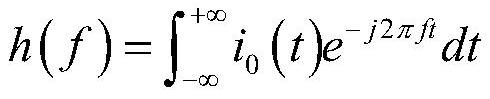A distribution network line selection method based on time-frequency domain traveling wave information
A line selection method and technology in the time-frequency domain, which are applied in the direction of measuring electricity, measuring electrical variables, and detecting faults according to conductor types. problems such as low performance, achieve good time-frequency aggregation, no dead zone for line selection, and clear principles.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0047] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
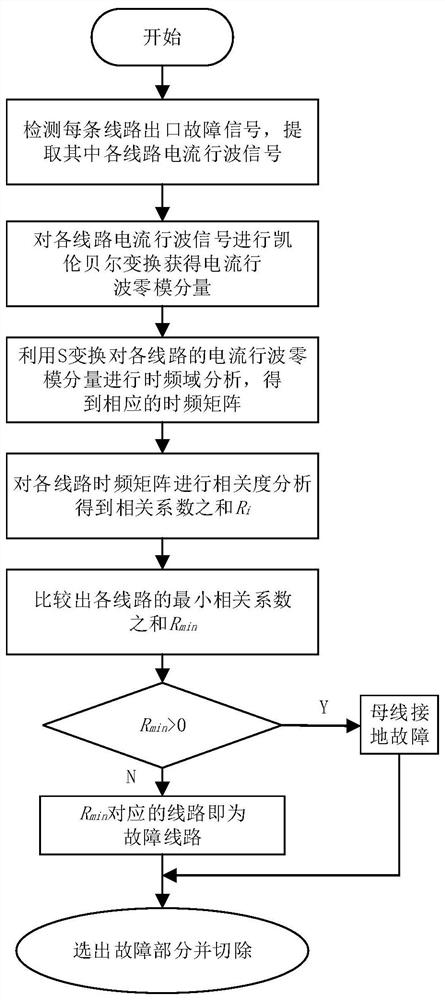
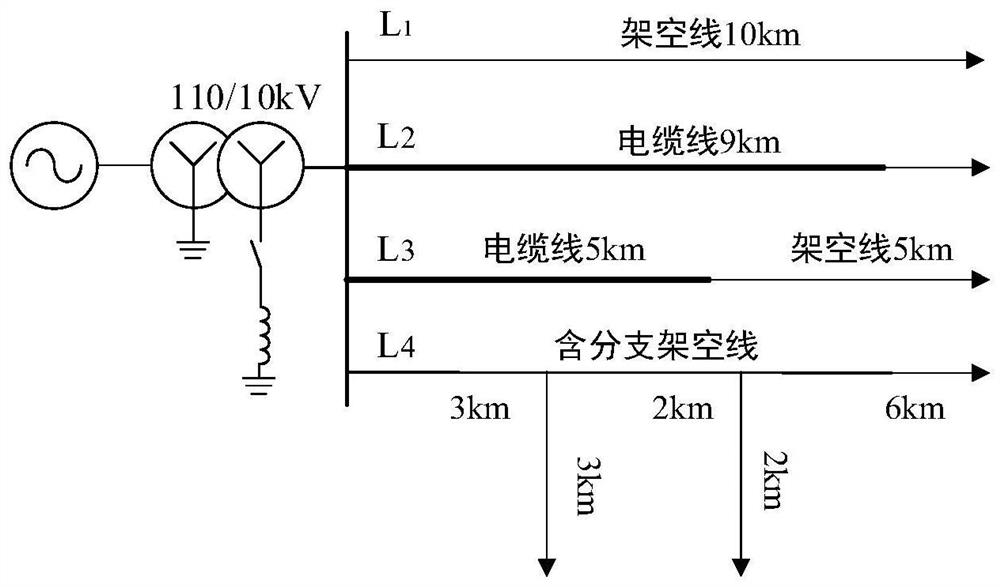
[0048] Such as figure 1 As shown, the distribution network line selection method based on time-frequency domain traveling wave information of the present invention, its steps are:
[0049] Step S1: Install a traveling wave sensor at the exit of each line bus to extract the current traveling wave signal on each line;
[0050] Step S2: Carrying out Karen Bell transformation on the current traveling wave signal of each line to obtain the zero-mode component of the current traveling wave;
[0051] In a specific application, in step S2 of this example, the specific steps are:
[0052]
[0053] where i α i β is the line-mode current, i 0 is the zero-mode current, i a i b i c is the phase current.
[0054] Step S3: Perform time-frequency domain analysis on the current traveling wave zero-mode component of each line by S-transformat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com