Salt-free printing and dyeing additive applied to blend fiber and preparation method of additive
A technology of blended fibers and printing and dyeing auxiliaries, which is applied in dyeing, textiles and papermaking, and can solve problems such as environmental damage, fiber-to-fiber color difference, and achieve environmental protection and good coloring effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] A preparation method for a salt-free printing and dyeing auxiliary applied to blended fibers, comprising the following steps:
[0026] A. At room temperature, add water to the reaction kettle, set the rotation speed to 350rpm, add ethylene glycol monobutyl ether, and stir for 22min;
[0027] B, then add sodium carboxymethylcellulose and polyoxyethylene alkylphenol ether, stir 12min;
[0028] C. Finally, raise the temperature to 68°C, adjust the rotation speed to 280rpm, add monoalkyl phosphate and rhamnose, and stir at constant temperature for 32min.
[0029] The salt-free printing and dyeing auxiliary agent applied to blended fibers is composed of the following components in weight percentage: 24% of ethylene glycol monobutyl ether, 8% of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, 7% of monoalkyl phosphate, 13% rhamnose, 5% polyoxyethylene alkylphenol ether and the balance of water;
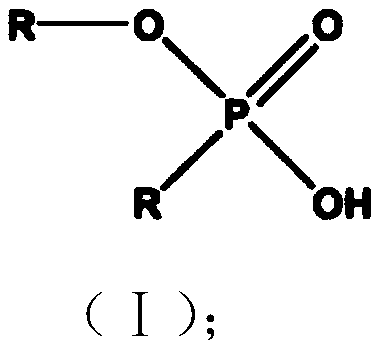
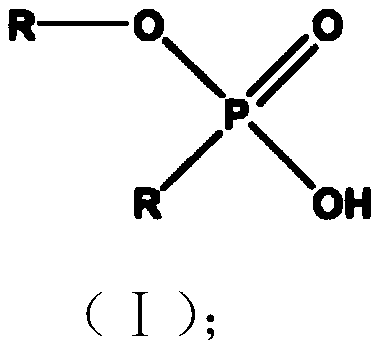
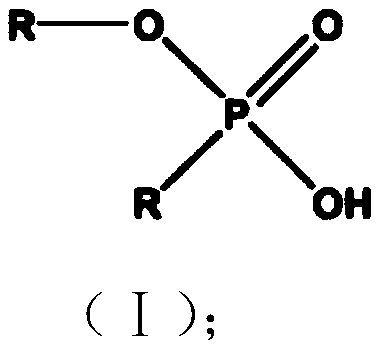
[0030] The structural formula (I) of described alkyl phosphate monoalkyl ester is as follows: ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] A preparation method for a salt-free printing and dyeing auxiliary applied to blended fibers, comprising the following steps:
[0035] A. At room temperature, add water to the reaction kettle, set the rotation speed to 400rpm, add ethylene glycol monobutyl ether, and stir for 15min;
[0036] B, then add sodium carboxymethylcellulose and polyoxyethylene alkylphenol ether, stir 15min;
[0037] C. Finally, raise the temperature to 60°C, adjust the rotation speed to 300rpm, add monoalkyl phosphate and rhamnose, and stir at constant temperature for 30 minutes.
[0038] The salt-free printing and dyeing auxiliary agent applied to blended fibers is composed of the following components in weight percentage: 30% of ethylene glycol monobutyl ether, 6% of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, 8% of monoalkyl phosphate, 8% rhamnose, 6% polyoxyethylene alkylphenol ether and the balance of water.
[0039] The structural formula (I) of described alkyl phosphate monoalkyl ester is as follo...
Embodiment 3
[0043] A preparation method for a salt-free printing and dyeing auxiliary applied to blended fibers, comprising the following steps:
[0044] A. At room temperature, add water to the reaction kettle, set the rotation speed to 300rpm, add ethylene glycol monobutyl ether, and stir for 25min;
[0045] B, then add sodium carboxymethylcellulose and polyoxyethylene alkylphenol ether, stir 8min;
[0046] C. Finally, raise the temperature to 70°C, adjust the rotation speed to 250rpm, add monoalkyl phosphate and rhamnose, and stir at constant temperature for 40 minutes.
[0047] The salt-free printing and dyeing auxiliary agent applied to blended fibers is composed of the following components in weight percentage: 20% ethylene glycol monobutyl ether, 10% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, 4% monoalkyl phosphate, 15% rhamnose, 3% polyoxyethylene alkylphenol ether and the balance of water.
[0048] The structural formula (I) of described alkyl phosphate monoalkyl ester is as follows:
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com