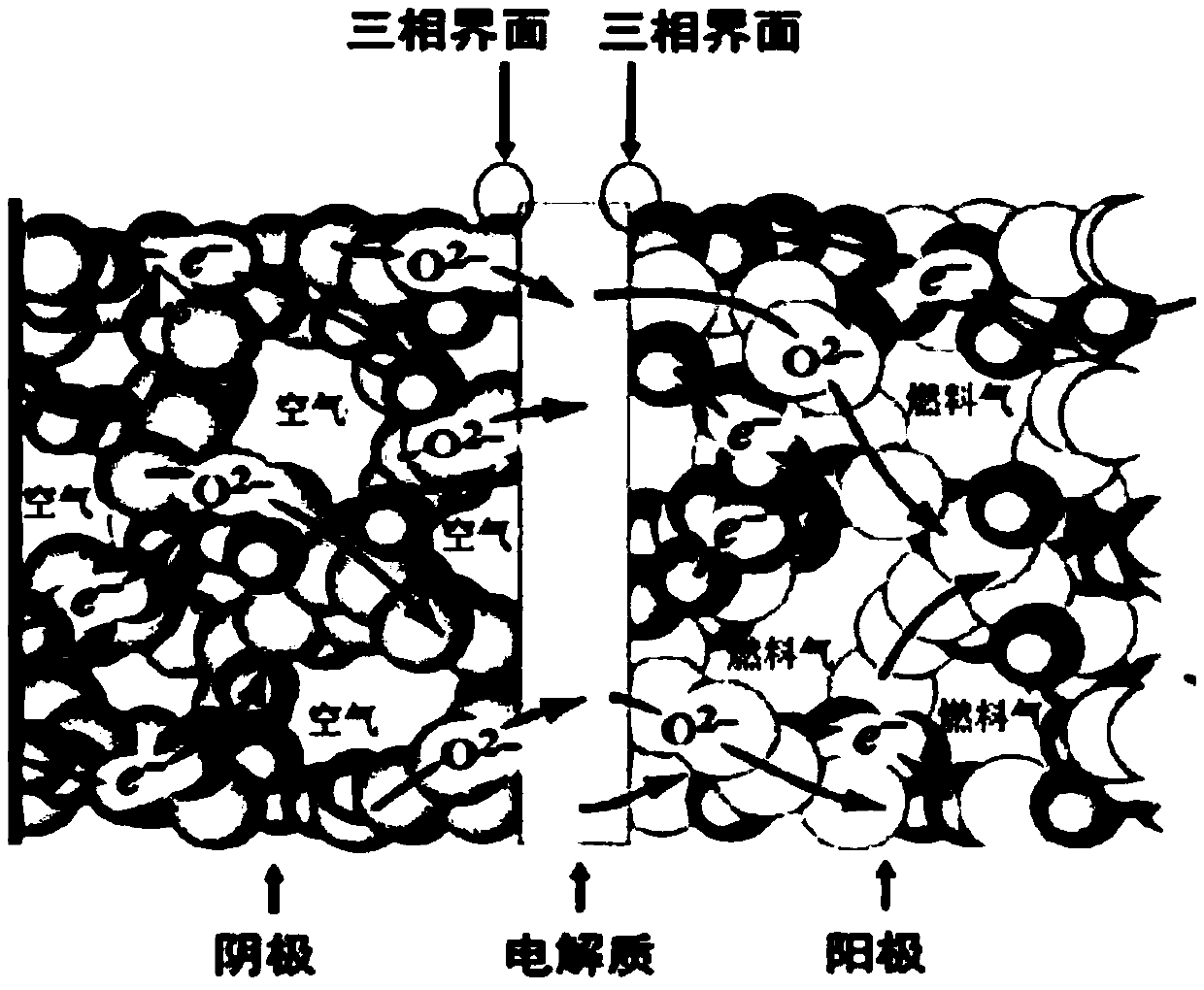
Heating starting method and heating device of solid oxide fuel cell stack
A fuel cell stack, solid oxide technology, applied in fuel cell heat exchange, fuel cells, fuel cell additives, etc., can solve the problems of reduced cell reaction efficiency, unbalanced cell heating, low heating efficiency, etc. Electric output performance, improving heating efficiency and heat balance, accelerating gas diffusion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
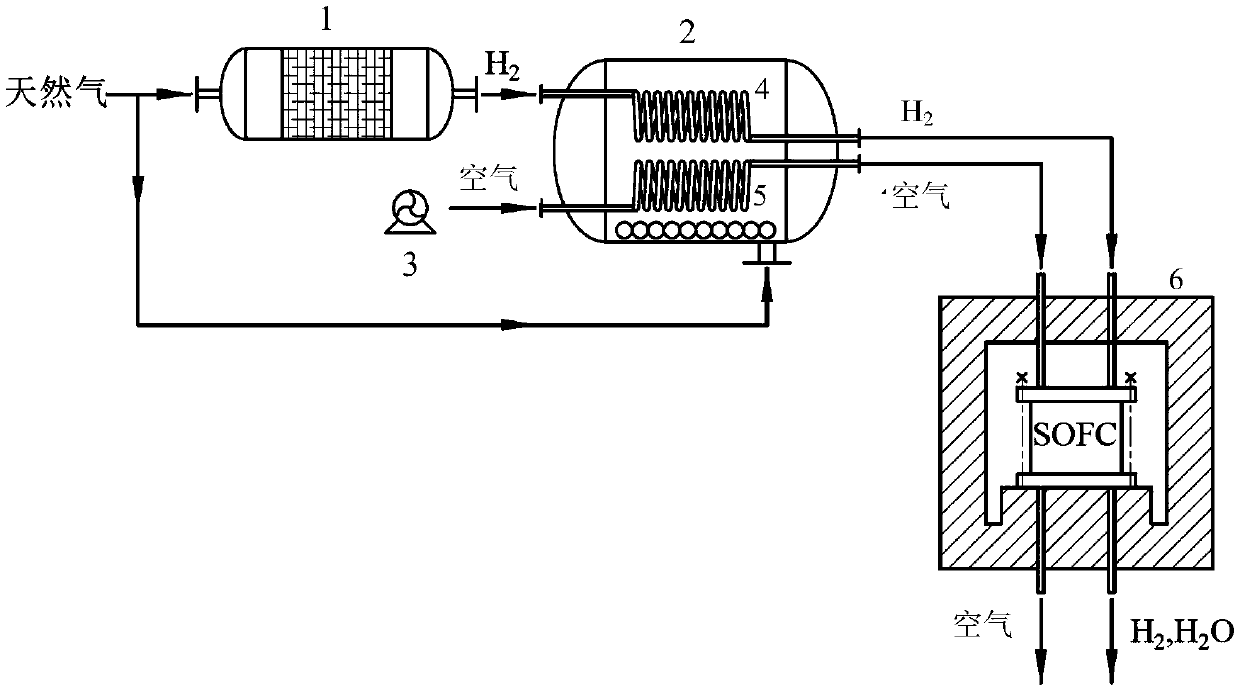
[0024] A heating device for a solid oxide fuel cell stack, such as figure 2 As shown, it includes a reformer 1 , a burner 2 and an air pump 3 . The burner 1 comprises at least two coiled pipes 4 and 5 .
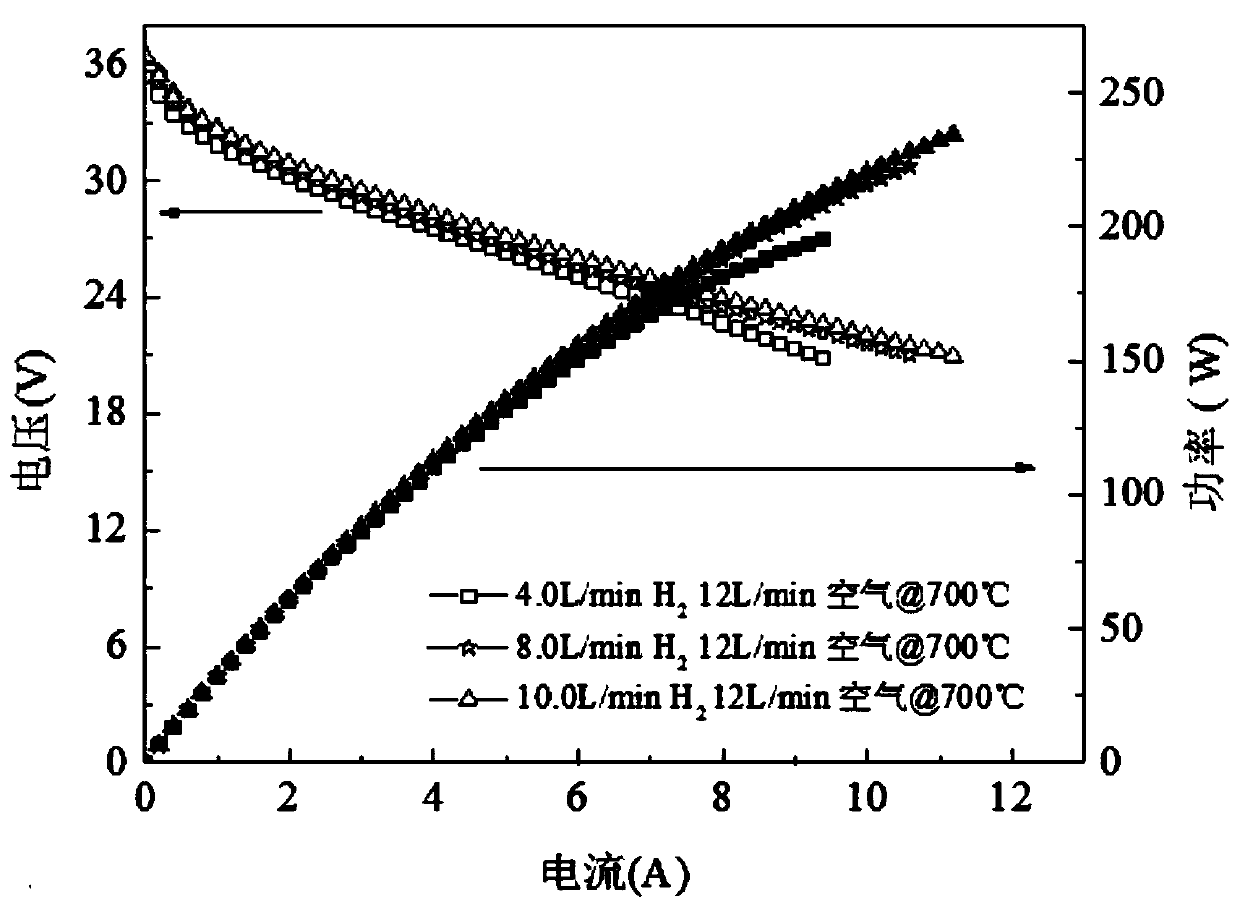
[0025] Natural gas is used as the input gas, a part of the natural gas is converted into hydrogen by the reformer 1 , and a part of the natural gas is used as the fuel of the burner 2 for heating the pipelines 4 and 5 in the burner 2 . The hydrogen produced by the reformer 1 is input into the pipeline 4 of the burner 2 at a flow rate of 4 liters / min for preheating to 700°C, and the air output by the air pump 3 is input into