Fuel consumption measuring method and device, computing equipment and storage medium
A fuel consumption and measurement method technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, relative volume flow measurement, liquid/fluid solid measurement, etc., can solve the problems of reduced accuracy of results, additional installation of flow meters, lack of measurement methods for fuel consumption, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
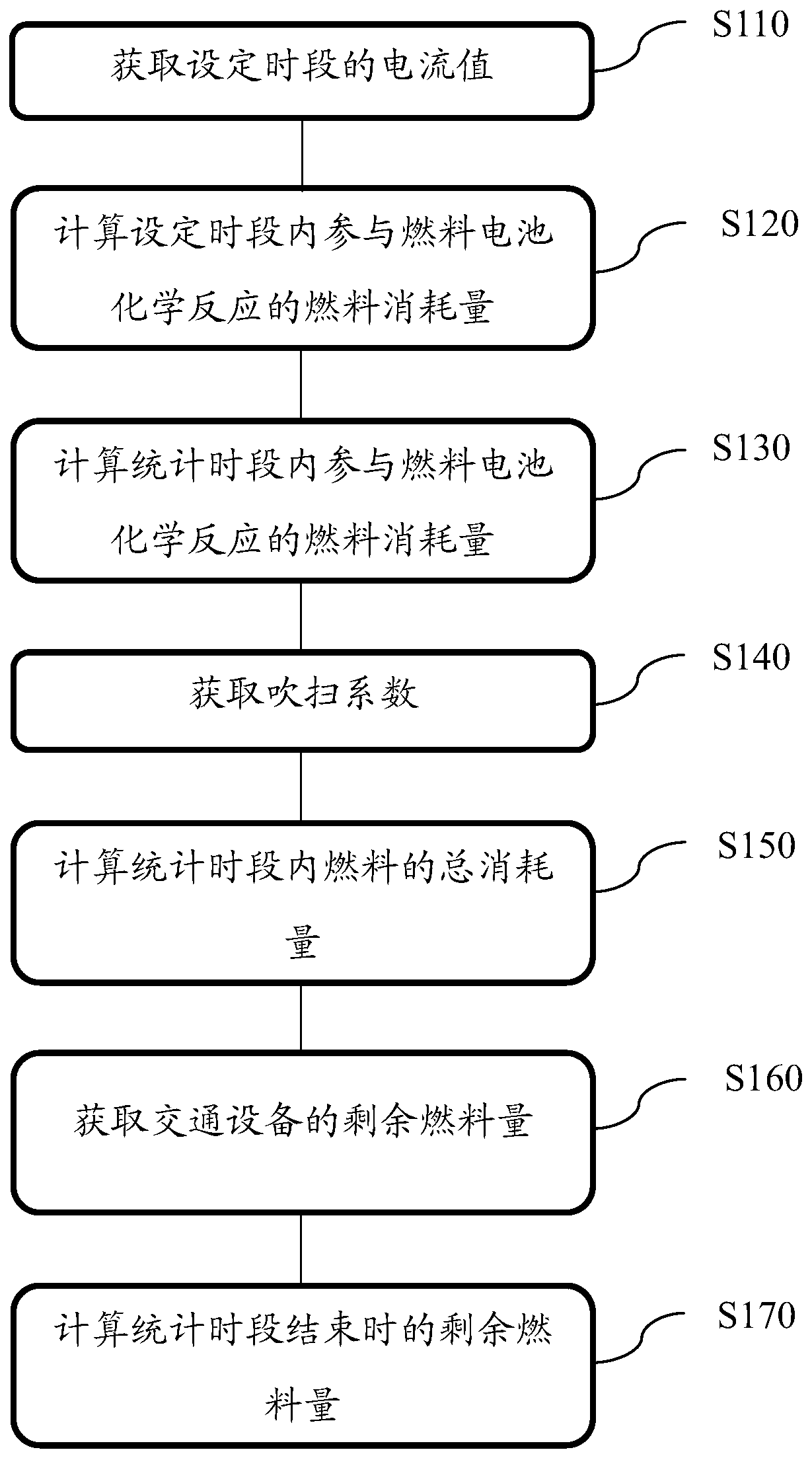
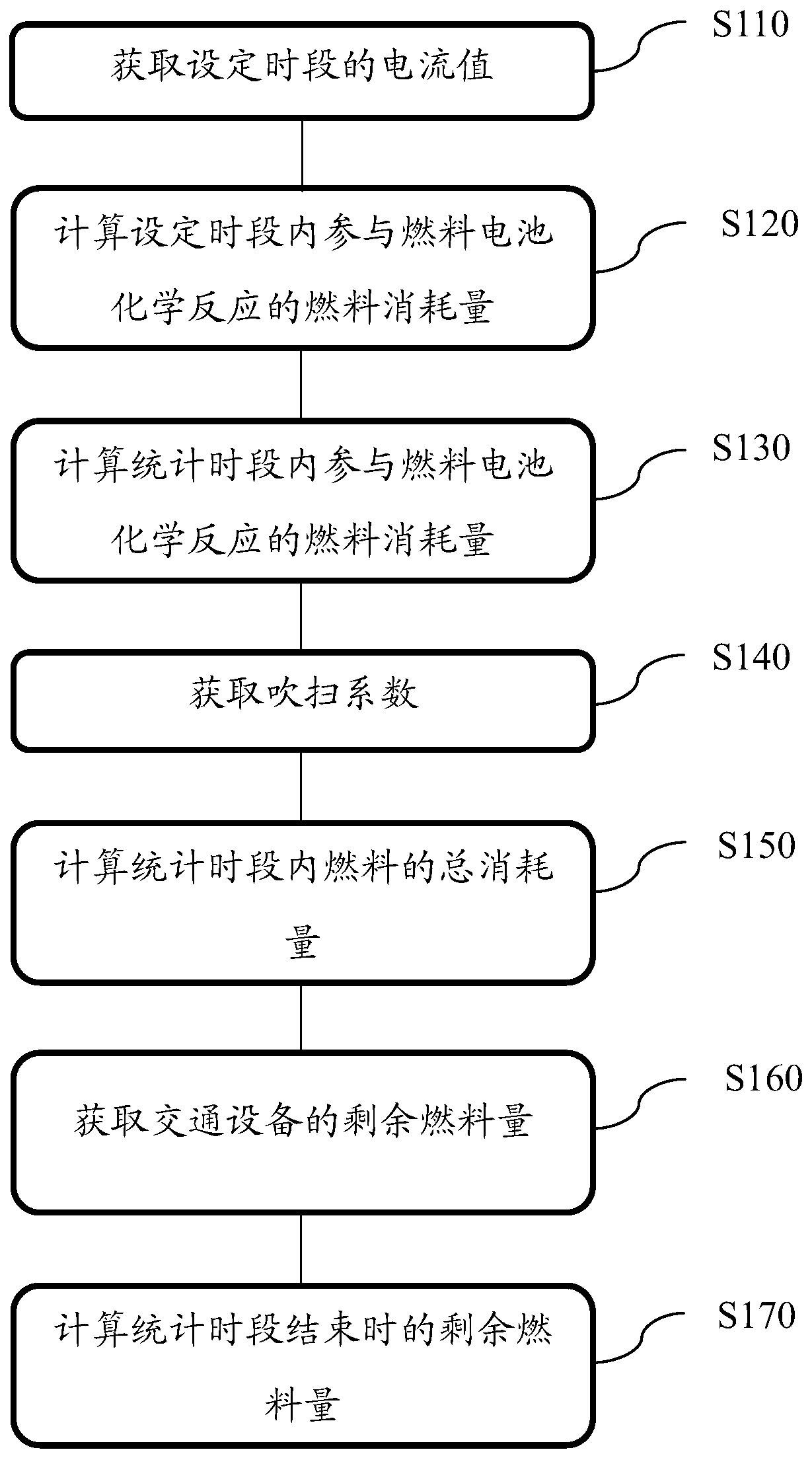
[0085] figure 1 A flow chart of a method for measuring fuel consumption provided by the present application is shown. In this embodiment, hydrogen is used as fuel to describe steps S110 to S130.
[0086] First, a current value within a set period is acquired (S110).
[0087] Taking a hydrogen fuel cell vehicle as an example, the fuel is hydrogen, and the transportation equipment is a vehicle. The fuel cell modules or systems of existing hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are equipped with current sensors to monitor the operating status of the fuel cells. If allowed, the current value measured by the current sensor in the fuel cell module can be directly obtained through the vehicle bus. When the current value cannot be obtained through the current sensor in the fuel cell module, an additional current sensor can be installed on the load circuit to obtain the current value.
[0088] Secondly, according to the measured current value, the number of single-chip fuel cells connected in ...
Embodiment 2
[0102] It is also possible to directly use the following calculation formula to obtain the hydrogen consumption involved in the chemical reaction of the fuel cell within a set period of time according to the measured current value:
[0103]
