A Fault-Tolerant Rim Propulsion Motor with Few Slots and Multipole Permanent Magnet
A permanent magnet fault-tolerant, rim propulsion technology, applied in magnetic circuits, electromechanical devices, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as increasing production cycle, and achieve the effect of improving running performance, large slot width, and large winding utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
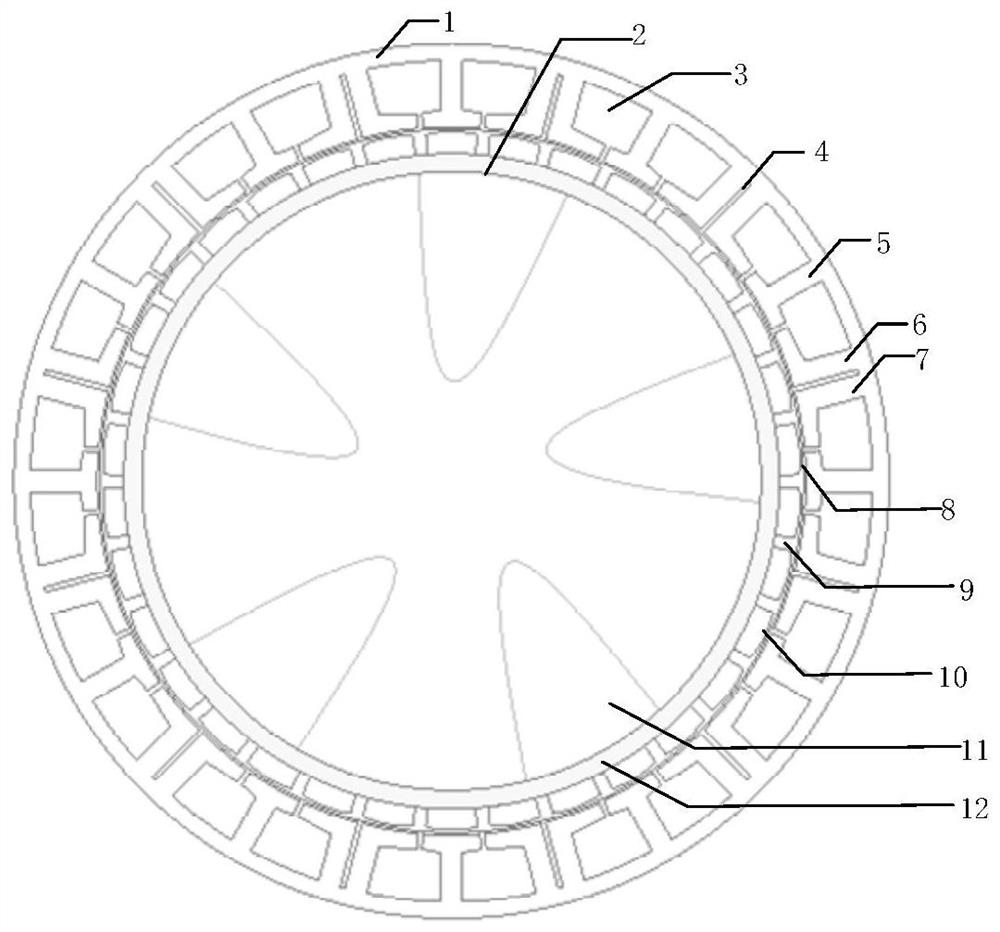
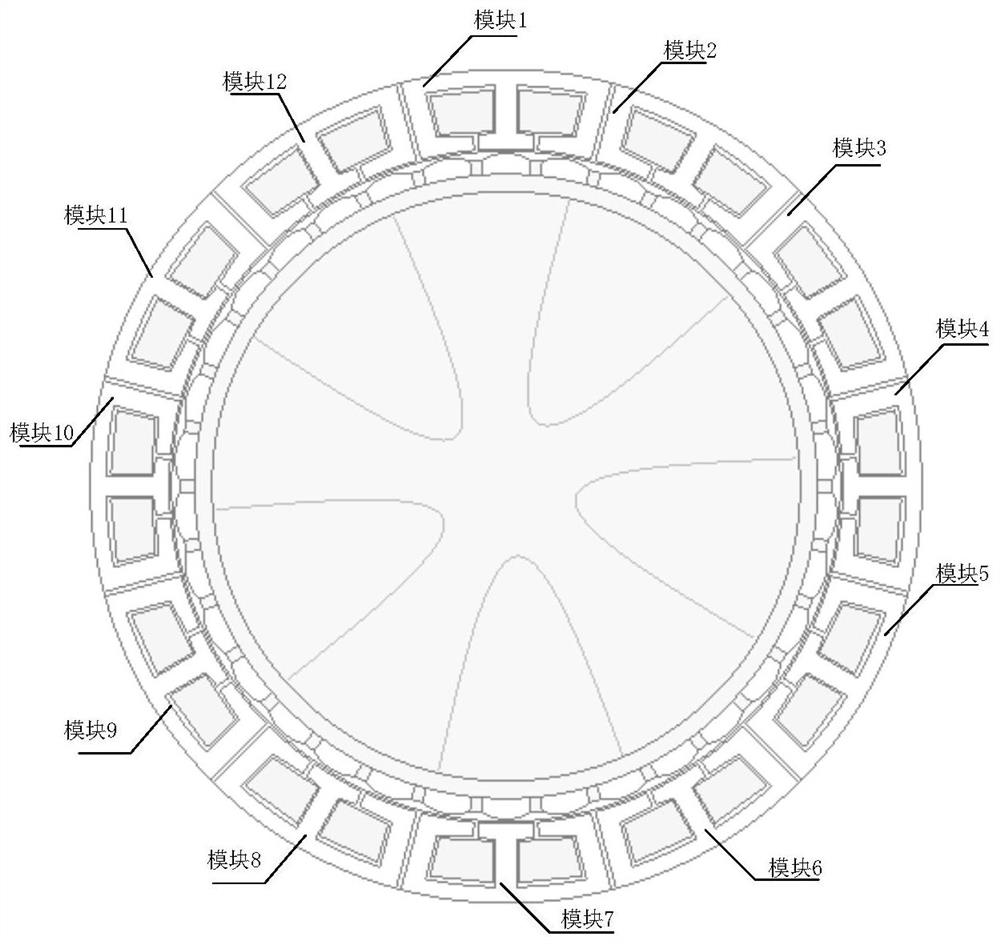
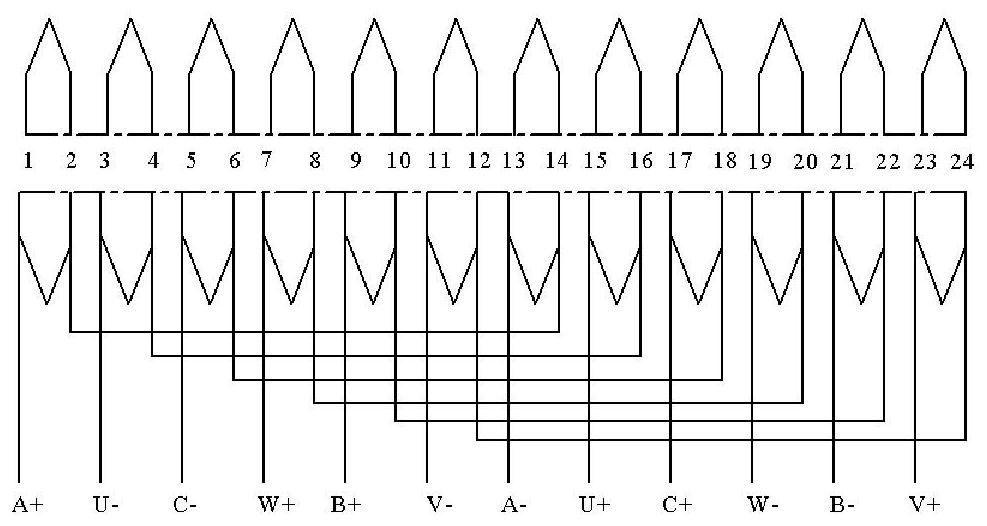
[0022] figure 1 For Example 1, figure 2 For embodiment 2; figure 2 The stator is divided to form a modular structure for easy maintenance. like figure 1 As shown, the few-slot multi-pole permanent magnet fault-tolerant rim propulsion motor consists of a stator and a rotor. The stator includes: winding slots 3 , isolation slots 4 , isolation teeth 1 , isolation teeth 2 , and armature teeth 5 . The windings of the multi-pole permanent magnet fault-tolerant rim propulsion motor with few slots are embedded in the winding slots, which is a single-layer centralized winding structure. The windings only surround the armature teeth. The winding distribution is as follows: image 3 shown.
Embodiment approach 2
[0023] The tooth widths of the spacer teeth 1, the spacer teeth 2, and the armature teeth 5 are equal, and the widths of the pole pieces are equal. The width of the isolation groove is adjustable, and the preferred width is the width that reduces the cogging torque ripple. The interior of the isolation slot is filled with non-magnetic, anti-corrosion and heat-insulating materials. Increased magnetic isolation and thermal isolation between phases. In Embodiment 2, the isolation slots divide the stator to form a modular structure.
