Photonic frequency up-conversion device and growth method thereof
A growth method and frequency technology, applied in the field of photon frequency up-conversion devices and their growth, can solve the problems of limiting the application of up-conversion devices, high cost, cumbersome preparation process, etc., and achieve low-cost large-scale preparation, compact structure, and high-quality devices Effect of Up-Conversion Efficiency Improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
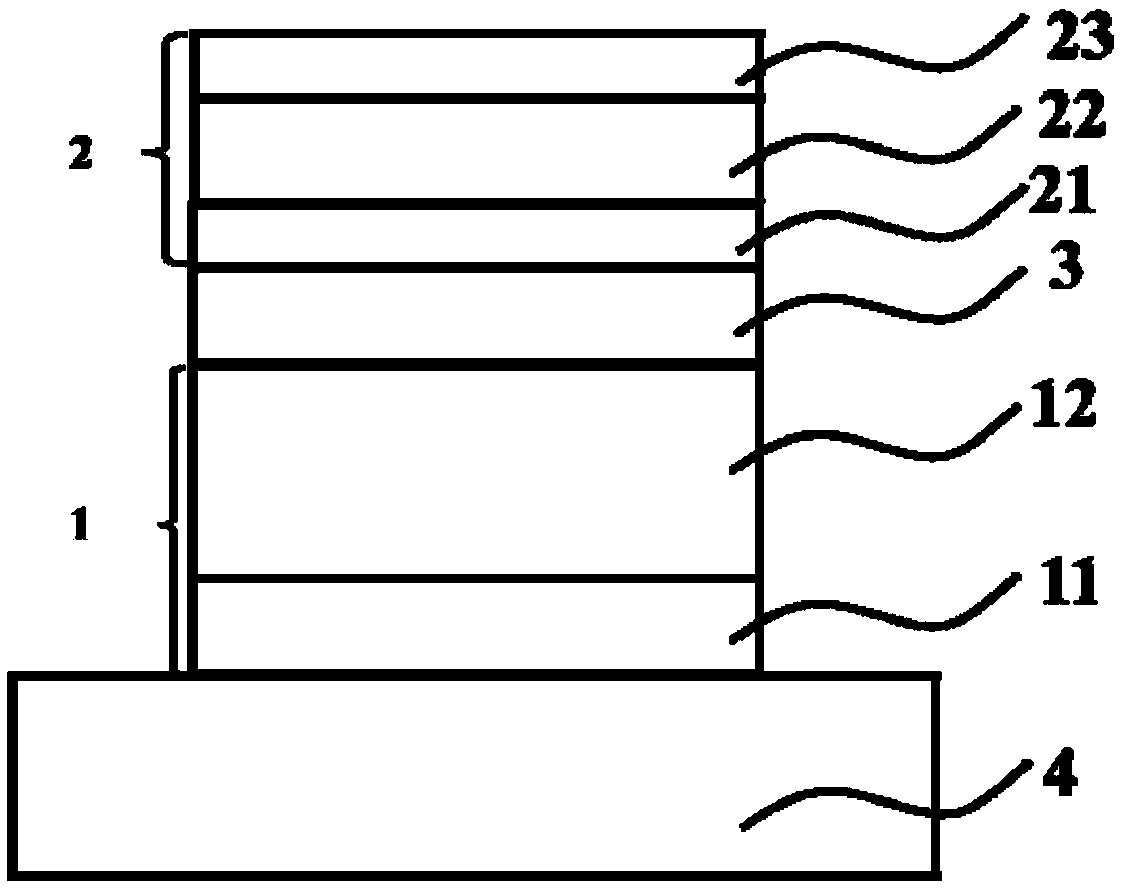
[0117] A photonic frequency upconversion device grown by direct epitaxial growth, such as Figure 8 As shown, it is a near-infrared photon frequency up-conversion device for direct epitaxial growth of the present invention, including three parts: a near-infrared detector 1, a graded layer 3 and a light-emitting diode 2; wherein the near-infrared detector 1 absorbs the incident near-infrared light signal, It is converted into photo-generated carriers, and the generated photo-generated carriers will migrate to the active region of the light-emitting diode 2 under the action of an electric field for radiative recombination to emit short-wave near-infrared photons or visible photons, thereby realizing up-conversion. During growth, the near-infrared photon frequency up-conversion device is obtained by direct epitaxial growth on a substrate with a thickness of 500 μm and a substrate layer 4 of InP by MBE method. During epitaxy, the near-infrared detector 1 is epitaxially grown on th...
Embodiment 2
[0122] A photonic frequency upconversion device grown by direct epitaxial growth, such as Figure 9 As shown, it is a near-infrared photon frequency up-conversion device for direct epitaxial growth of the present invention. During growth, the near-infrared photon frequency up-conversion device is directly epitaxially grown on a substrate with a thickness of 700um and a substrate layer 4 of InP by MOCVD method get. During epitaxy, the near-infrared detector 1 is epitaxially grown on the InP first, then the gradient layer is epitaxially grown on the p-type InP of the near-infrared detector 1 , and finally the light-emitting diode 2 is epitaxially grown on the gradient layer 3 .
