Devices and methods for delivering therapeutics
A therapeutic agent and pancreas technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, pharmaceutical equipment, microorganisms, etc., can solve bulky and bulky problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0167] Film manufacturing
[0168] This example describes the manufacture of membranes (eg, electrospun polymer membranes). The membrane preparation process is carried out using a climate-controlled electrospinning equipment (EC-CLI, IME Technologies), which consists of a single emitter with a 19-gauge needle and a rotating drum collector with a diameter of 6 cm running at 500 rpm, both The distance is between 5 and 17 cm. The polymer solution (6% w / v) was fed into the emitter through a 0.8 mm PTFE tube at a flow rate of 16.7 μL / min under 50% humidity and 23°C. The transmitter is set between 15kV and 18kV, and the collection drum is kept at -4kV. After satisfactory fiber formation, the x-axis translation stage of the transmitter was set to repeat a linear pattern with a speed of 100 mm / s and a delay of 200 ms at the edge. The total collection time after activating the translation stage is 140 min. Films (e.g., electrospun polymer films) can also be collected on the patterned ...
Embodiment 2
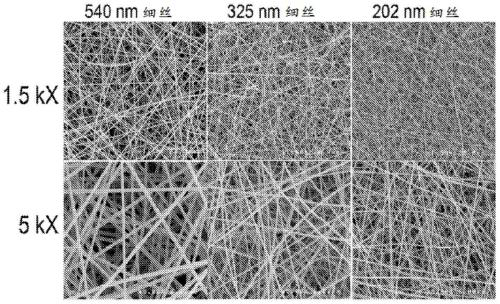
[0171] PAN film with different diameters
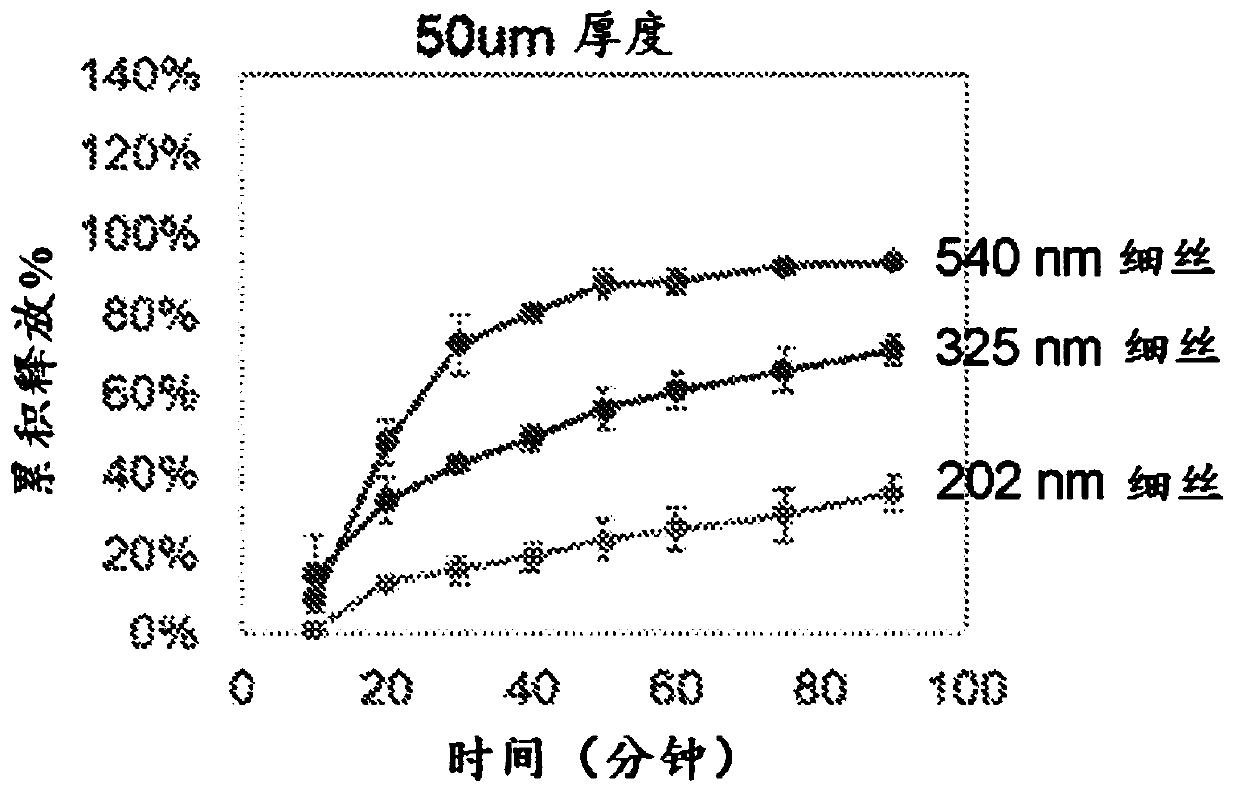
[0172] This example describes scanning electron microscopy and the cumulative release of proteins from PAN membranes with different diameters (eg, electrospun polymer membranes). A film (for example, an electrospun polymer film) was manufactured according to Example 1. A 6% (w / v) PAN polymer solution was used to electrospin the PAN polymer. The diameter of the filaments in the resulting electrospun polymer film is changed by controlling the polymer concentration and voltage. Table 1 shows the electrospinning parameters, including polymer solution concentration (w / v), positive and negative voltage settings (kV), feed rate, distance and electrospinning time. These electrospinning parameters are used to obtain 540nm, 325nm and A 50μm thick polymer film of 202nm diameter fibrous filaments.
