Method for regulating and controlling stress relaxation and reprocessing molding temperature of vitrimer material by using content of dynamic bonds
A polymer material and stress relaxation technology, applied in the direction of plastic recycling, recycling technology, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in releasing stress, inability to recycle, inability to reprocess and shape, and achieve the effect of accelerating application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
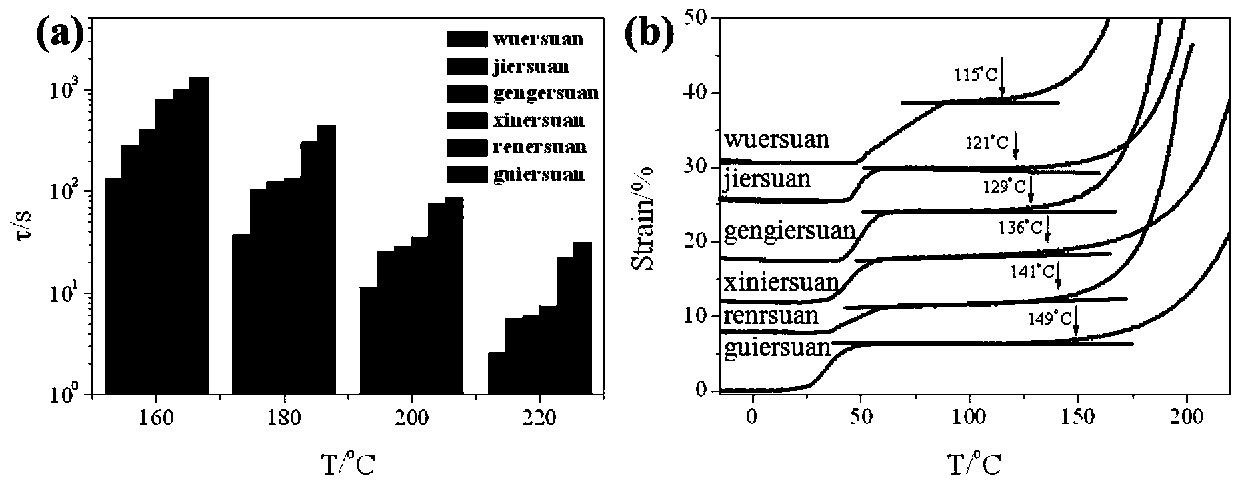
[0019] The curing agent with different contents of carboxylic acid is used to react with epoxy resin to carry out cross-linking, so as to obtain dynamic carboxylate bond type glass epoxy polymers with different contents. The specific preparation process is as follows: bisphenol A glycidyl ether is used as a reactive monomer, and glutaric acid, adipic acid, pimelic acid, suberic acid, azelaic acid and sebacic acid are used as curing agents respectively, 1 , 5,7-Triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene was used as a catalyst and reacted at 180°C for 4 hours to prepare glass-like epoxy polymers with different contents of dynamic carboxylate bonds. Glutaric acid-based glass-like epoxy polymers had the highest content of dynamic carboxylate linkages and sebacic acid-based glass-like epoxy polymers had the lowest content of dynamic carboxylate linkages. Although both the reactive monomer and the curing agent are double crown energy compounds, the hydroxyl group generated by the reaction of car...
Embodiment 2
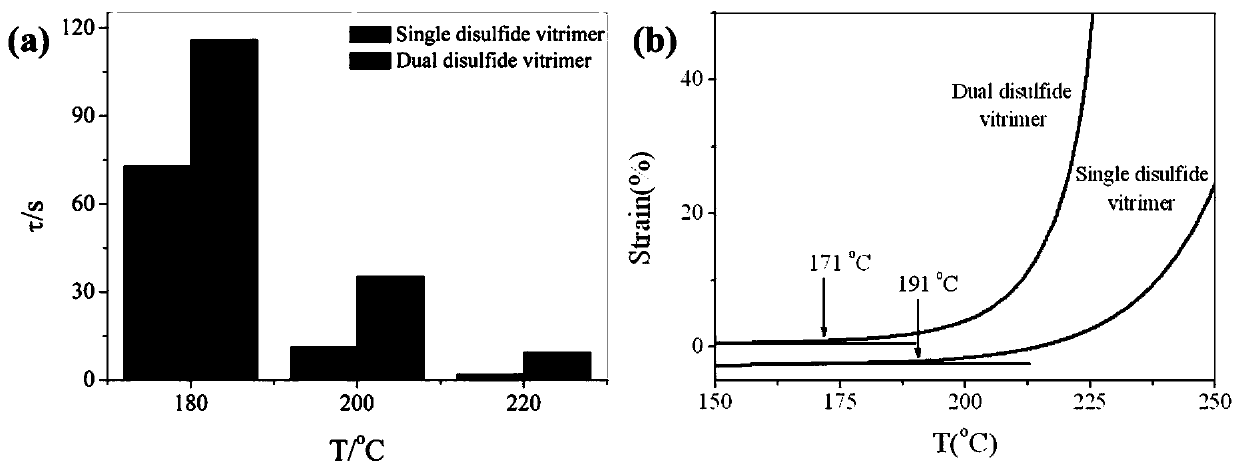
[0021] Use epoxy monomers with aromatic disulfide bonds and epoxy monomers without aromatic disulfide bonds to react with epoxy curing agents with aromatic disulfide bonds at high temperatures to obtain aromatic disulfide bonds with different contents. Glass-like epoxy polymer. The specific preparation process is as follows, using dithiodiphenyl diglycidyl ether or bisphenol A diglycidyl ether as the epoxy monomer, dithiodiphenylamine as the epoxy curing agent, and reacting at 160 degrees for 3 hours, Prepare glass-like epoxy polymers with different contents of aromatic disulfide bonds (because the activity of aromatic disulfide bonds is higher, the exchange reaction does not require a catalyst, so there is no need to add a catalyst here). Among them, the content of aromatic disulfide bonds in the glass-like epoxy polymer based on dithiodiphenyl diglycidyl ether is higher than that of the glass-like epoxy polymer based on bisphenol A diglycidyl ether. Such as figure 2 It is...
Embodiment 3
[0023] The curing agent with different contents of carboxylic acid is used to react with epoxy resin to carry out cross-linking, so as to obtain dynamic carboxylate bond type glass epoxy polymers with different contents. The specific preparation process is as follows: bisphenol A glycidyl ether is used as a reactive monomer, and sebacic acid, azelaic acid, suberic acid, pimelic acid, adipic acid and glutaric acid are respectively used as curing agents, 1 , 5,7-Triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene was used as a catalyst and reacted at 180°C for 4 hours to prepare glass-like epoxy polymers with different contents of dynamic carboxylate bonds. The glass-like epoxy polymer based on sebacic acid had the lowest content of dynamic carboxylate linkages, and the glass-like epoxy polymer based on glutaric acid had the highest content of dynamic carboxylate linkages. Although both the reactive monomer and the curing agent are double crown energy compounds, the hydroxyl group generated by the re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com