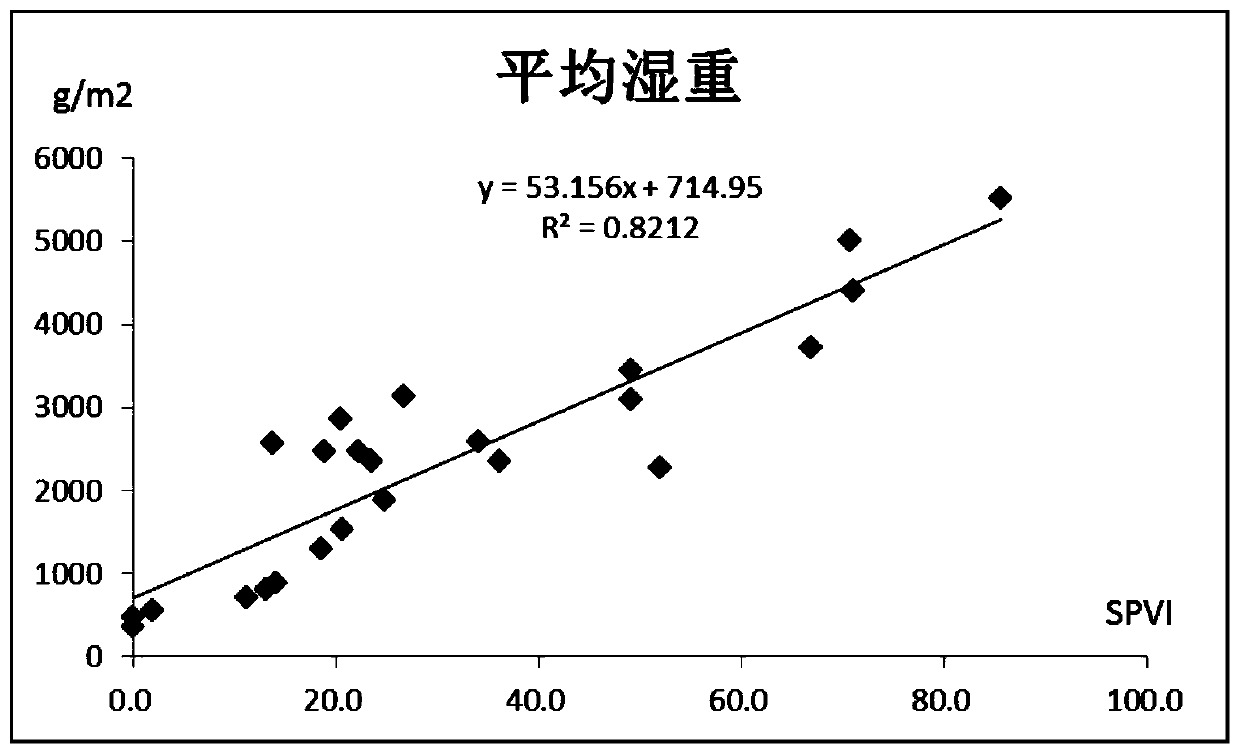
[0035] Taking the investigation of the submerged plant biomass in a certain water area of Hangzhou West Lake as an example, the main communities of the submerged plant in this water area are bitter grass and black algae, and the method of the present invention can be utilized to investigate the submerged plant biomass in this water area.
