Using targeted radiotherapy (TRT) to drive Anti-tumor immune response to immunotherapies
A targeted and immunomodulatory technology, applied in radiotherapy, anti-tumor drugs, anti-animal/human immunoglobulin, etc., can solve problems such as xRT cannot be used in combination, destroy immunotherapy, systemic immunosuppression, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0221] Example 1: Background Support Data
[0222] The Sondel lab has demonstrated that tumor-specific mAb+IL2 activates innate immune cells to mediate ADCC in mice [2], with clinical benefit in children with neuroblastoma [3]. In mice, intravenous administration of hu14.18-IL2 IC was more effective than intravenous administration of anti-GD2 mAb+IL2 [2,10]. This can provide significant antitumor effects in recently established very small GD2+ tumors or very small micrometastases, possibly explaining the clinical utility of this approach in patients who are in remission but are at high risk of recurrence [3]. Target measurably large tumors [i.e. ~50 mm when injected IC intratumorally (IT-IC) rather than IV (intravenously) 3 GD2+ tumors] have a stronger anti-tumor effect [4,5].
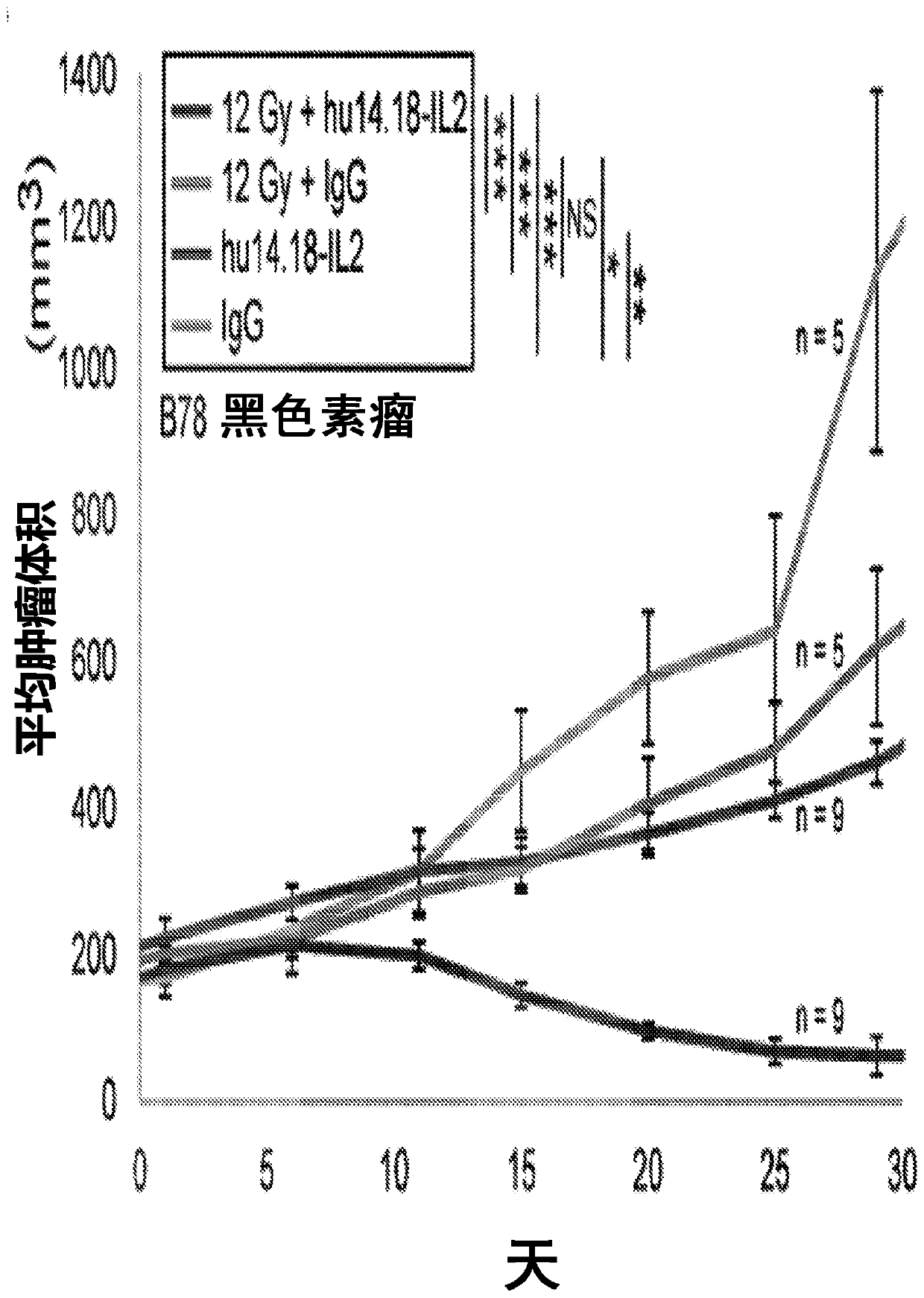
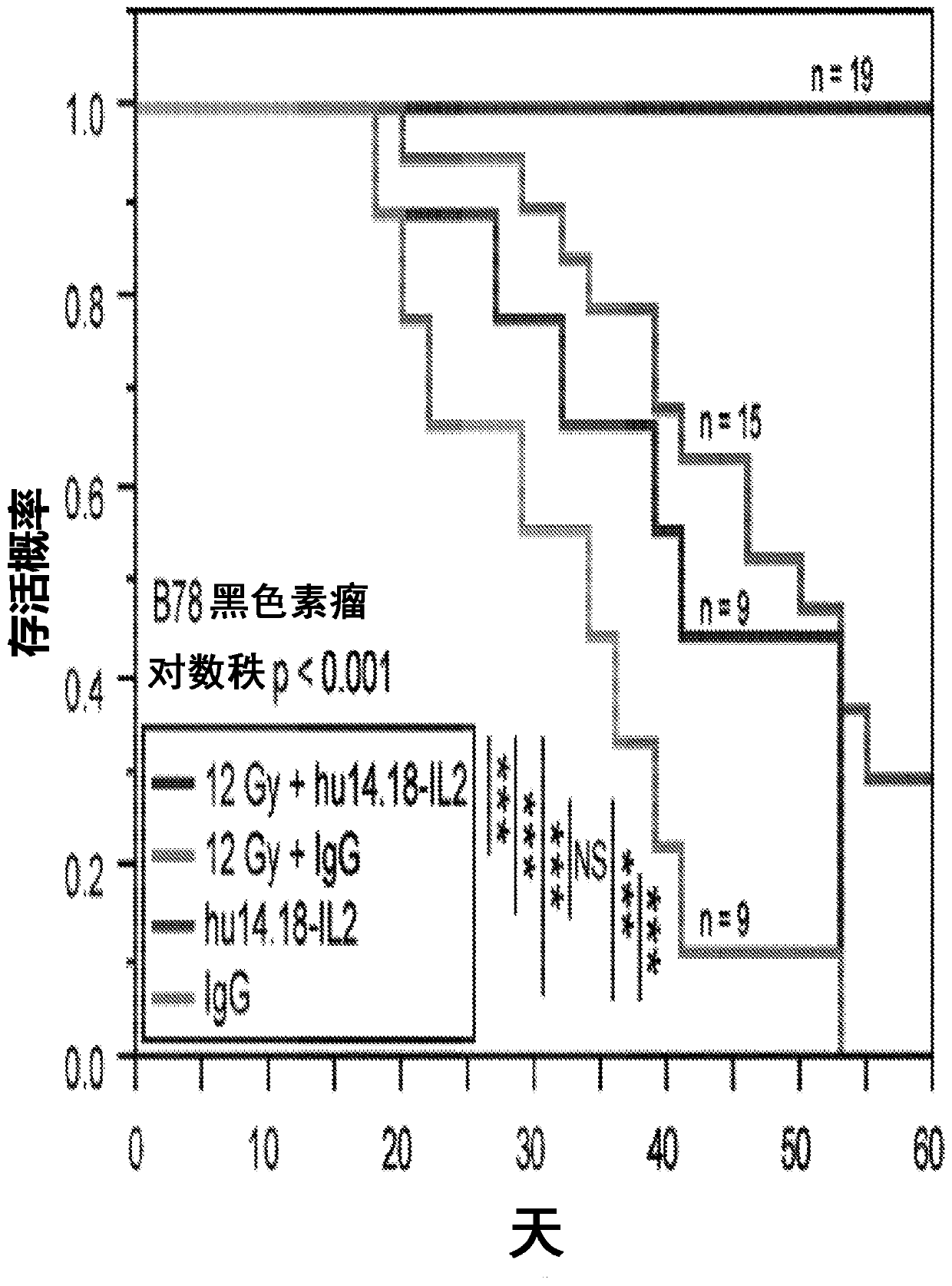
[0223] We are now focusing on ways to provide benefit to larger macroscopic tumors. Established 5 weeks ago to carry medium size (200mm 3 ) B78 melanoma tumors in mice that did not respond to IV-I...
