Application of akadama soil, method for removing phosphorus in farmland ditch, and plant cultivation matrix
A technology of red jade soil and ditches, applied in the field of agriculture, achieves the effects of wonderful ideas, pollution improvement and scientific design
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] This embodiment provides matrix screening experiments, specifically:
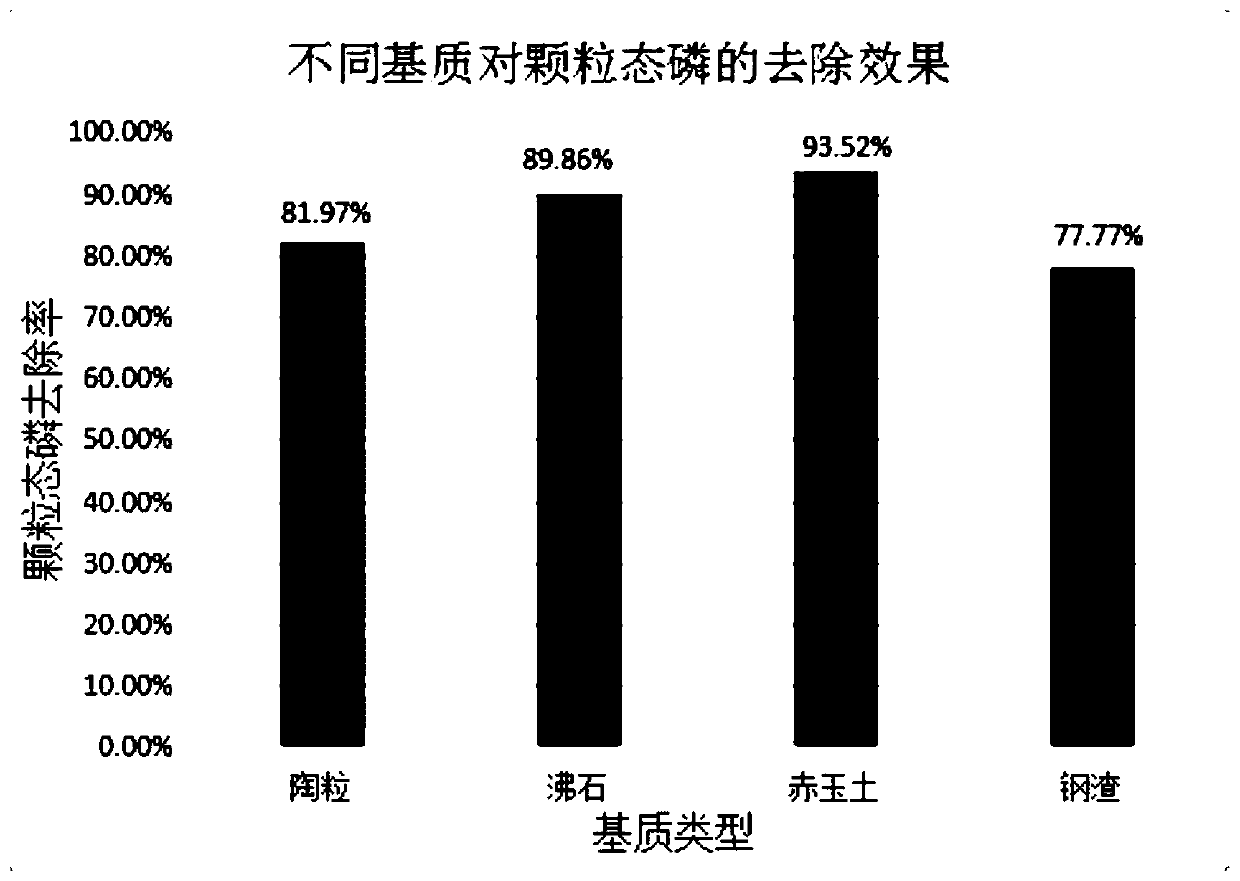
[0036] According to the literature review and comparison of some substrates with adsorption properties for phosphorus, and referring to their market prices, this study initially selected common and economical clinoptilolite, ceramsite, steel slag and red jade soil as the fillers used in the experiment and screened them . Before carrying out the experiment, soak the four fillers in clear water that has been tested to contain no phosphorus, and clean them up. Then put fillers with the same particle size and mass into perforated PVC pipes, and inject artificial water with a phosphorus concentration of 0.9-1 mg / L. Three repetitions were set up for each packing, and after standing for a period of time, the water samples filtered through the packing were taken to measure the concentration of TP, PP and DP, and the adsorption effects of various packings on TP and PP were analyzed, and the combination was s...