another pipeline 5 of the burner at 12 liters / min for preheating. When heated to 700°C, the preheated hydrogen and air are delivered to the inside of the solid oxide fuel cell stack 6 . Adjust the preheating temperature of fuel gas and air by monitoring the temperature of solid oxide fuel cell stack 6. When the preheating temperature of fuel gas and air...
Embodiment 2
[0038] A heating device for a solid oxide fuel cell stack, such as figure 2 As shown, it includes a reformer 1 , a burner 2 and an air pump 3 . The burner 1 comprises at least two coiled pipes 4 and 5 .
[0039] Natural gas is used as the input gas, a part of the natural gas is converted into hydrogen by the reformer 1 , and a part of the natural gas is used as the fuel of the burner 2 for heating the pipelines 4 and 5 in the burner 2 . The hydrogen produced by the reformer 1 is input into the pipeline 4 of the burner 2 at a flow rate of 8 liters / min for preheating to 700°C, and the air output by the air pump 3 is input into another pipeline 5 of the burner at 12 liters / min for preheating. When heated to 700°C, the preheated hydrogen and air are delivered to the inside of the solid oxide fuel cell stack 6 . Adjust the preheating temperature of fuel gas and air by monitoring the temperature of solid oxide fuel cell stack 6. When the preheating temperature of fuel gas and air...
Embodiment 3
[0042] A heating device for a solid oxide fuel cell stack, such as figure 2 As shown, it includes a reformer 1 , a burner 2 and an air pump 3 . The burner 1 comprises at least two coiled pipes 4 and 5 .
[0043]Natural gas is used as the input gas, a part of the natural gas is converted into hydrogen by the reformer 1 , and a part of the natural gas is used as the fuel of the burner 2 for heating the pipelines 4 and 5 in the burner 2 . The hydrogen produced by the reformer 1 is input into the pipeline 4 of the burner 2 at a flow rate of 10 liters / min for preheating to 700°C, and the air output by the air pump 3 is input into another pipeline 5 of the burner at 12 liters / min for preheating. When heated to 700°C, the preheated hydrogen and air are delivered to the inside of the solid oxide fuel cell stack 6 . Adjust the preheating temperature of fuel gas and air by monitoring the temperature of solid oxide fuel cell stack 6. When the preheating temperature of fuel gas and air...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com