Hedging energy dissipation type debris flow diversion system
A shunt system and mud-rock flow technology, applied in water conservancy projects, artificial waterways, buildings, etc., can solve the problems of unsatisfactory prevention and control of mud-rock flow, and achieve the effect of strong anti-geological disaster ability, reduced impact force and destructive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
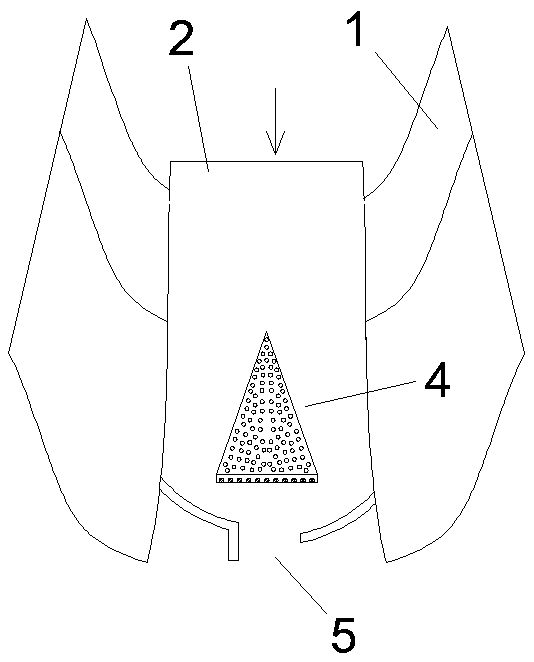
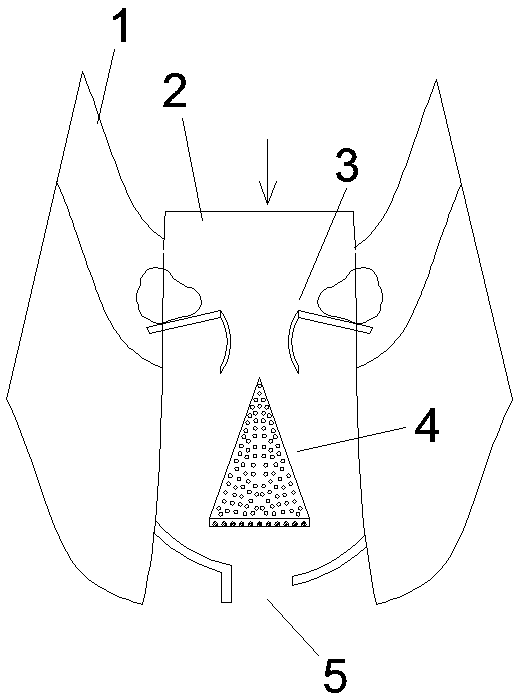
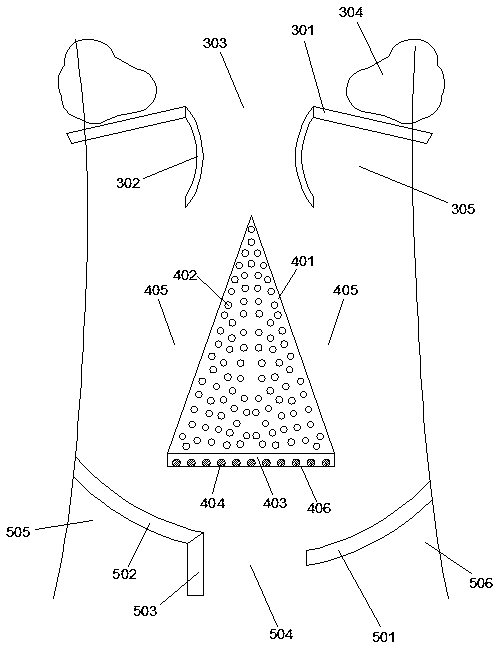
[0036] Such as figure 1 with 3 As shown, an opposing energy dissipation type debris flow diversion system is arranged in the debris flow channel 2 formed between the highlands 1 on both sides. The diversion system includes a diversion dam 4 and an opposite guide device 5, wherein the The diversion dam 4 includes a half-conical first dam body 401 arranged in the middle of the debris flow channel 2, and the tip of the semi-conical shape faces the direction of the debris flow, thereby forming two first diversion channels 405 on both sides thereof;
[0037] The opposing guide device 5 includes a first arc-shaped guide dam 501 and a second arc-shaped guide dam 502 which are respectively arranged in front of the flow direction of the two first branch channels 405, wherein the first arc-shaped guide dam 501 and the second arc The guide dams 502 are arranged obliquely on both sides of the debris flow channel 2, and the first arc-shaped guide dam 501 and the second arc-shaped guide dam 502...
Embodiment 2
[0045] This embodiment is an improvement scheme made on the basis of embodiment 1. Its basic structure is the same as that of embodiment 1. The improvement is as follows: Image 6 As shown, the two sides of the middle of the first dam body 401 are symmetrically provided with an impact redirecting plate 407. The free end of the impact redirecting plate 407 is inclined to extend in the upstream direction, and its free end is connected to the side of the debris flow channel 2. There is a gap, so that the debris flow of the first branch channel 405 impacts on the impact direction changing plate 407 and then changes direction again and slows down, thereby enclosing a stagnation zone between its front surface and the side wall of the first dam 401, The back water surface and the side wall of the first dam body 401 enclose a stagnant area.
Embodiment 3
[0047] This embodiment is an improvement scheme made on the basis of embodiment 2. Its basic structure is the same as that of embodiment 2. The improvement is as follows: Figure 7 As shown, the two sides of the rear part of the first dam body 401 are symmetrically provided with secondary diverging plates 408, the secondary diverging plates 408 are V-shaped distributed along the direction of the debris flow, and the upstream end of the secondary diverging plate 408 is connected to the impact direction changing plate 407. There is a gap between the free ends to form an overflow channel, and another overflow channel is formed between the upstream end and the side of the debris flow channel 2; the V-shaped tip of the secondary splitter plate 408 is located on the side of the debris flow channel 2, thereby A debris flow deceleration zone 409 is formed between the secondary diversion plate 408 and the high ground 1 on the side.
[0048] In this embodiment, the upstream end of the secon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com