Indica Target Lines for Gene Stacking for Recombinase-Mediated Site-Specific Sites
A technology of recombinase and indica rice, applied in the field of indica rice target lines, can solve problems such as difficulty in genetic transformation, and achieve the effects of reducing separation sites, reducing breeding workload, and reducing release evaluation costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1 Vectors suitable for gene stacking
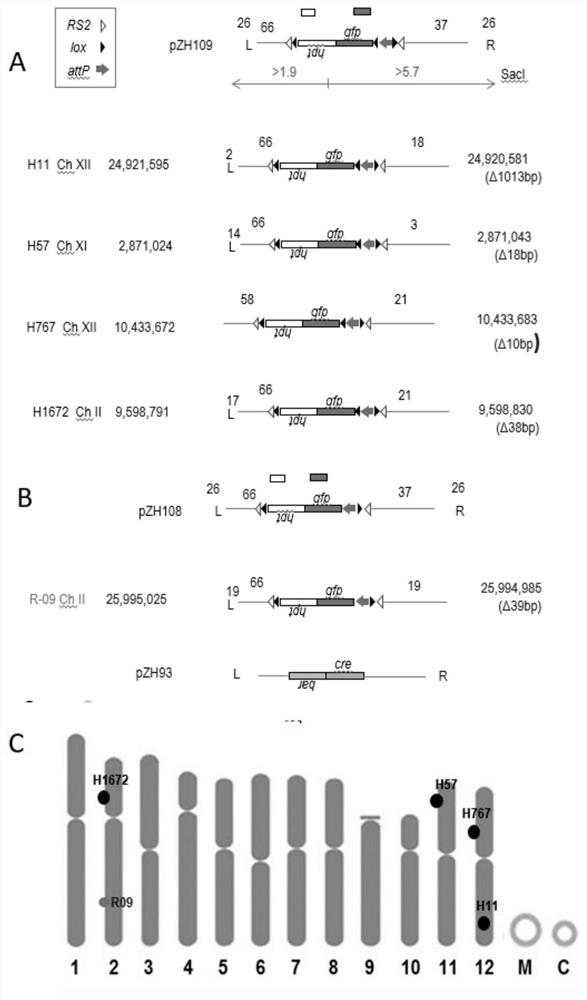
[0045] The structures of the vectors pZH109, pZH108 and pZH93 are as follows figure 1 shown, it was constructed with reference to standard DNA recombination methods. Phusion high-fidelity polymerase (NEB Beijing, USA) was used in all PCR reactions. The sugarcane baculovirus (ScBV) promoter and terminator octopine synthase (ocs) control the initiation and termination of the green fluorescent reporter gene gfp, respectively. The rice actin promoter and terminator cauliflower virus (CaMV35s) control the initiation and termination of the hygromycin gene hpt, respectively. The CaMV 35S promoter and terminator control the initiation and termination of the herbicide resistance gene bar, respectively. The promoter of the cre recombinase gene is the CaMV35S promoter, and the terminator is the nopaline synthase (nos) terminator.
[0046] The present application employs two strategies to obtain indica stacked starting target lin...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2 Screening of initial target lines
[0050] method:
[0051] Agrobacterium-mediated transformation
[0052] About 2000 indica rice Huanghuazhan or 500 indica rice R900 immature embryos were infected with Agrobacterium. One part was infected with Agrobacterium EHA105 containing the target line vector pZH109, and the other part was co-transformed with Agrobacterium containing pZH108 and Agrobacterium containing pZH93. For specific transformation methods, please refer to Hiei Y. and Komari T. 2008. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of rice using immature embryos or calli induced frommature seed. Nature Protocol (3) 824–834.
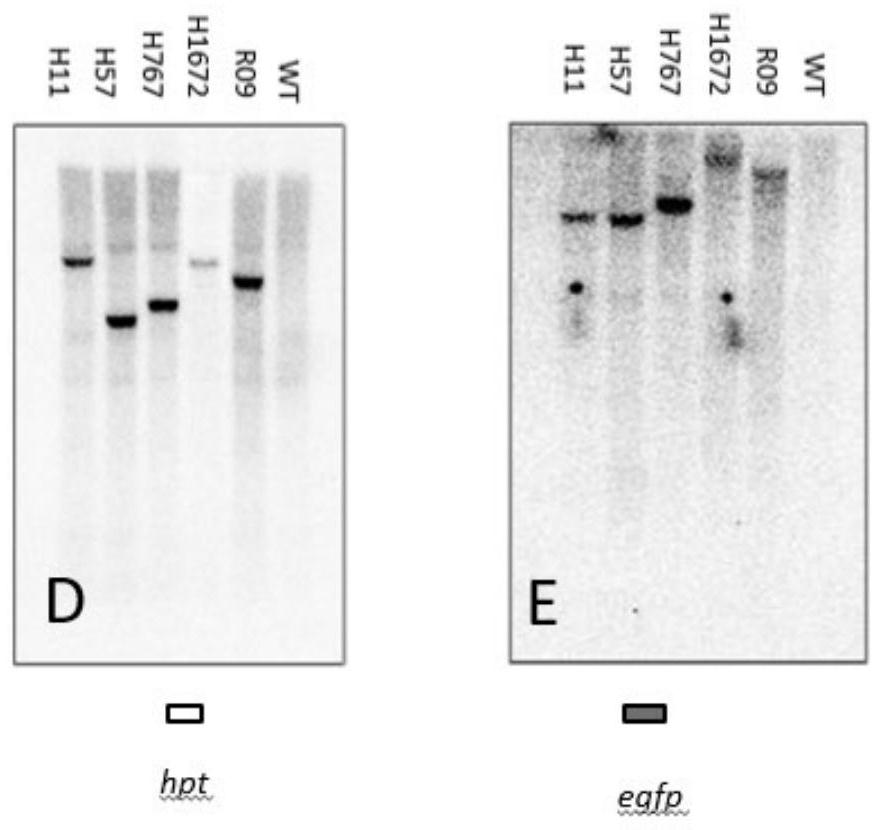
[0053] GFP observation
[0054] The expression of GFP was observed by a Leica inverted fluorescence microscope DMI6000B (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany). The wavelength range of excitation filter used is 440-520nm, and the wavelength of barrier filter is 510LP.