Embodiment 2
[0228] Example 2: Determining the dose of xRT
[0229] Our data suggest these four hypotheses: (1) the dose of xRT we use to treat individual tumors causes modest direct in vivo tumor death and increases susceptibility to immune-mediated death (via ADCC and T cells); (2) Strong T cell responses provided by the addition of IT-IC but not IT mAbs suggest that in the presence of IL2, mAb binding to irradiated tumor cells promotes antigen presentation and enhanced induction of adaptive immunity; (3) presence of a second tumor As a result, xRT+IT-IC can hardly cause any antitumor effect on the first tumor, which is mainly due to tolerance caused by the systemic effects of immunosuppressive cells present in the second tumor [such as Treg and possibly myeloid-derived suppressor cells ( MDSC)]; by consuming Treg( Figure 4 ) or irradiated second tumor ( image 3 ) can avoid this tolerance; (4) the dose of RT required for the second tumor to avoid tolerance can be much lower than the ...
Embodiment 3
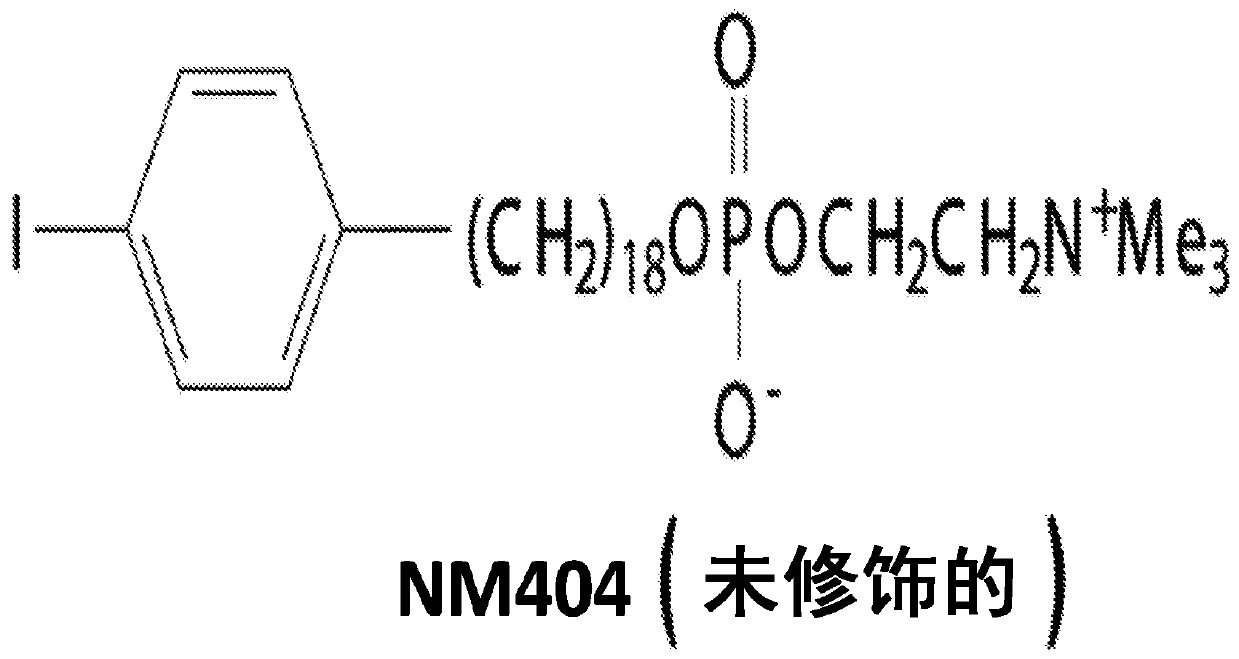
[0241] Determined with TRT and immunosuppression from TRT in C57BL / 6 mice 131 Dose of I-NM404 and evaluate the effect on immune function dosimetry
[0242] 131 I-NM404 showed selective in vitro uptake in >95% of tumor lines (human and mouse), poor uptake by non-malignant cells, and similar tumor specificity was observed in vivo. This includes selective in vivo uptake by B78 tumors ( Figure 5 ). In our preliminary dosimetry studies, we administered C57BL / 6 mice 124 I-NM404, and characterize the time course of TRT exposure by serial PET / CT imaging (eg Figure 5 shown). Monte Carlo dosimetry calculations based on this study [16-18] show that during the 4-week decay period, about 60 μCi of 131 I-NM404 delivered approximately 3Gy to established B78 tumors. After these 4 weeks, the remaining TRT dose to B78 tumors will be less than 0.25 Gy. We will use xRT to replicate the data we obtained in a dual tumor model ( image 3 ), but using the lowest possible dose of targeted ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com