Strengthening-toughening treatment process for high-strength martensite/ferrite dual-phase steel, and dual-phase steel
A treatment process and ferrite technology, applied in the field of steel processing, can solve the problems of unfavorable plasticity increase, inability to obtain high strength, reduction and other problems, and achieve the effect of improving strength and toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
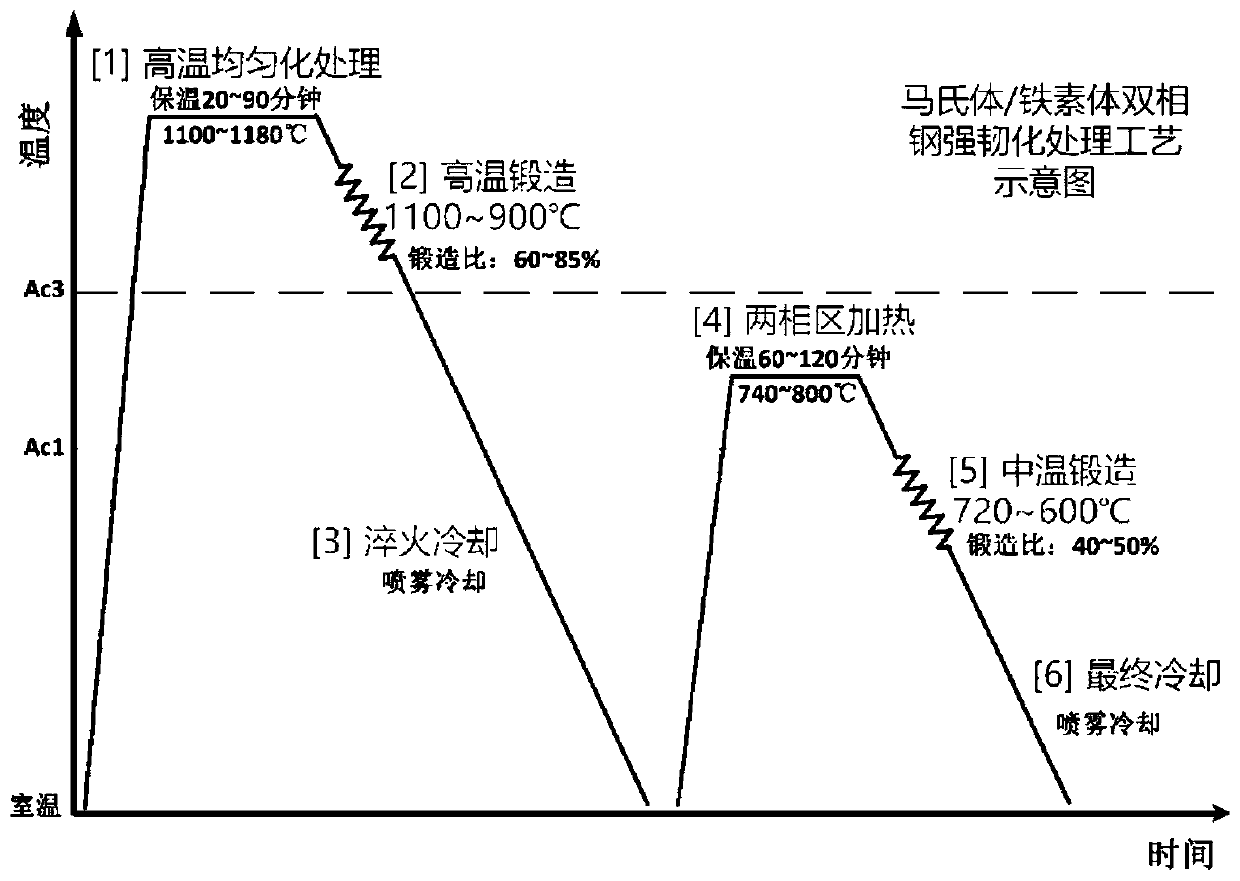
[0038] A high-strength martensitic / ferritic dual-phase steel strengthening and toughening treatment process, the material is 15Mn2Si2Cr1Mo, the weight is 16Kg, and the main components are C: 0.15%, Mn: 2.3%, Si: 1.5%, Cr: 1%, Also contains a small amount of Mo (<0.5%).
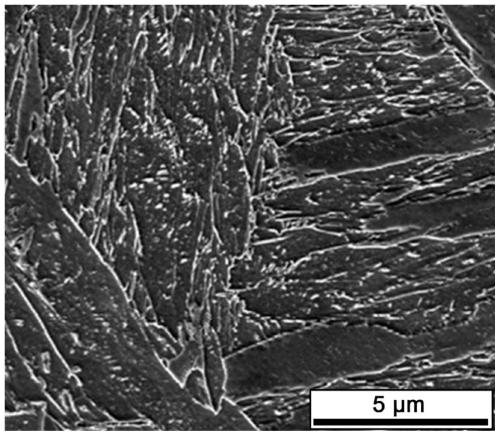
[0039] The specific process is: (1) high-temperature homogenization treatment: the steel ingot is heated to 1150°C in an atmosphere protection furnace, and held for 60 minutes for high-temperature homogenization treatment to obtain a single-phase austenite structure; (2) high-temperature forging: the steel ingot is heated by an atmosphere Take it out of the protective furnace, and immediately carry out high-temperature forging. The final forging temperature is about 920°C, and the forging ratio is about 85%; (3) Quenching and cooling: After high-temperature forging, the ingot is spray-cooled to room temperature to obtain a fine lath martensitic structure ,like figure 2 shown; (4) Heating in the two-phase zon...
Embodiment 2
[0042] A high-strength martensite / ferrite dual-phase steel strengthening and toughening treatment process, the material is 18Mn2Si1Cr1Mo, and the weight is 10Kg. The difference from Example 1 is that the homogenization treatment temperature is 1120°C, the high-temperature forging ratio is 75%, the heating temperature in the two-phase zone is 760°C, and the medium-temperature forging ratio is 50%. Carry out mechanical property test to embodiment 2, tensile strength σ b =1370±20MPa, yield strength σ s =820±15MPa, elongation δ≈16%.
Embodiment 3
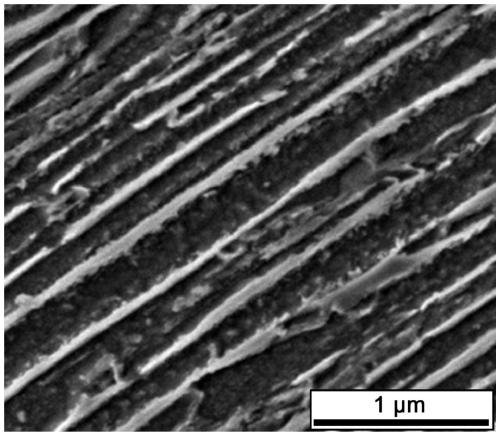
[0044] This case is used for comparison with Case 1 and Case 2, and the material of this comparative example is 18Mn2Si1Cr1Mo. The traditional process is used for processing, first heating to 920°C, holding for 20 minutes, then cooling to 780°C, holding for 30 minutes, and finally spraying and cooling to room temperature (without high-temperature homogenization treatment, high-temperature forging and medium-temperature forging). After this process, the microstructure of the dual-phase steel has coarse particles, and no lamellar structure is observed, such as Figure 4 shown. Tensile strength σ b =915±10MPa, yield strength σ s =560±10MPa, elongation δ≈6%. It can be seen that the strength and toughness of the "lamellar ferrite + lamellar lath martensite" dual-phase steel after the strengthening and toughening treatment by the process of the present invention can be significantly improved.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com