An Optimal Method for Arrangement of Irregular Subarrays Achieving High Gain
An optimization method and irregular technology, applied in the field of antennas, can solve problems such as gain drop, poor applicability, and increased gain loss, and achieve low sidelobe effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
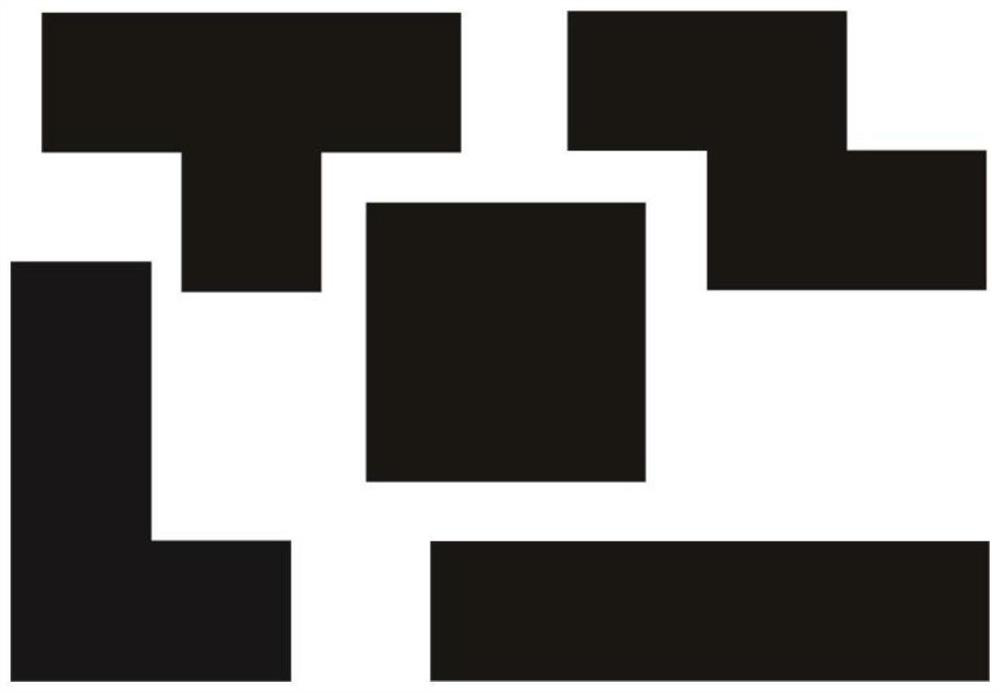
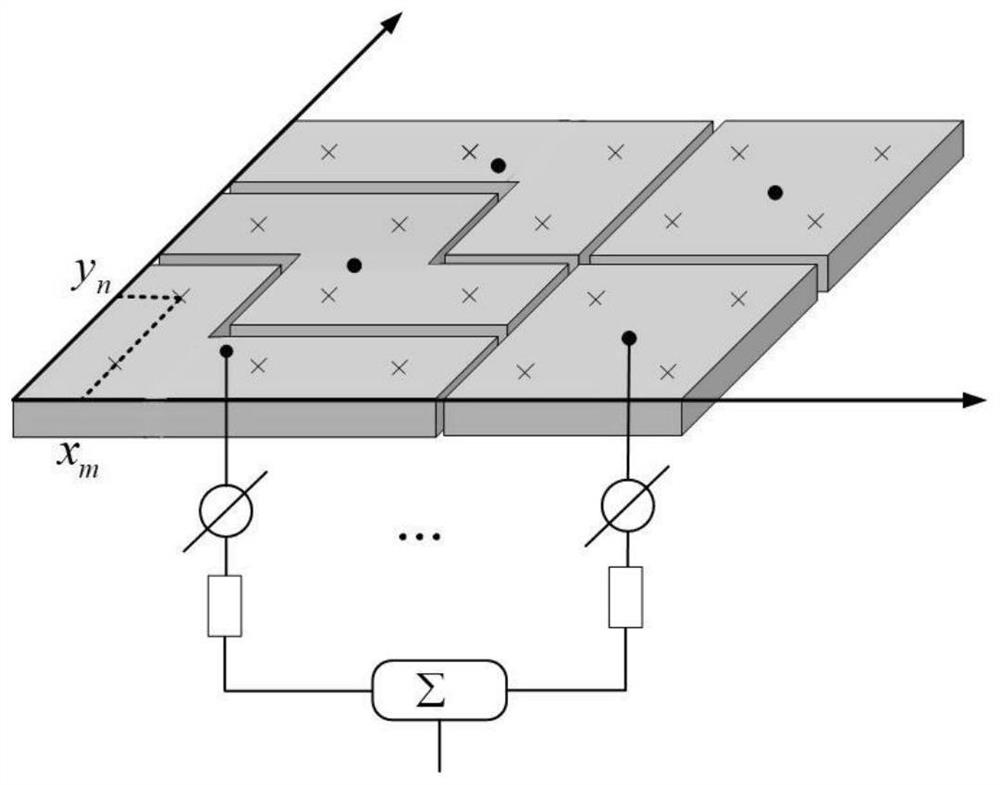
[0033] Consider an irregular array, the size of the array is M×N=16×16, considering that the irregular sub-array is composed of 4 array units, so there are 16×16 / 4=64 sub-arrays in total, and the antenna units in the sub-array The excitation amplitude and excitation phase are the same, and the difference between the array information entropy and the limit value of information entropy is set to σ=0.05. The reference array is a Chebyshev planar array with 16×16=256 units.
