Four-electrode lithium ion battery and potential measurement method thereof
A lithium-ion battery and four-electrode technology, which is applied in electrostatic field measurement, secondary batteries, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of lithium metal consumption and dissolution, and short service life of measurement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] Example 1: Battery Assembly
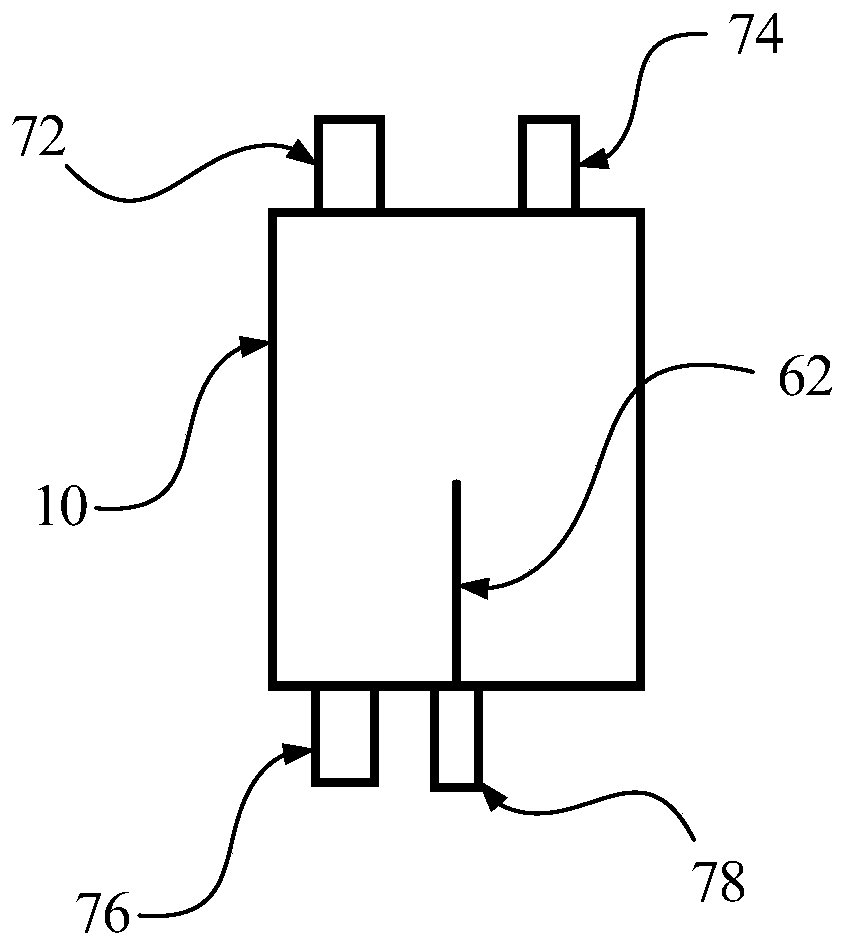
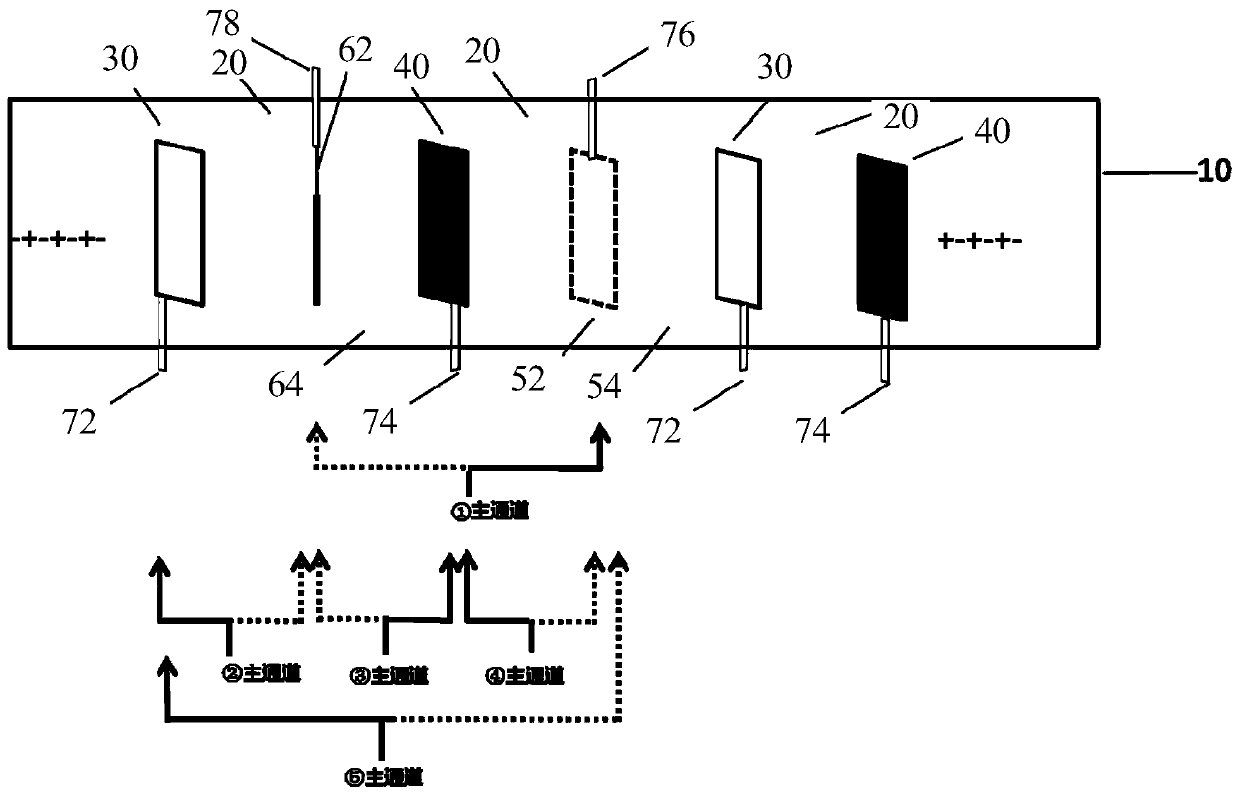
[0071] refer to figure 2 , the positive and negative electrodes are alternately separated between the diaphragms, and the tabs are drawn on the same side. Through ultrasonic welding, the positive tabs are welded to the positive pole through the current collector, and the negative tabs are welded to the negative pole through the current collector; The auxiliary reference electrode and the main reference electrode (the same material as the positive electrode sheet) are respectively placed between the positive electrode sheet and the negative electrode sheet of different layers and are separated by a diaphragm (the auxiliary reference electrode diaphragm and the main reference electrode diaphragm), and are placed on the positive electrode The opposite side of the lug and the negative lug is the lug, and the auxiliary reference lug is welded to the auxiliary reference electrode through ultrasonic welding, and the main reference lug is welded t...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Example 2: Test Equipment Connection