[0123] The near-infrared detector 1 is InP / In containing a P-type cap layer 13 0.53 Ga 0.47 As p-i-n infrared detector: the n-type cap layer 11 is n-type InP with a thickness of 400nm; the intrinsic absorption layer 12 is InGaAs with a thickness of 2μm, and the p-type cap layer 13 is p-type InP with a...
Embodiment 3
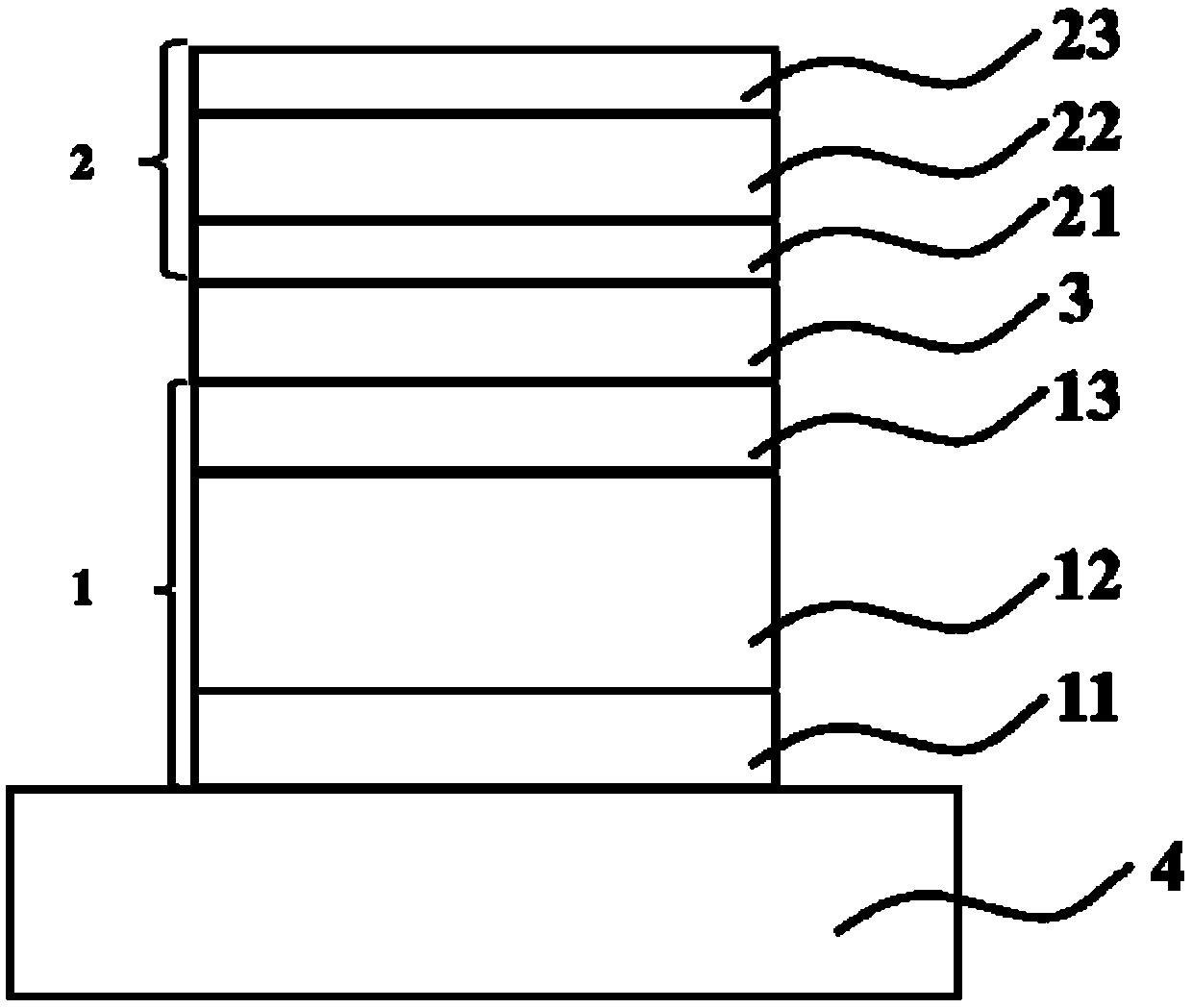
[0127] A photonic frequency upconversion device grown by direct epitaxial growth, such as Figure 10 As shown, it is a near-infrared photon frequency up-conversion device grown by direct epitaxial growth in the present invention, which includes a near-infrared detector 1 , a graded layer 3 and a light-emitting diode 2 . During growth, the near-infrared photon frequency up-conversion device is obtained by direct epitaxial growth on a substrate with a thickness of 600 um and a substrate layer 4 of InP by CVD. During epitaxy, the near-infrared detector 1 is epitaxially grown on InP first, then the gradient layer 3 is epitaxially grown on the intrinsic absorption layer 12 of the near-infrared detector 1 , and finally the light-emitting diode 2 is epitaxially grown on the gradient layer 3 .
[0128] The near-infrared detector 1 is an InP / InGaAs n-i infrared detector without a p-type cap layer: the n-type cap layer 11 is n-type InP with a thickness of 600 nm; the intrinsic absorptio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Luminous wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com