[0036] A method for measuring the biomass of submerged plants without damage in situ, the steps are:
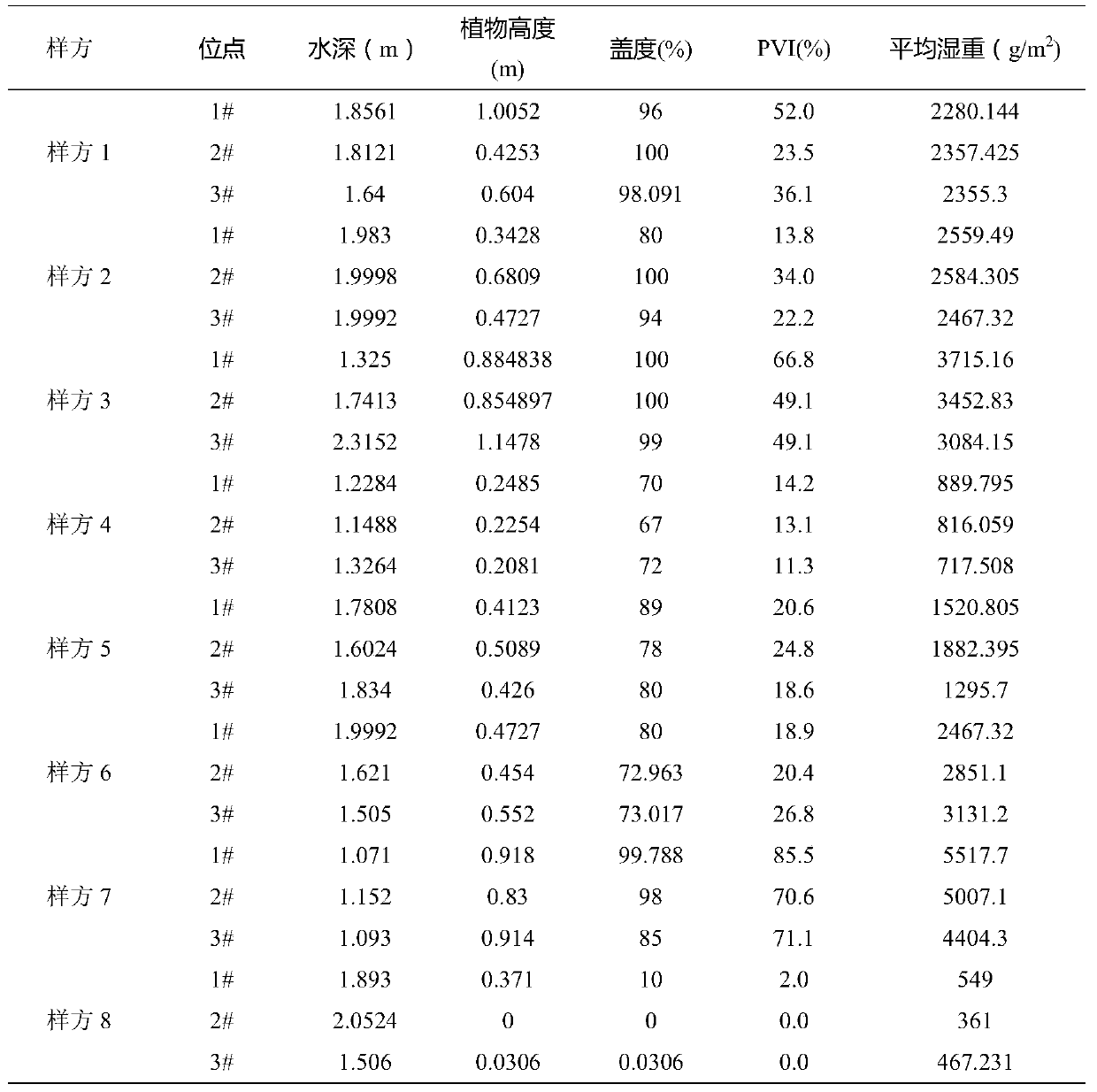
[0037] (1) Fence the waters and set up cross-sections: 8 waters quadrats will be enclosed in a certain waters of Hangzhou West Lake under investigation, and marked in order. The average area of the waters quadrats is 4000m 2 , the cross-section design is carried out in the sample quadrat, the average section interval is 8m, each sample has 3 sampling points, and the surveyed water area is 38000m 2 .
[0038] (2) Determination of the characteristic parameters of submerged plants: the survey was carried out with the average ship speed of...