Embodiment 2
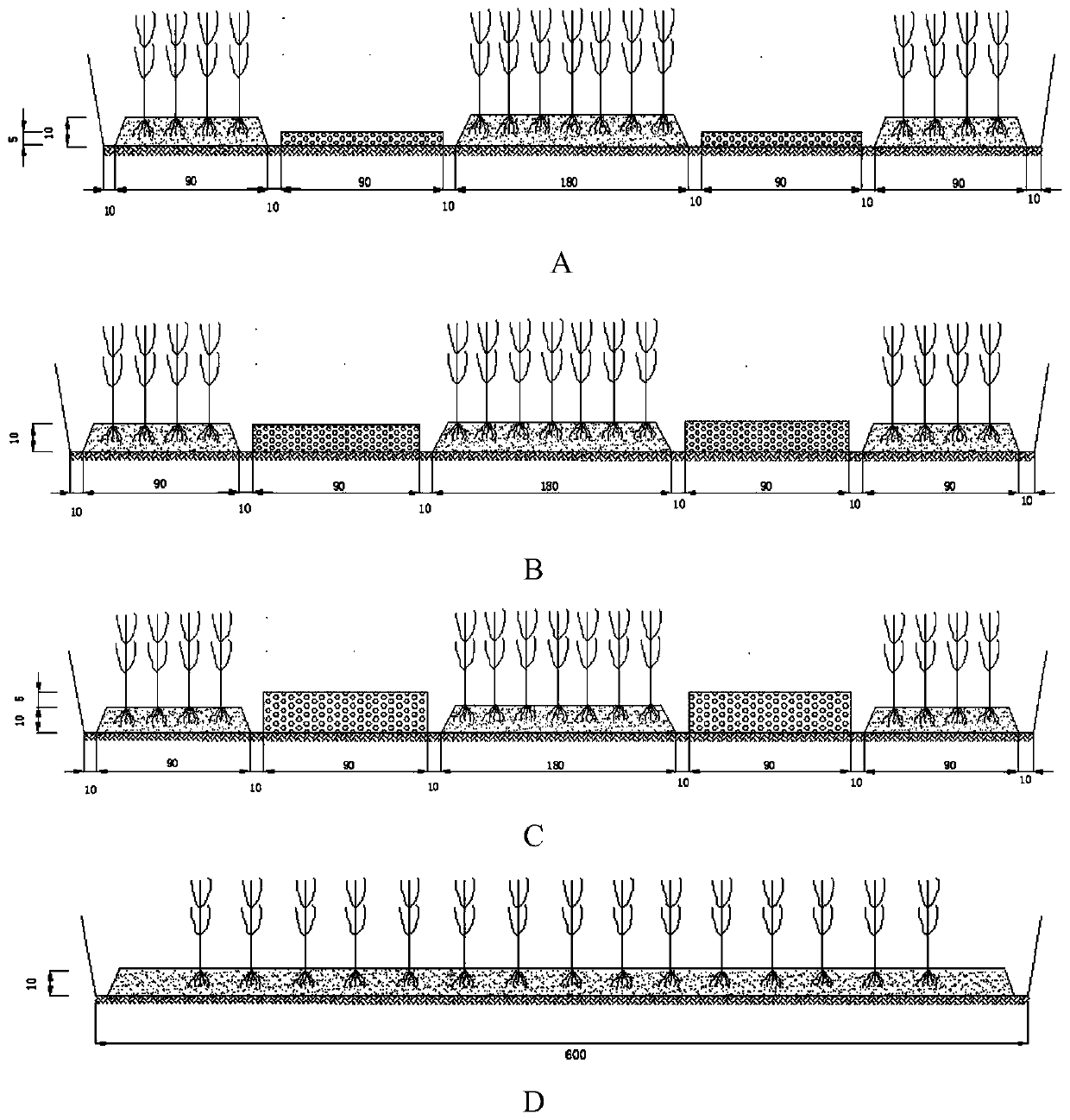
[0041] This embodiment provides the layout experiment of the matrix dam using red jade soil as the matrix, specifically:
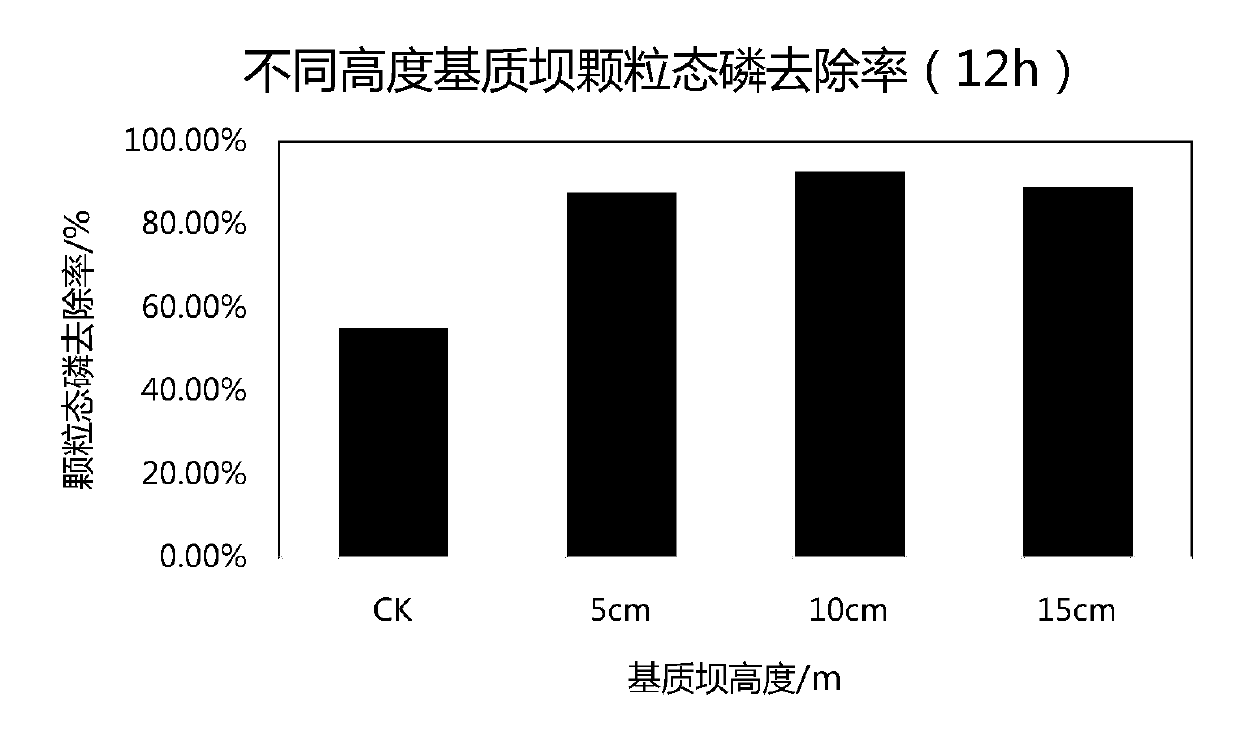
[0042] The soil layer height of the ecological ditch is 10cm, and matrix dams with a height of 5cm, 10cm and 15cm are respectively set in the ditch, and the ecological ditch without filler is used as a blank control, see figure 2 . The influent water samples of the ditch are artificially distributed, and the influent flow rate is 5L / d. After the system is stabilized, the water inlet of the matrix ditch, the front end and the back end of each matrix barrier are collected respectively at 0h, 12h, 24h, 36h, 48h, and 60h. And 100ml of water samples from the outlet of the ditch, and 100ml of water samples from the water inlet and outlet of the control ditch, and the determination of granular phosphorus and total phosphorus, the results are shown in Table 2-4. Among them, in Table 2-4, section 1 is the soil layer water inlet of the ecological ditch; section 2 ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] This embodiment provides the matrix dam laying experiment that adopts red jade soil as matrix, compared with embodiment 2, the soil layer height of ecological ditch is 30cm in the present embodiment, and height is 15cm, 30cm and 45cm respectively in the ditch. Red jade soil matrix dam, other conditions are the same.
[0053] The results show that for the matrix dam with a height of 30cm, the removal rates of granular phosphorus and total phosphorus at 6 sections of the section are the highest at 0h, 12h, 24h, 36h, 48h, and 60h. That is, when the height of the matrix dam is consistent with the height of the soil layer of the ecological ditch, the removal rate of phosphorus is the best.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com