[0104] Wherein, m is the hydrogen consumption participating in the fuel cell chemical reaction within the set period of time; N is the number of single-chip batteries connected in series in the fuel cell, which is 180 pieces; m 0 is the mass of a single hydrogen molecule, which is 3.32×10 -24 g; n is the number of electrons corresponding to a single hydrogen molecule participating in the fuel cell reaction process, which is 2; e is the charge carried by a single electron, which is 1.602176634×10 -19 Coulomb, I is the current value of the fuel cell in the set time period, t 0 For the set period, it is 50 milliseconds.
[0105] The above known quantity can be substituted into the above calculation formula, combined with the measured cu...
Embodiment 3
[0108] figure 1 A flow chart of a method for measuring fuel consumption provided by the present application is shown, and steps S140 and S150 are described in this embodiment using hydrogen as fuel.
[0109]During the reaction process of the fuel cell, the hydrogen gas on the hydrogen side of the fuel cell can only go in and out, and the impurity gas in the hydrogen gas cannot react and will accumulate and increase over time, which will lead to a decrease in the purity of the hydrogen gas and affect the power generation efficiency. Impurity gases such as carbon monoxide also have catalyst toxicity, and continuous accumulation will lead to catalyst poisoning. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly discharge the hydrogen on the hydrogen side to reduce the accumulation of impurities. This process is generally referred to as purging in the field of fuel cell technology. The purge is controlled by the hydrogen side purge valve. Therefore, the total hydrogen consumption is equal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com