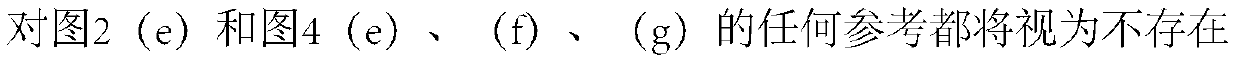Therapeutic nanoconjugates and uses thereof
A kind of use and therapeutic agent technology, applied in drug delivery, fusion polypeptide, antibody mimic/scaffold, etc., can solve the problems of complicated antibody structure and obstacles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
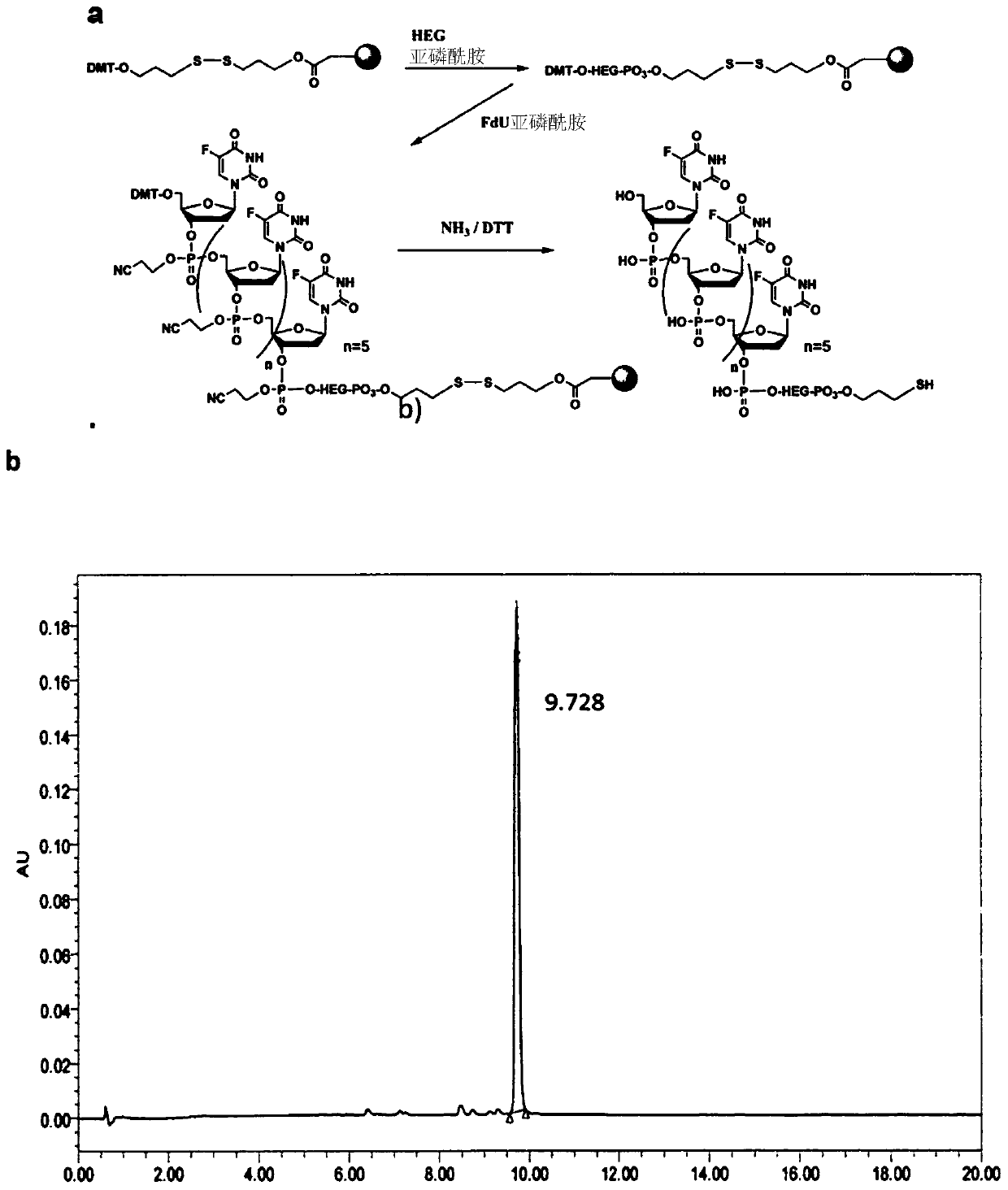
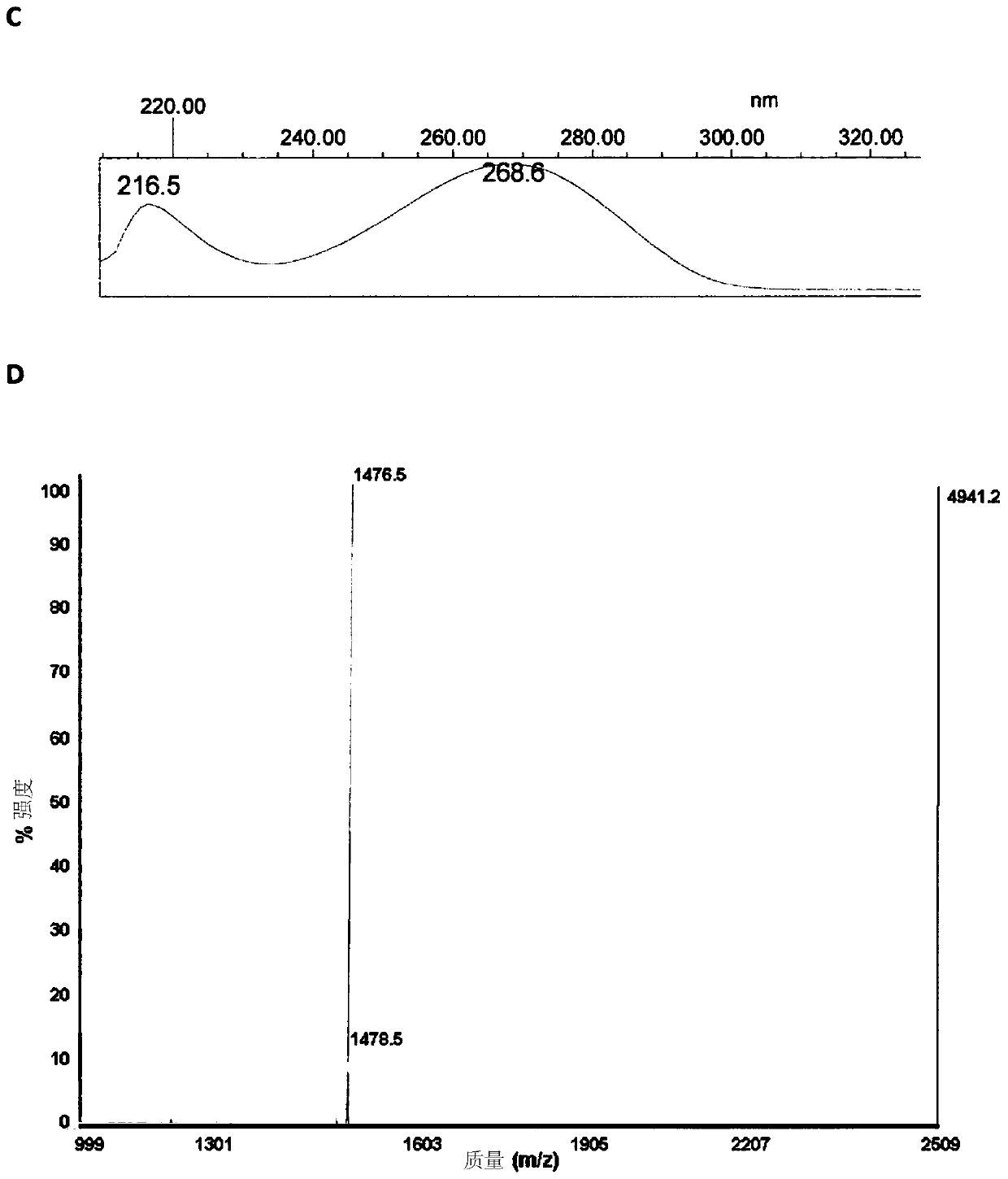
[0456] Example 1: Physicochemical characterization of HS-oligo-FdU
[0457] Functionalized pentameric FdU-HEG-SH was quantified by absorbance at 260 nm and confirmed by MALDI mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF), resulting in a MW of 1976.2, expected MW of 1974.0. The control pentanucleotide (free oligo-FdU) characterized by mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF) obtained a MW of 1476.5, expected MW: 1478.1.
Embodiment 2
[0458] Example 2: Physicochemical Characterization of T22-GFP-H6-FdU Nanoconjugate and Determination of Drug to Nanoparticle Ratio
[0459] Analysis of the conjugated product by MALDI-TOFF spectroscopy identified the figure 2 The indicated MW peaks correspond to one or two molecules of FdU pentaoligonucleotides bound to nanoparticles. The size of T22-GFP-H6-FdU determined by dynamic light scattering was 14.6 + 0.14, compared to the size of control T22-GFP-H6 nanoparticles of 13.4 + 0.11, which is consistent with the size determined by transmission electron microscopy unanimous. The