LiDAR point cloud no-initial-value registration method based on planar feature constraint
A plane and point cloud technology, applied in image data processing, instrumentation, calculation, etc., can solve problems such as incorrect results, non-convergence of functions, weak selection dependence, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
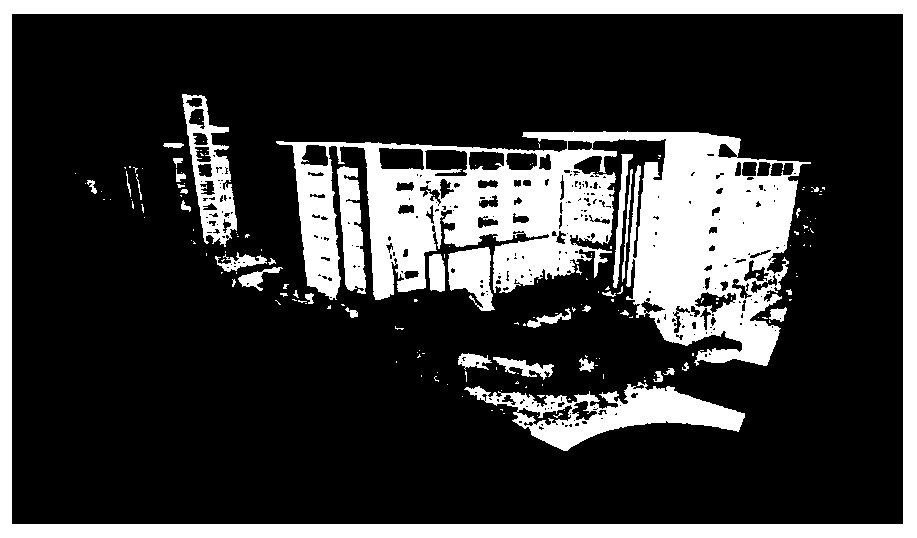
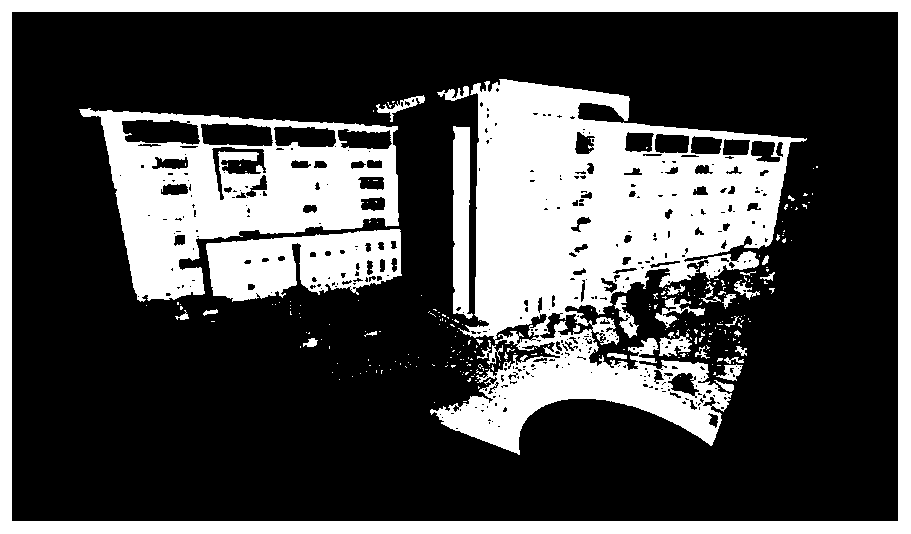
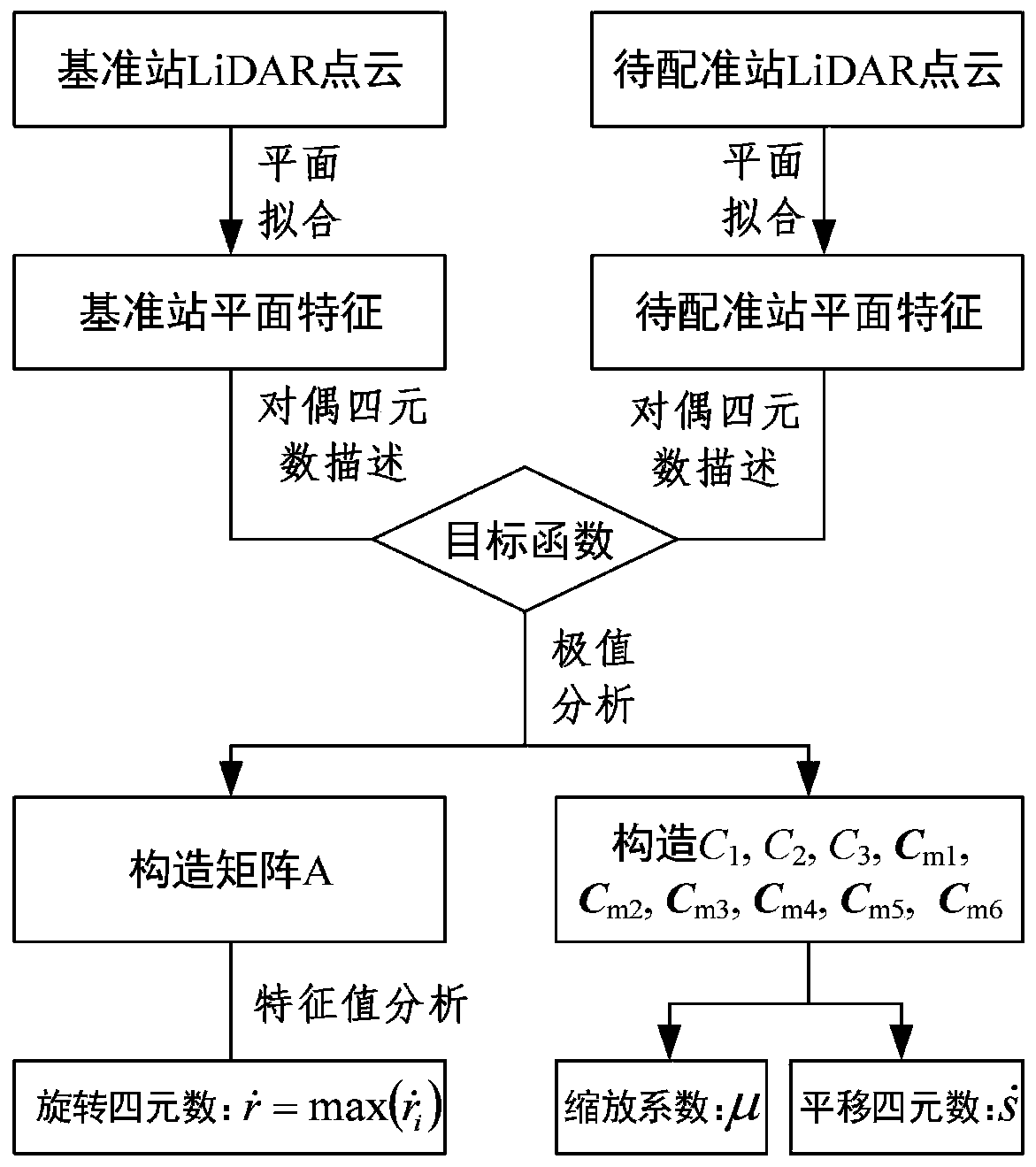
[0046] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, as figure 1 The illustrated invention includes the following steps.
[0047] 1. Planar feature extraction and expression based on LiDAR point cloud
[0048] Determine and select the LiDAR point cloud belonging to the target plane feature through human-computer interaction, and realize the fitting of the plane feature according to the least squares criterion.
[0049] In order to realize the uniqueness of the mathematical expression of the planar features in the three-dimensional space, the extracted planar features are processed as follows:
[0050] 1) Unitize the normal direction of the plane, namely
[0051] 2) The distance m from the coordinate origin to the plane (also known as the modulus of the plane) is used as the fourth element of the plane expression, and the normal vector of the plane is known with any point it passes through The expression modulo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com