Microbial in-situ sand consolidation method for loose sandstone reservoir
A technology for sandstone reservoirs and microorganisms, which is applied in earthwork drilling, production fluids, wellbore/well components, etc., to achieve the effects of reducing sand production, increasing liquid production, and facilitating field promotion and application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
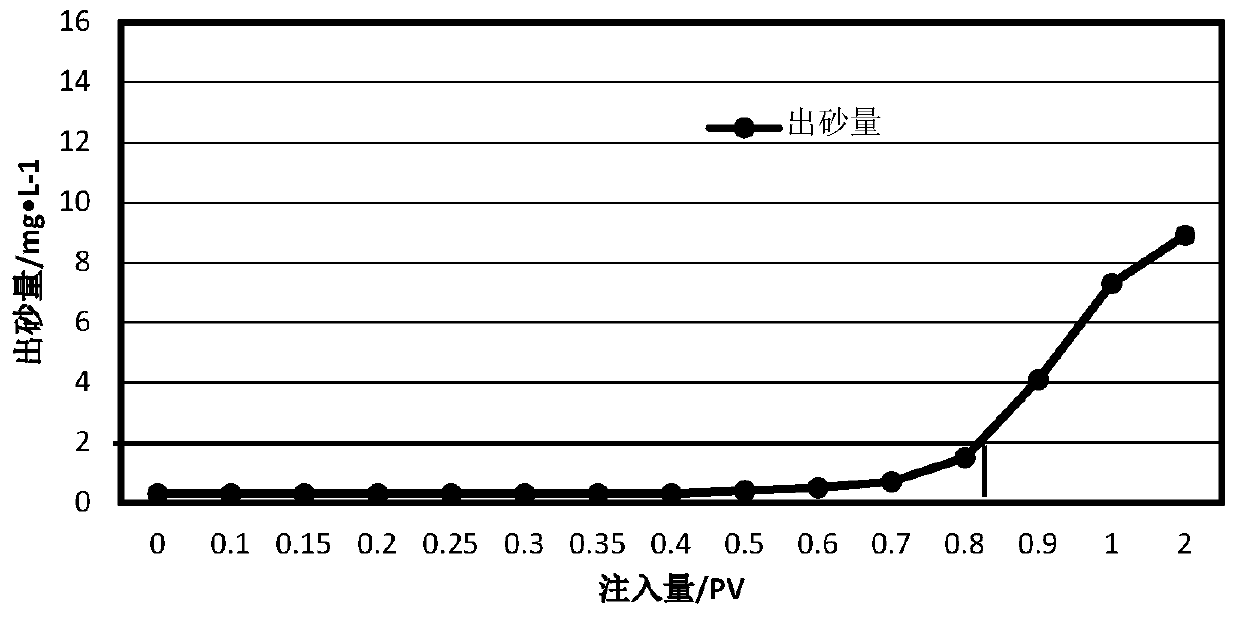
[0044] GN in a block of Shengli Oilfield 11 Reservoir temperature is 40°C, porosity is 32%, average permeability is 1200×10 -3 μm 2 , belonging to unconsolidated sandstone reservoirs, with a shale content of 18%. Before the test, the comprehensive water content of the block was 97.5%, the daily oil production was 2.5t / d, and the daily liquid production was 50m 3 / d. There is a serious sand production problem in this block, which leads to the phenomenon of low oil well fluid volume and poor productivity in this block. The sand content and ion composition in the produced fluid of this block were measured. The test results are shown in Table 1. Using the method of the present invention to block GN 11 Implement sand control and increase fluid production in this block.
[0045] Table 1 Block GN 11 Produced fluid performance test results
[0046] parameter Sand content total salinity water type Calciummg / L Magnesiummg / L Ferrous mg / L Potassium mg / L ...
Embodiment 2
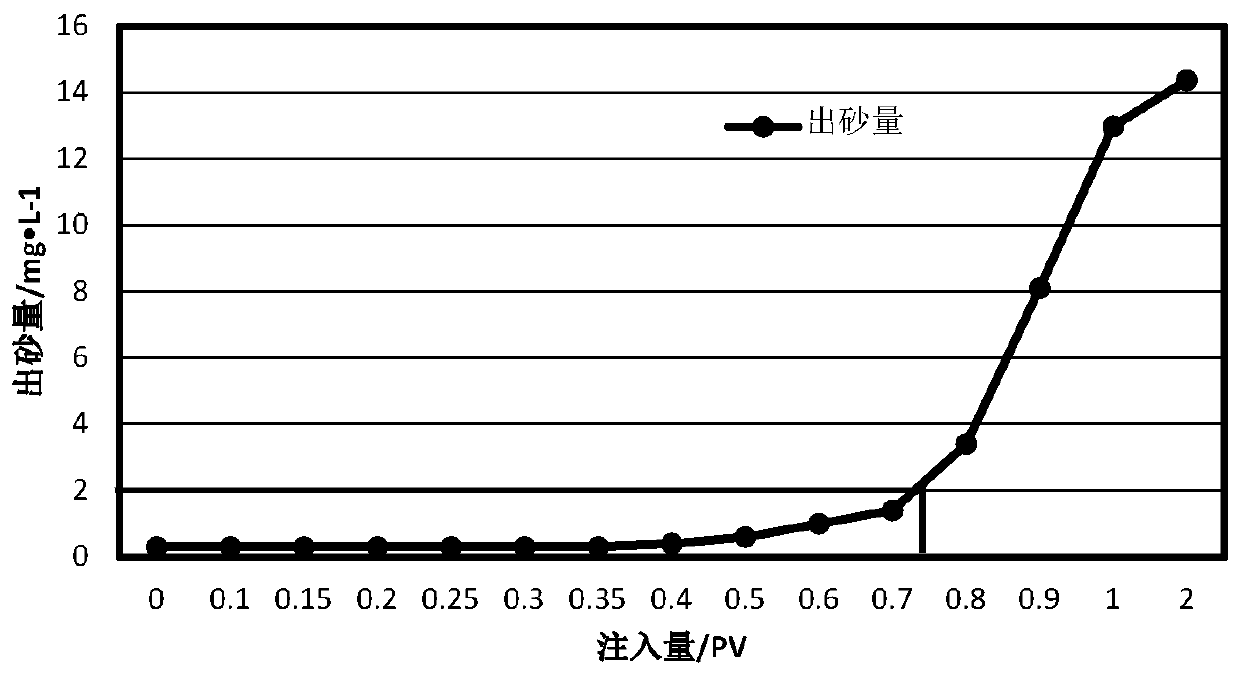
[0073] A block B of Shengli Oilfield 43 The reservoir temperature is 55°C, the porosity is 28%, and the average permeability is 2500×10 -3 μm 2 , belonging to unconsolidated sandstone reservoirs, with a shale content of 22%. Before the test, the water content of the block was 88.5%, the daily oil production was 3.5t / d, and the daily liquid production was 60m3 / d. The block B 43 There is a serious problem of sand production, which leads to the phenomenon of low fluid volume and poor productivity in this well. The sand content and ion composition of the produced fluid in this block were measured. The test results are shown in Table 5. Utilize the method of the present invention to block B 43 Implement sand control and increase fluid production in this block.