Embodiment 2
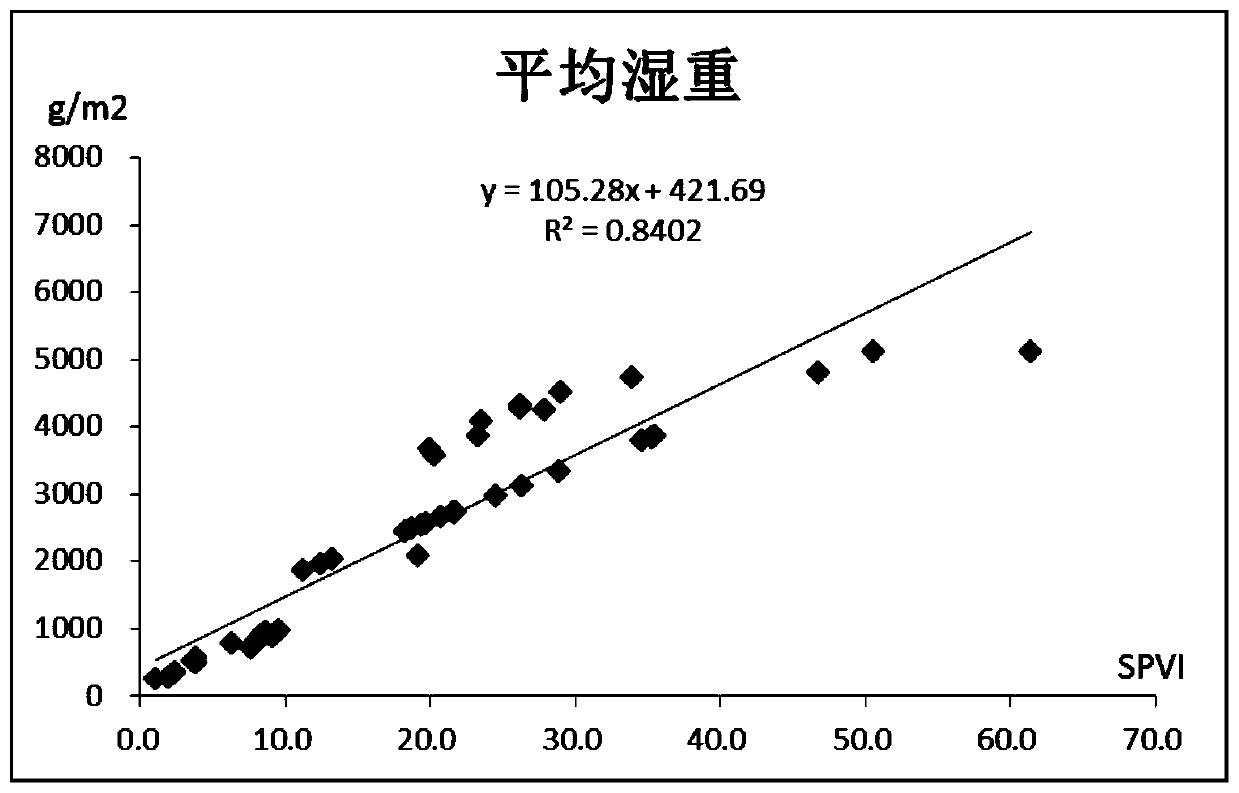
[0053] Taking the investigation of the submerged plant biomass in a certain water area of Wuhan East Lake as an example, the main communities of the submerged plant in this water area are hornwort, galeria, and black algae. The method of the present invention can be used to investigate the submerged plant biomass in this water area.
[0054] A method for measuring the biomass of submerged plants without damage in situ, the steps are:
[0055] (1) Fence waters and set up cross-sections: 15 waters quadrats were enclosed in a certain waters surveyed in Wuhan East Lake, and marked in order. The average area of waters quadrats was 3300m 2 , the cross-section design is carried out in the quadrat, the average cross-section interval is 10m, each quadrat has 3 sampling points, and the surveyed water area is 50000m 2 .
[0056] (2) Determination of the characteristic parameters of submerged plants: the survey was carried out with an average ship speed of 1.8km / h, and the water dept...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com