[0024] Further, the rotor includes: a rotor yoke 12 , a permanent magnet 10 , an anticorrosion protective layer 9 and a protective sleeve 8 . The rotor yoke 12 is an integral steel structure without punching, and the propeller 11 is directly welded on the inner diameter of the rotor. The permanent magnet 10 is a surface-mounted permanent magnet with a centrifugal height or a Halbach array structure. The exterior of the permanent magnet 10 is fille...
Embodiment 1
[0026] The structural parameters of Example 1 are shown in Table 1, and the comparison structure of the 36-slot 30-pole permanent magnet fault-tolerant motor is as follows: Figure 4 As shown, the structural parameters are shown in Table 2:
[0027] Table 1 Embodiment 1 Structural parameters
[0028]
[0029]
[0030] Table 2 Structural parameters of 36-slot 30-pole comparative structure
[0031]
[0032] Example 1 has a larger winding factor of 0.996, and the comparative structure has a winding factor of 0.966. Example 1 no-load back EMF such as Figure 5 As shown, the no-load back EMF of the comparative structure is as follows Image 6 shown. It can be seen that the no-load back electromotive force of Example 1 is not much different from that of the comparative structure, and the winding utilization rate is basically unchanged.
[0033] Embodiment 1 can effectively reduce the cogging torque pulsation. The cogging torque pulsation in Embodiment 1 is as follows: ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com