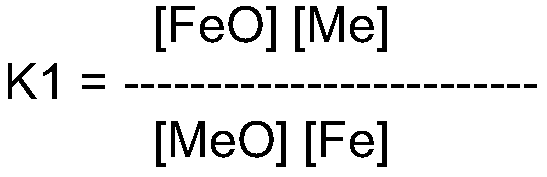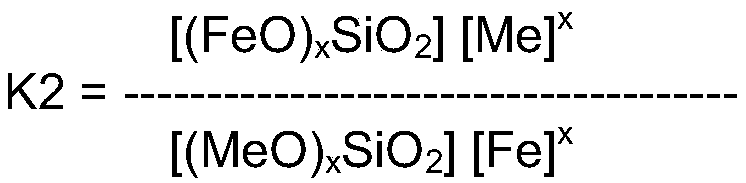Improved pyrorefining process
A technology for copper refining and refining slag, applied in the direction of process efficiency improvement, welding medium, welding/cutting medium/material, etc., can solve the problems of reducing copper recovery rate, low solder output, occupying furnace volume, etc., and achieves widening acceptance standards Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0248] In an embodiment, the method according to the invention further comprises the step of: cooling the first coarse solder metal composition and / or the second coarse solder metal composition and / or the pre-refined solder metal composition to a temperature of at most 825°C, to produce a bath containing a first upper layer of dross that floats under the force of gravity above the first liquid melt conditioned solder phase. Applicants discovered that this further downstream processing step was able to remove significant amounts of copper and other unwanted metals from the raw solder. More details of this step can be found in WO 2018 / 060202 A1. Applicants have further discovered that this cooling step, in combination with some other downstream processing steps of the lead / tin stream, can at least partially replace the pretreatment with silicon metal mentioned elsewhere herein. This is advantageous because metallic silicon is a relatively rare process chemical, and it would be ...
Embodiment
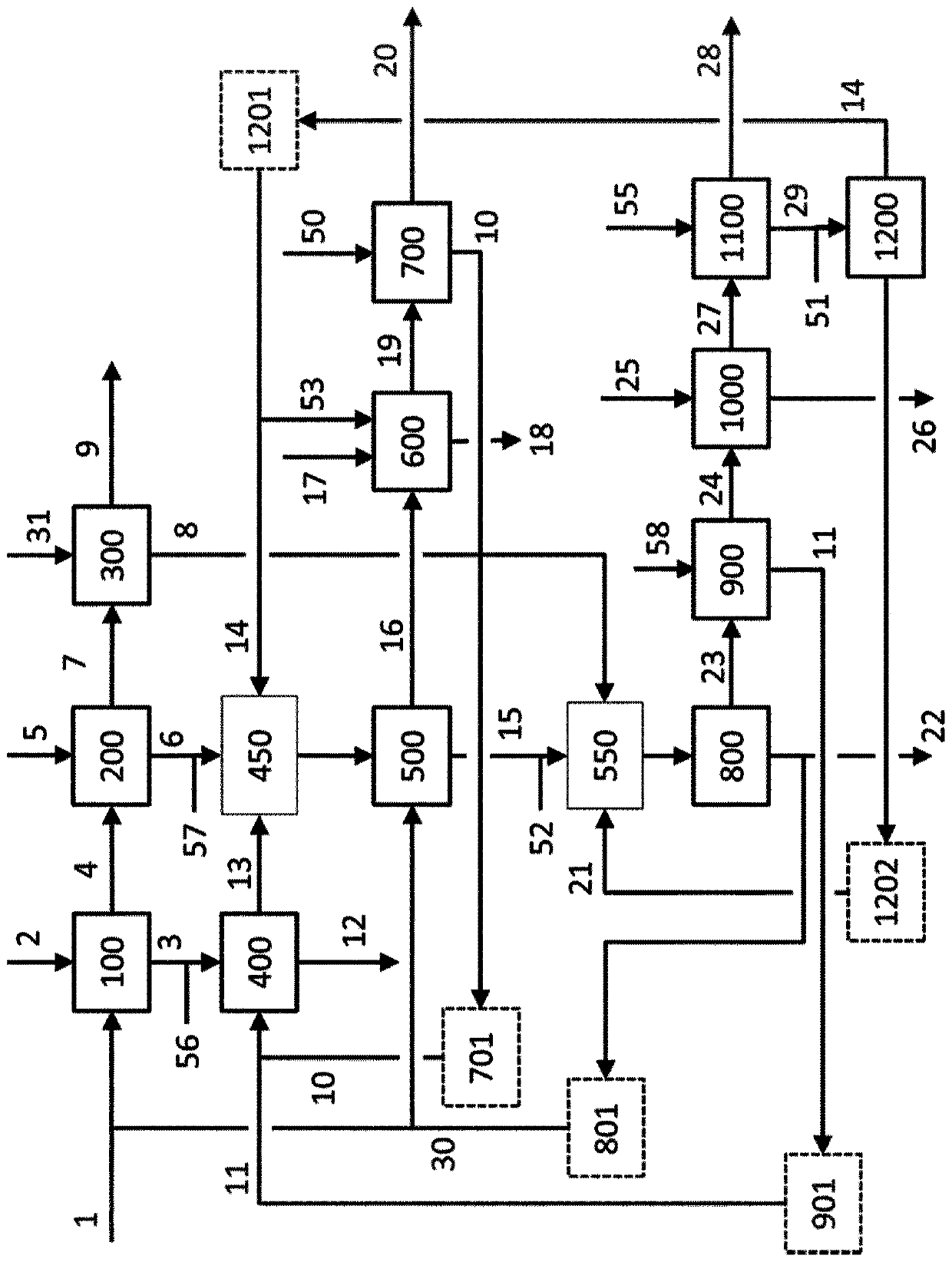
[0271] The following examples illustrate preferred embodiments of the invention. This example is in figure 1 is further shown, where figure 1 A flowchart showing the core parts of the method according to the invention. In this process, starting with a black copper composition 1, a refined anodic grade copper product 9, a high copper metal composition by-product 22, two crude solder metal composition products 18 and 26 and three Kinds of waste residues 12, 20 and 28 etc.
[0272] exist figure 1 In , numbers indicate the following claimed features:
[0273] 1. to the black copper composition feeding of step b) (100)
[0274] 2. Fresh feed to step b) (100)
[0275] 3. The first copper refining slag
[0276] 4. The first copper-enriched metallic phase
[0277] 5. Fresh feed to step h) (200)
[0278] 6. Second copper refining slag
[0279] 7. Second copper-rich metal phase
[0280] 8. The third copper refining slag
[0281] 9. The third copper-rich metal phase - anodic ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com