molecular weight of T22-GFP-H6 nanoparticles determined by SEC-MALS was 477 kDa. Considering the molecular weight of the T22-GFP-H6 polypeptide is 30,691 kDa, this results in approximately 15 monomers per nanoparticle. Based on the UV spectra of T22-GFP-H6 and T22-GFP-H6-FdU nanoconjugates, for the products obtained in the T22-GFP-H6-FdU nanoconjugate synthesis reaction, the obtained drug / nano...
Embodiment 3
[0460] Example 3: A targeting CXCR4 + Development of nanoconjugate T22-GFP-H6-FdU in CRC cells
[0461] It has been previously shown that overexpression of CXCR4 (CXCR4 + ) colorectal cancer (CRC) cells have metastasis initiation capacity (MIC) [Croker, A.K. & Allan, A.L. 2008. J Cell MolMed 12, 374-390; Zhang, S.S. et al. 2012. BMC Med 10, 85 (2012)], and the inhibitory effect of CXCR4 downregulation on MIC [Murakami, T. et al. 2012. BMC Med 10, 85; Wang, T.B. et al. 2014. Int J Oncol 44, 1861-1869] identified these cells as Metastatic Stem Cells (MetSC). On this basis, the inventors generated nanoconjugates targeting CXCR4 to evaluate whether they could selectively eliminate CXCR4 + CRC cells to achieve anti-metastatic effect. figure 1 , 2 The structural and physicochemical characterization of this new T22-GFP-H6-FdU nanoconjugate is described in and 4a–c. The conjugate contains T22 (a ligand targeting the CXCR4 receptor), green fluorescent protein (allowing its in v...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com