Polymeric ordered porous films, methods for their preparation, and applications for capturing and controllable glucose-responsive insulin release
A porous film and polymer technology, which is applied in the application field of polymer ordered porous film materials, capture and controllable sugar-responsive insulin release, can solve the problems of less attention to the film system, and achieve simple and convenient equipment, mild conditions, Efficient load and release effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
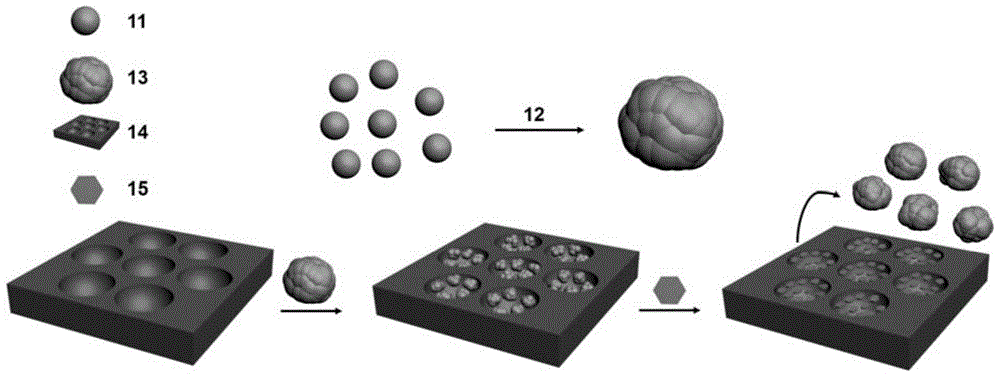
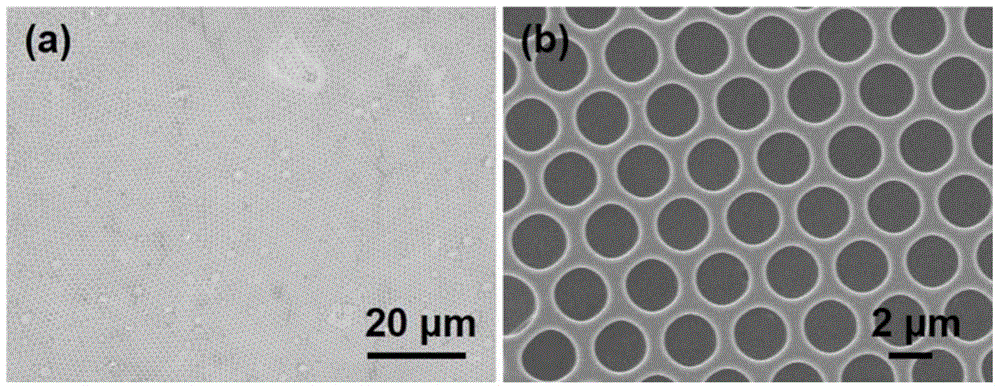
[0031] Dissolve 30mg PS (purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, molecular weight: 350,000) and 2.5mg DDA in 5mL dichloromethane solution to prepare polymer organic solution, take 50μL deionized water into 1mL volumetric flask, and then add polymer Take the organic solution to the marked line, shake it for about 1 min to obtain a microemulsion, and pour the microemulsion on a clean glass substrate under the conditions of humidity of 35% and temperature of 27°C. After the organic solvent and water were completely volatilized, an ordered porous film with a pore diameter of about 2 μm, a pore depth of 1 μm, and a film thickness of 35 μm was obtained.
[0032] The obtained ordered porous film was immersed in a 3wt% PAA solution for 30 minutes, the film was taken out, washed three times in deionized aqueous solution, and then placed in the air to dry naturally.
[0033] Soak the PAA-loaded porous film in a mixed solution of 7.5mM APBA and 12.5mM EDC for 3h, remove the film, wash it three tim...
Embodiment 2
[0040] As shown in Example 1, with other conditions unchanged, the mass of DDA was changed to 1.5 mg, and an ordered porous film with a pore diameter of about 2 μm, a pore depth of 1 μm, and a film thickness of 20 μm was prepared.
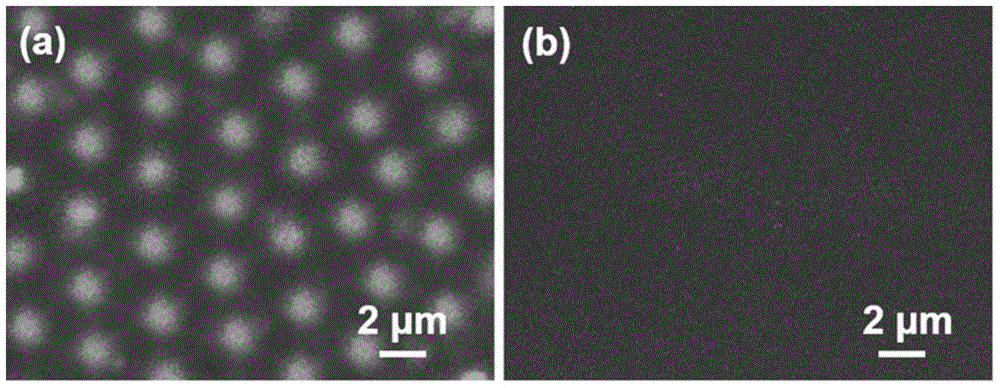
[0041] Then according to the steps of Example 1, the modification of PAA, APBA and Alg in the hole, the positioning assembly of insulin aggregates, and the in situ release study in the hole were respectively realized. Under this condition, the insulin release efficiency was 95%.
Embodiment 3
[0043] As shown in Example 1, with other conditions unchanged, the surfactant DDA was replaced by DDAB, and an ordered porous film with a pore diameter of about 4 μm, a pore depth of 2 μm, and a film thickness of 50 μm was prepared.
[0044] Then according to the steps of Example 1, the modification of PAA, APBA and Alg in the hole, the positioning assembly of insulin aggregates, and the in situ release study in the hole were respectively realized. In this case, the insulin release efficiency was 95%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| release amount | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| release amount | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com