[0075] Use the Xinwei test cabinet to test the cycle stability of the four-electrode battery, and use the Agilent tester to monitor the positive electrode-auxiliary reference electrode, negative electrode-auxiliary reference electrode, positive electrode-main reference electrode, negative electrode-main reference electrode, Auxiliary reference electrode-primary reference electrode potential change (wiring and description as figure 2 shown), the charge and discharge curves of the positive electrode, negative electrode, and full battery were obtained respectively. The range of test conditions is 25°C, 1C rate current charge and discharge.
[0076] The specific wiring of the Agilent tester is as follows: ①The high-voltage solid line of the main channel is connected to the main reference tab, and the low-voltage dotted line is connected to the auxiliary reference tab to monitor the potential difference between the two reference elect...
Embodiment 3
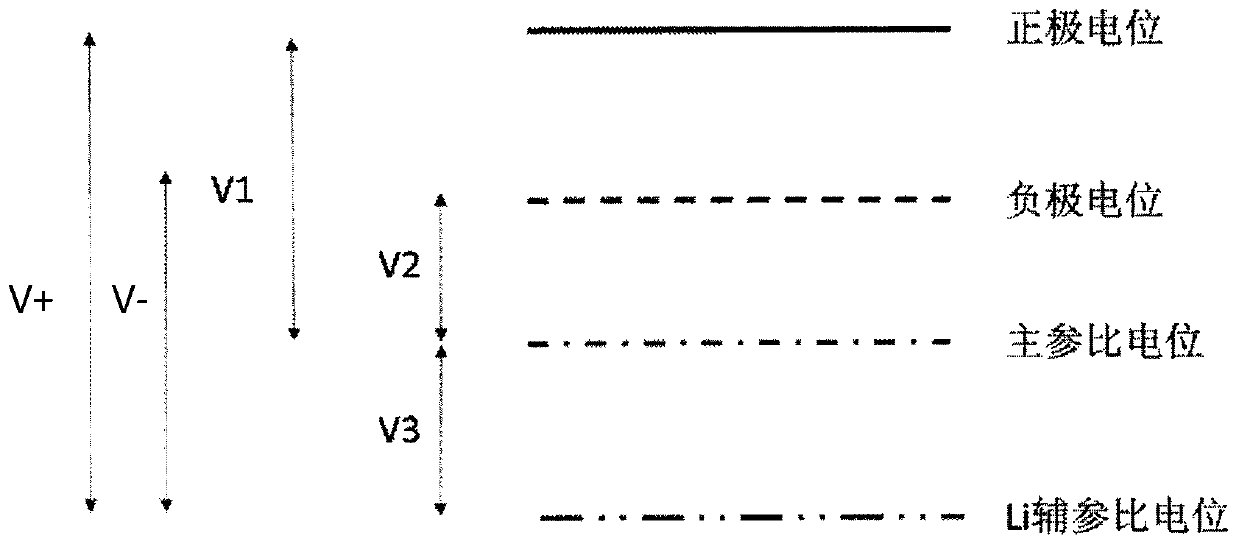
[0084] By measuring the potential of positive pole-auxiliary reference electrode, negative pole-auxiliary reference electrode, positive pole-main reference electrode and negative pole-main reference electrode of four-electrode lithium ion battery (obtained in embodiment 1), obtain as follows Image 6 The positive electrode, negative electrode, and full battery of the shown four-electrode lithium ion battery (obtained in Example 1) are charged and discharged curves fitted.
[0085] Depend on Image 6It can be seen that the potential difference of the main reference potential is calibrated by the positive and negative potentials respectively plus the auxiliary reference potential, and the two are fitted to obtain the potential of the positive and negative electrodes relative to Li, which can more intuitively reflect the lithium analysis potential of the negative electrode; In addition, the potential of the positive electrode is subtracted from the potential of the negative elect...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com