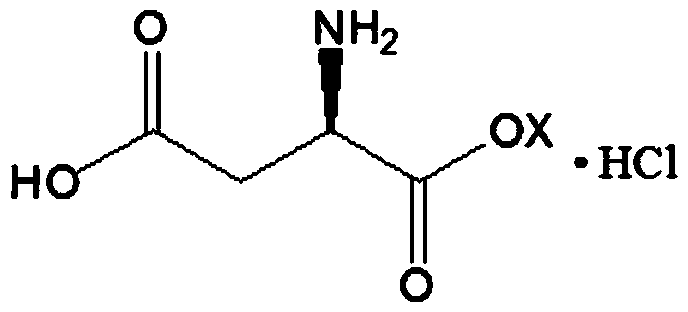
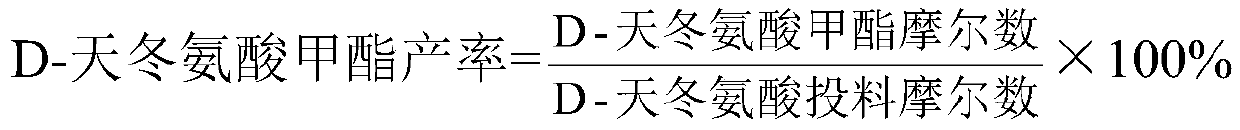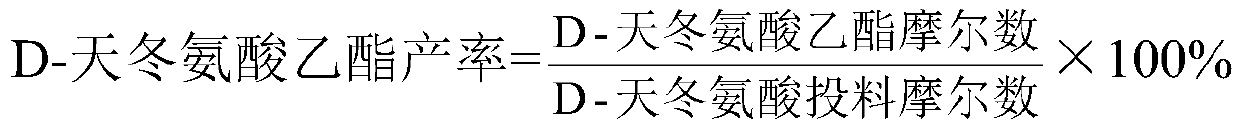D-aspartic acid derivative and preparation method thereof
A technology of aspartic acid and derivatives, applied in the field of D-aspartic acid derivatives and their preparation, can solve the problems of many side reactions, long reaction time, low yield and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] This example provides a preparation method of D-aspartic acid derivatives.
[0022] Specifically include the following steps:
[0023] 1. Preparation of D-Aspartic Acid
[0024] Dissolve DL-aspartic acid at a concentration of 13.3g / L (0.1-4M) in water at 20°C, and control the pH range from 2.0 to 12.0, and cells containing L-aspartic acid-α-decarboxylase (detection activity meets every gram per hour> 120 μ mol) drop in the substrate, the addition amount of L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase is 1 / 2 of the substrate, heat preservation reaction is transformed completely to the substrate, and the gained material is liquid-solid After liquid separation, acid was added to adjust the pH of the obtained filtrate to 2.8-2.9, and the temperature was maintained at 48-50°C, and white crystals were precipitated from the filtrate. Filter after 30 minutes, wash the obtained white crystals with 0.2 times the volume of water, and vacuum dry at 100-120°C to obtain the finished product...
Embodiment 2
[0030] This example provides a preparation method of D-aspartic acid derivatives.
[0031] Specifically include the following steps:
[0032] 1. Preparation of D-Aspartic Acid
[0033] DL-aspartic acid with a concentration of 133g / L (1M) was dissolved in water at 40°C, and the pH range was controlled within 2.0 to 12.0, and the cell extract containing L-aspartic acid-α-decarboxylase ( The detected activity conforms to the per hour per gram > 120 μmol) into the substrate, the amount of L-aspartic acid-α-decarboxylase added is 1 / 3 of the substrate, and the reaction is incubated until the substrate is completely converted, and the obtained material is liquid-solid-liquid After separation, acid was added to adjust the pH of the resulting filtrate to 2.9-3.0, and the temperature was maintained at 46-48°C, and white crystals were precipitated from the filtrate. After 30 minutes, filter, wash the obtained white crystals with 0.5 times the volume of water, and vacuum-dry at 80-100°C...
Embodiment 3
[0039] This example provides a preparation method of D-aspartic acid derivatives.
[0040] Specifically include the following steps:
[0041] 1. Preparation of D-Aspartic Acid
[0042] Dissolve DL-aspartic acid hydrochloride with a concentration of 266g / L (2M) in water at 50°C, and control the pH range from 2.0 to 12.0, and the cells containing L-aspartic acid-α-decarboxylase and its extract (detection activity conforms to >120 μmol per hour per gram) into the substrate, the amount of L-aspartic acid-α-decarboxylase added is 1 / 5 of the substrate, and the reaction is incubated until the substrate is completely converted. After the solid-liquid separation of the obtained material and liquid, acid is added to adjust the pH of the obtained filtrate to 2.8-2.9, and the temperature is maintained at 44-56° C., and white crystals are precipitated from the filtrate. Filter after 30 minutes, wash the obtained white crystals with 1 volume of water, and vacuum dry at 60-80°C to obtain t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com