Group-of-soybean quantitative trait QTL loci and screening method thereof
A technology of quantitative traits and screening methods, applied in the field of molecular genetics, can solve problems such as phenotypic differences and gene loci that cannot be directly analyzed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
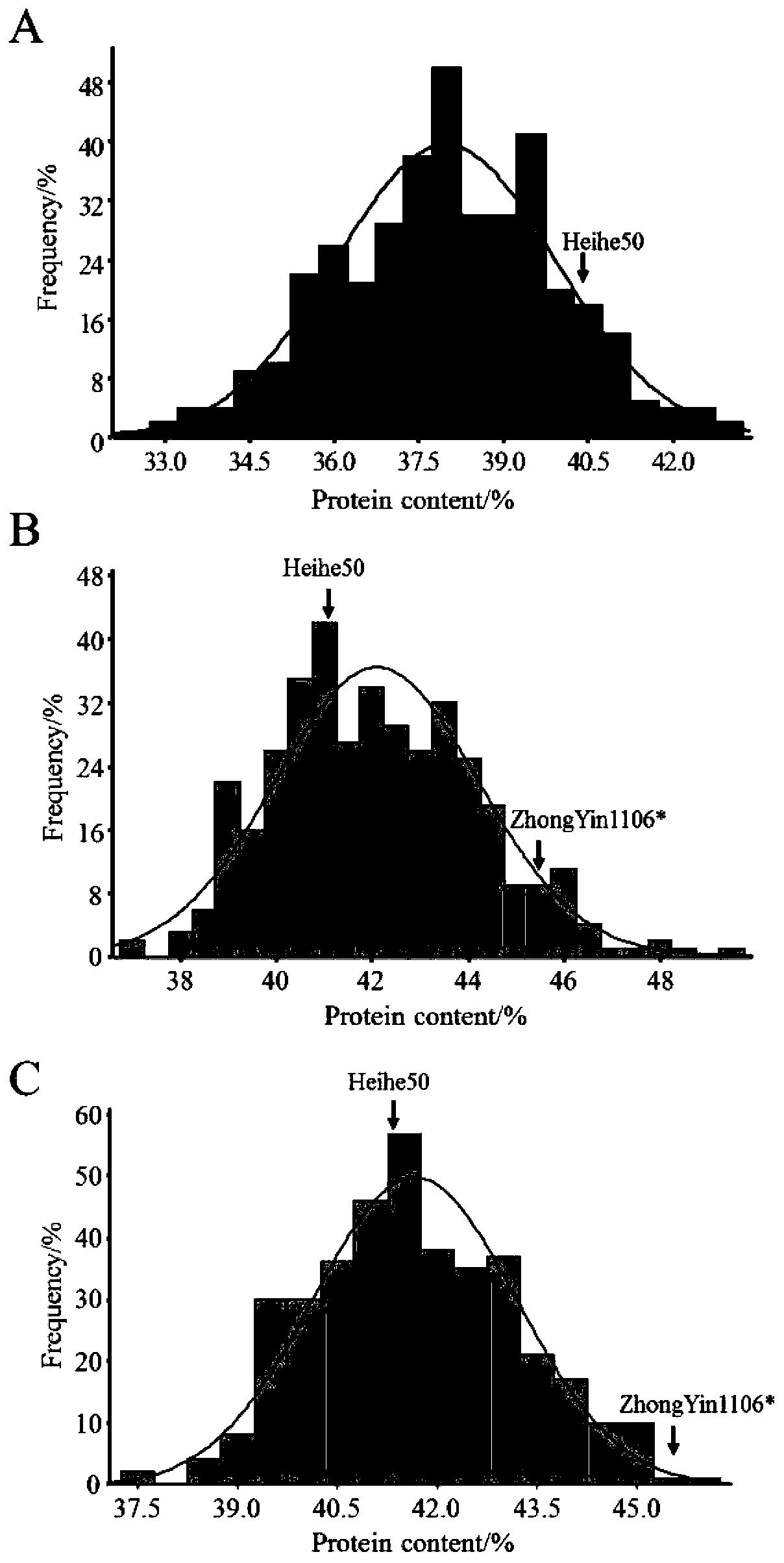
[0037] Example 1 QTL mapping analysis of soybean protein content: BC1 population constructed by Heihe 50 and Zhongyin 1106
[0038] 1) Screening of parents
[0039] Heihe 50 from the Heihe Branch of Heilongjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences and Zhongyin 1106, which were bred from Heilongjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and Zhongyin 1106 were selected. Heihe 50 was used as the female parent. The male parent is mainly characterized by late maturity and lodging resistance, with a protein content of 45.88%.
[0040] 2) Genetic population construction
[0041] In 2011, both Heihe 50 and Zhongyin 1106 were planted in the experimental base of Heihe City, Heilongjiang Province, artificially pollinated and crossed, and obtained F 1 , planted F in the experimental field of Heihe Branch in 2012 1 , planted F in 2013 2 , from which a single plant with a protein content of 45.79% was selected and crossed with Heihe 50 to construct a backcross population, and the BC 1 f 1 ,...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Example 2 QTL mapping analysis of soybean protein content: RIL population constructed by Zhonghuang 35 and Tokachi Changye
[0078] 1) Screening of parents
[0079] The high-oil and high-yield Zhonghuang 35 was selected as the female parent, and the protein content was 40.31% and 39.25% respectively for two consecutive years; the high-protein variety Tokachi Changye introduced from Japan was used as the male parent, and the protein content was 46.21% for two consecutive years. % and 44.47%.
[0080] 2) Genetic population construction
[0081] F 2 group. Using the method of single-grain transmission, we carried out additional generation breeding in Beijing and Hainan, and formed a stable recombinant inbred line population consisting of 199 families (F 15 and F 16 ).
[0082] 3) Determination and distribution of protein content
[0083] The protein content assay method is the same as in Example 1.
[0084] Using SPSS19.0 to F 15 and F 16 The protein content of t...
Embodiment 3
[0104] Example 3 QTL mapping analysis of soybean branch number
[0105] 1) Screening of parents
[0106] The multi-branched variety KN24 was selected as the female parent and the less-branched variety KF19 was used as the male parent to prepare a hybrid combination. In 2015, the number of branches of KN24 was 6.0, and that of KF19 was 0.6; in 2016, the number of branches of KN24 was 7.9 , and the number of branches of KF19 is 1.1.
[0107] 2) Genetic population construction
[0108] F 1 , selfing produces F 2 , F 2 by 3 strains of F 1 produced by selfing, F 2 A total of 549 individual plants were planted in Keshan County, Heilongjiang Province, under conventional field management. After the soybeans matured, the side plants were removed, and the agronomic traits of each individual plant, such as plant height, number of main stem nodes, and number of branches, were measured.
[0109] 3) Identification and distribution of branch numbers
[0110] KN24×KF19 population F 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com