[0173] Table 1 Polyelectrospinning parameters
[0174]
[0175] The electrospun polymer film was spun to a thickness of 50 μm. The electrospun membrane...
Embodiment 3
[0179] Protein release from PAN electrospun polymer membrane
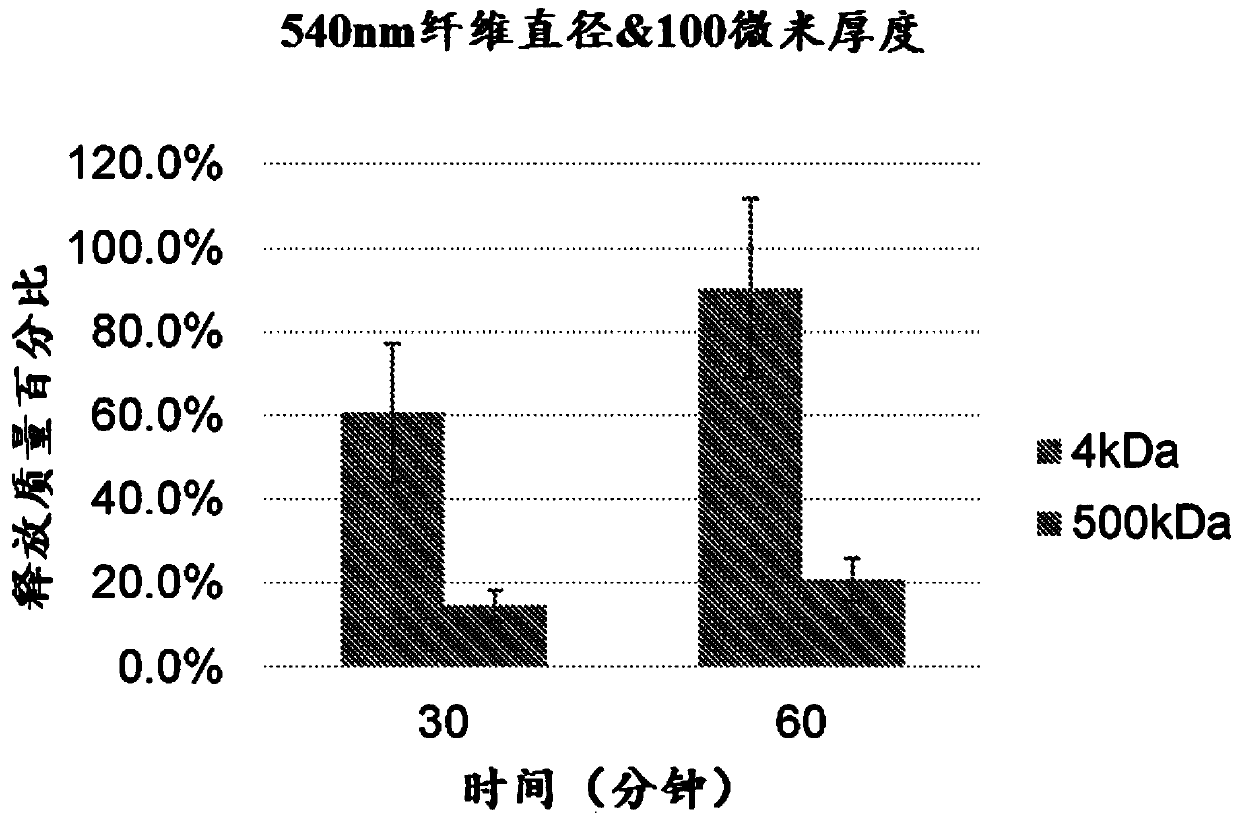
[0180] This example describes the release of proteins of different molecular weights from PAN electrospun polymer membranes. According to Example 1, an electrospun polymer film was manufactured. PAN polymer is electrospun with 6% (w / v) polymer solution. The release study was performed as described in Example 2 above.
[0181] Figure 2 shows the diffusion of 4kDa FITC-dextran molecules and 500kDa FITC-dextran molecules from a base polymer blend that is electrospun to produce 540nm filament diameter or 202nm filament diameter . Figure 2A Shows the diffusion of 4kDa FITC-dextran molecules and 500kDa FITC-dextran molecules from a base polymer blend at 30min and 60min, which is electrospun into filaments with a diameter of 540nm 100 micron thick film. Figure 2B Shows the diffusion of 4kDa FITC-dextran molecules and 500kDa X moieties from a base polymer blend at 30min and 60min, which is electrospun into a 100-micron thi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com