Semiconductor layered device with data bus inversion
A data bus, bus technology, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, transistors, digital memory information, etc., can solve long-term problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
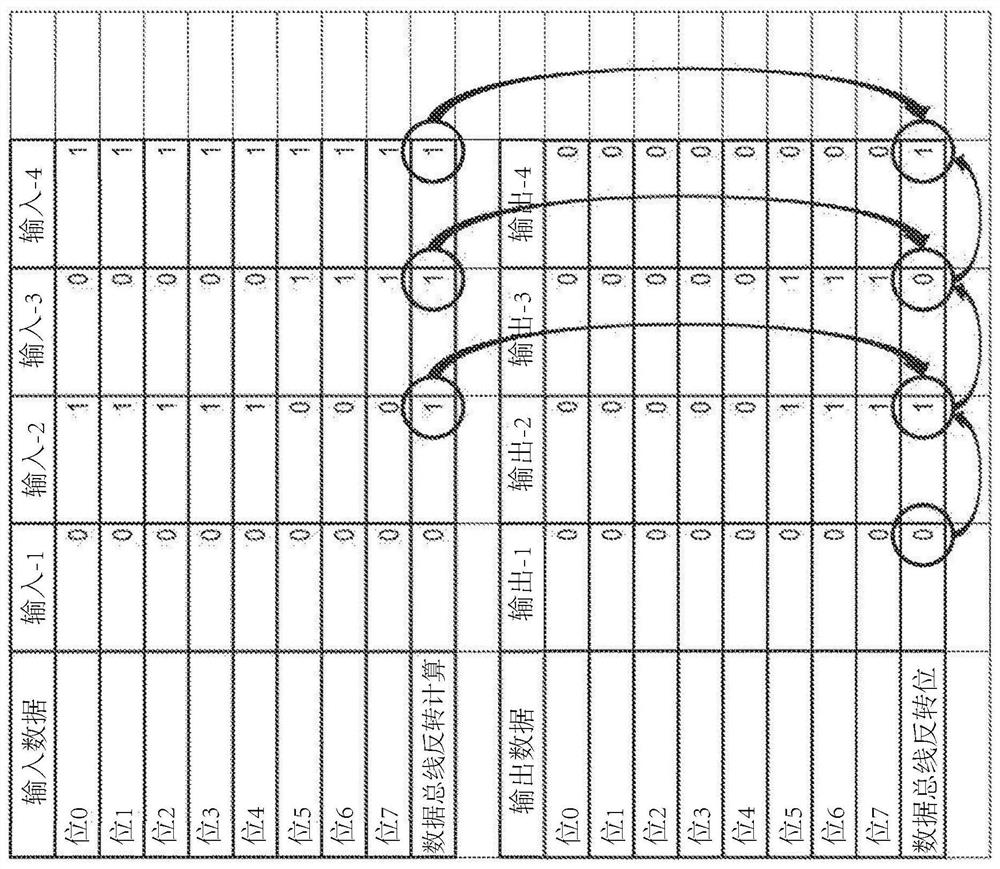
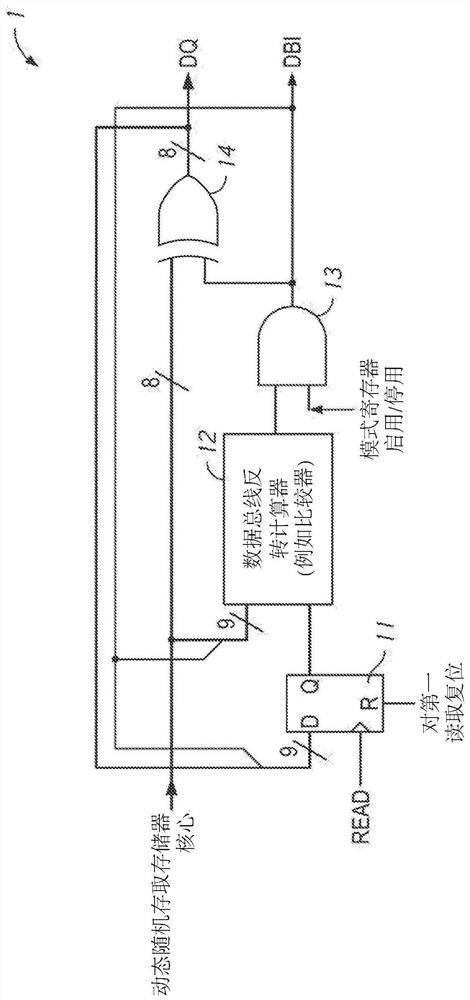
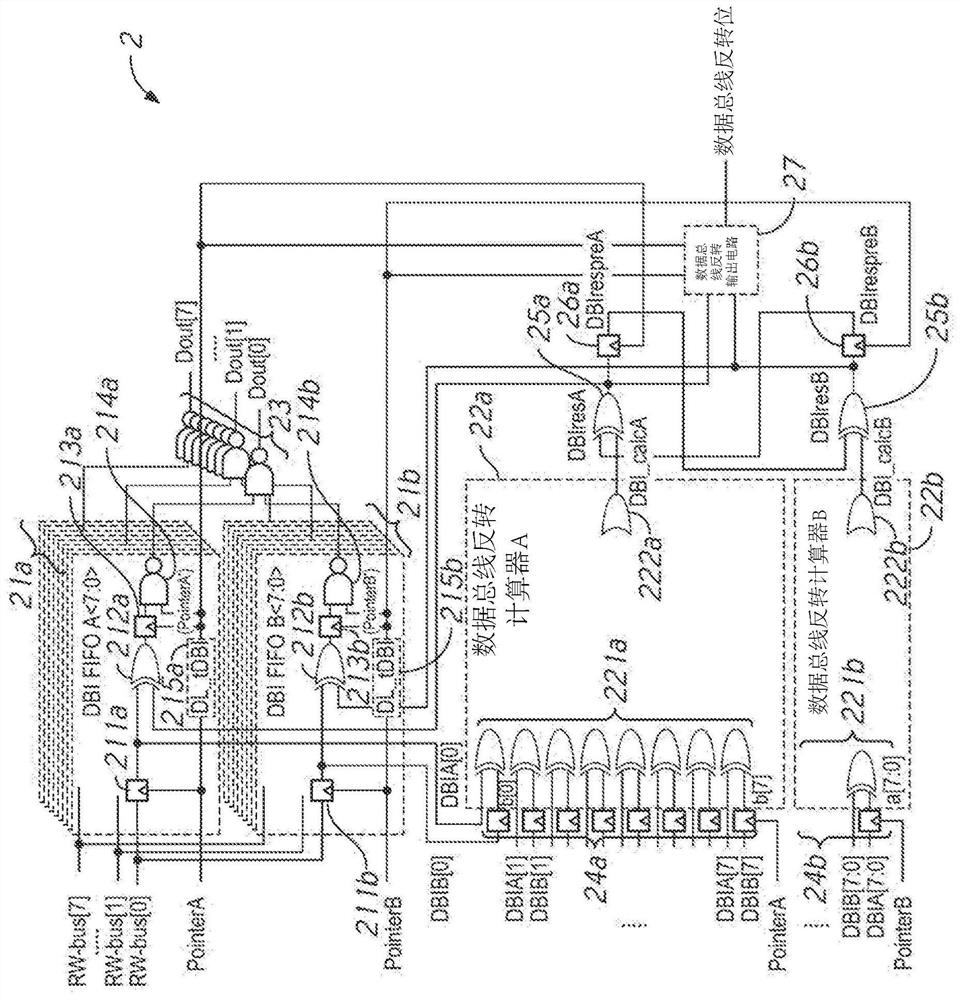
[0030] Various embodiments of the present invention will be explained in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings. The following detailed description refers to the accompanying drawings, which show by way of illustration certain aspects and embodiments in which the invention may be practiced. This description provides sufficient detail to enable one skilled in the art to practice the embodiments of the invention. Other embodiments may be utilized and structural, logical, and electrical changes may be made without departing from the scope of the present invention. The various embodiments disclosed herein are not necessarily mutually exclusive, as some disclosed embodiments can be combined with one or more other disclosed embodiments to form new embodiments.
[0031] Figure 2A is a schematic diagram of a DBI circuit 2 according to an embodiment of the present invention. Figure 2B is a timing diagram of signals in the DBI circuit 2 during a DBI operation accor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com