[0055] PCR analysis
[0056] About 100 mg of fresh or cryopreserved GFP-exp...
Embodiment 3
[0091] Example 3 Genome mapping of initial target line
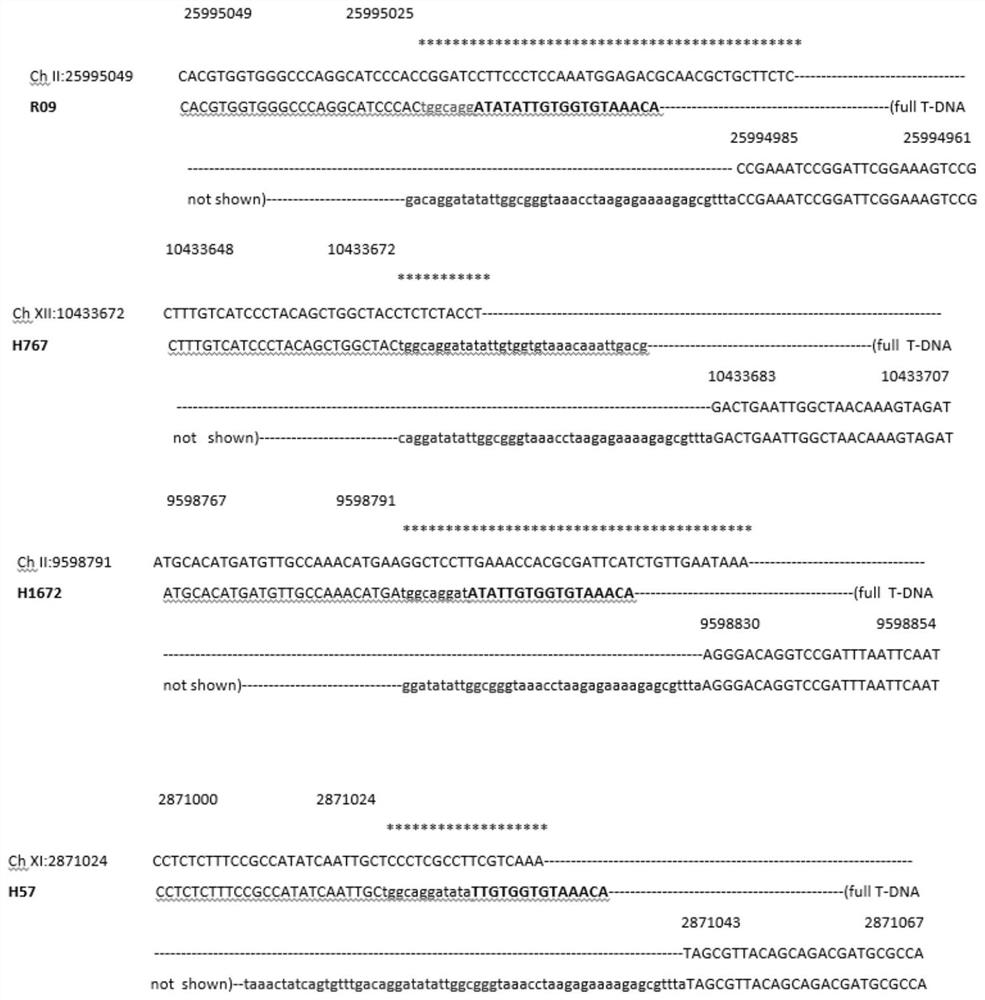
[0092] figure 1 The insertion position shown in C was determined by the DNA sequences flanking the left and right ends with the Rice Genome Database (Wang, J., Kong, L., Zhao, S., Zhang, H., Tang, L., Li, Z., Gu , X., Luo, J., and Gao, G. 2011. Rice-Map: a new-generation rice genome browser. BMC Genomics. 12, 165) alignment. For detailed DNA sequence see Figure 4 and Figure 5 . Important features of each insertion site are listed here (insertion sites are as figure 1 A and 1B are drawn from the left border to the right border of T-DNA), that is, five genomic loci suitable for indica rice gene stacking in the present invention:
[0093] The target site of the target line H11: located between 24,920,581 and 24,921,595 on the long arm of chromosome 12, with a 21 bp genomic sequence deletion from 24,921,594 to 24,920,581. At the left end of the T-DNA, the first 24 bp of the 26 bp LB was deleted. At the right end of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com