[0074] Table 5 Block B 43 Produced fluid performance test results
[0075] parameter Sand content total salinity water type Calciummg / L Magnesiummg / L Ferrous mg / L Potassium mg / L value / ...
Embodiment 3
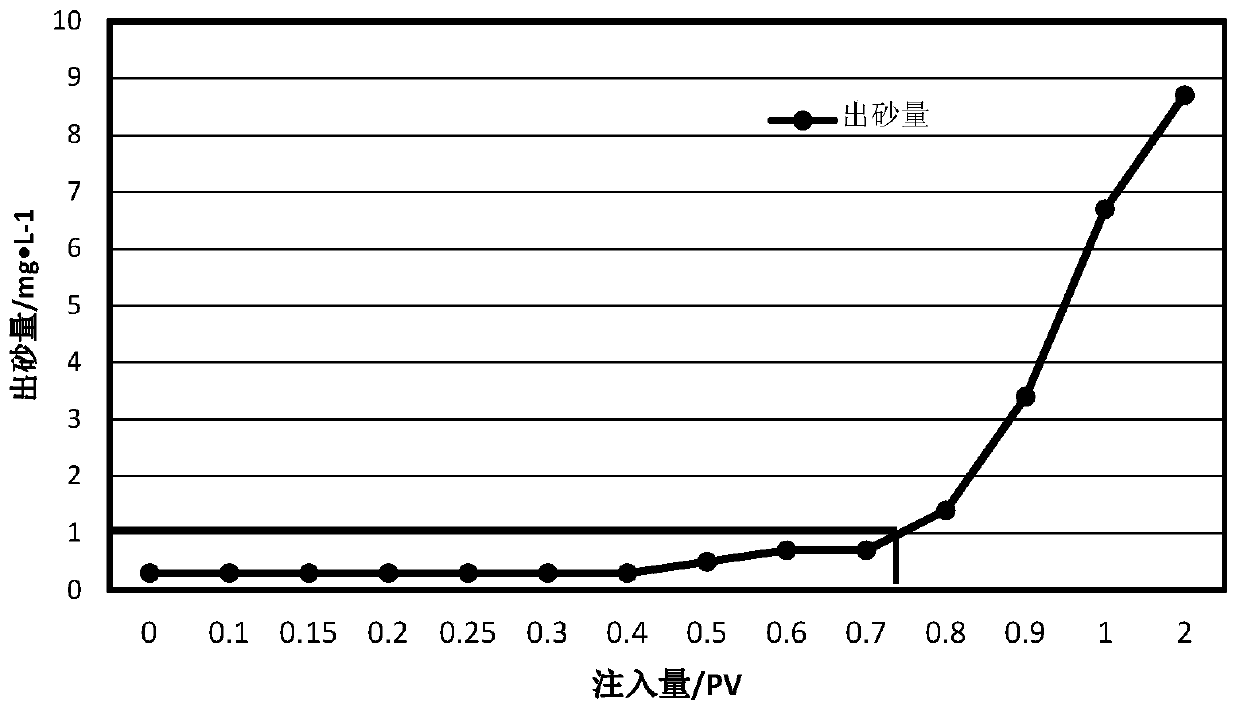
[0102] SH in a block of Shengli Oilfield 18 The reservoir temperature is 65°C, the porosity is 30.2%, and the average permeability is 3500×10 -3 μm 2 , belonging to unconsolidated sandstone reservoirs, with shale content of 29%. Before the test, the water content of the block was 94.5%, the daily oil production was 2.6t / d, and the daily liquid production was 25m 3 / d. There is a serious problem of sand production in this block, which leads to the phenomenon of low fluid volume and poor productivity in this well. The sand content and ion composition in the produced fluid of this block were measured. The test results are shown in Table 9. Using the method of the present invention to block SH 18 Implement sand control and increase fluid production in this block.
[0103] Table 9 Block SH 18 Produced fluid performance test results
[0104] parameter Sand content total salinity water type Calciummg / L Magnesiummg / L Ferrous mg / L Potassium mg / L valu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com