[0034] Other main parameters are as follows:
[0035] d=d x = d y =0.5λ
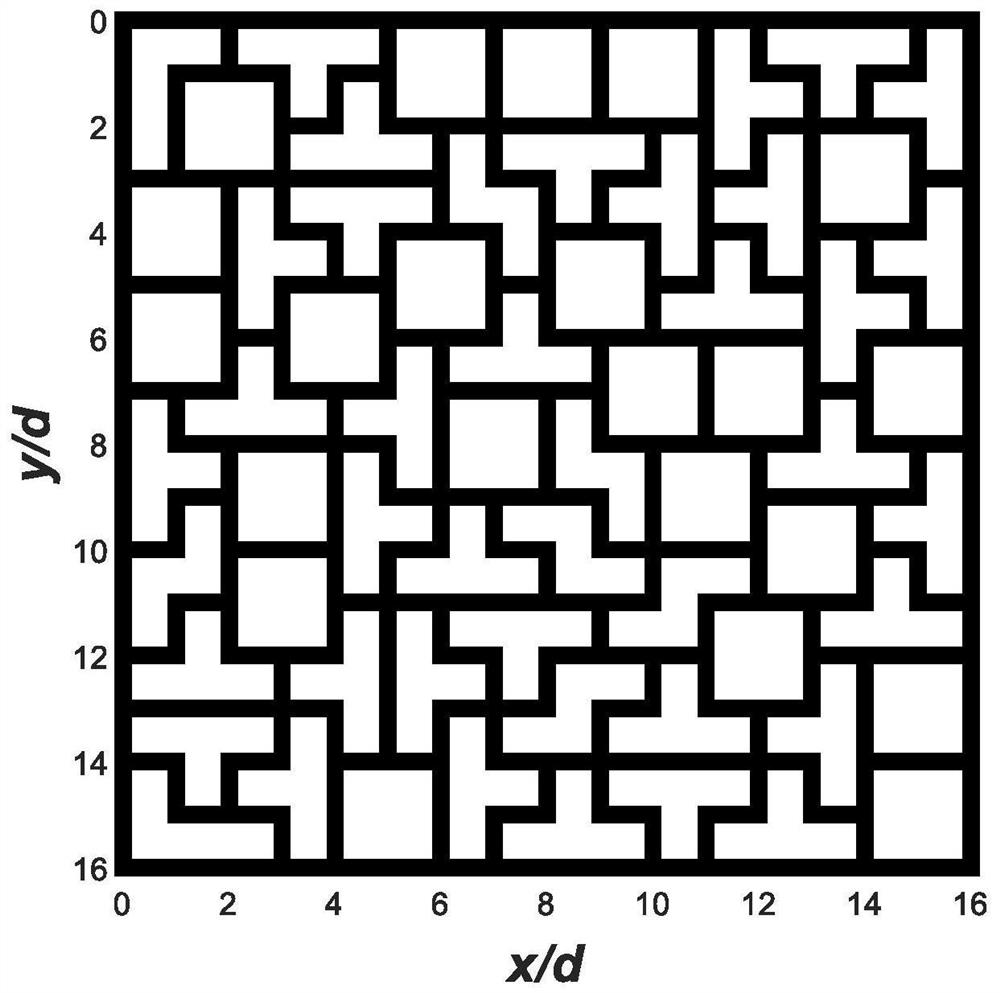
[0036] The first step is to optimize the arrangement of irregular sub-arrays through a commercial solver, such as image 3 , to obtain an irregular array with a total of 64 sub-arrays, the optimized information entropy of the array is H=6.6639, and the limit value of information entropy is log 2 (MN / 2)=7. In the second step, the amplitude and phase distribution under the desired pattern are obtained by optimizing the convex optimiza...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com