Method for recovering free starch in papermaking white water
A papermaking white water and anionic starch technology, applied in the field of pulp and papermaking, can solve the problems of wastewater biological treatment, starch sticky matter deposition, increased microbial growth, etc., to achieve the goal of reducing starch consumption, reducing COD concentration, and improving recycling rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0236] The structure of hydrophobic group in embodiment 1 starch binding agent is to the influence of binding agent and starch reaction
[0237] In this example, the reaction of starch binders with different structures and native starch (only cured, not modified) was tested.
[0238] Experimental steps: (1) take a cornstarch sample and prepare 7% "standard starch solution"; (2) take an appropriate amount of standard starch solution and dilute it with deionized water until the starch concentration is 1600mg / L; (3) take the prepared starch concentration Put 500mL of the solution in a beaker and put it into a preset constant temperature water bath at 45°C; (4) According to the concentration of the prepared starch complexing agent, add 3-30mg / L starch complexing agent to make the starch : Complexing agent weight ratio is 50: 1, reacts 30 minutes then, obtains modified starch solution; (5) sampling is centrifuged (4000x g) 5 minutes, gets supernatant liquid test starch content and ...
Embodiment 2
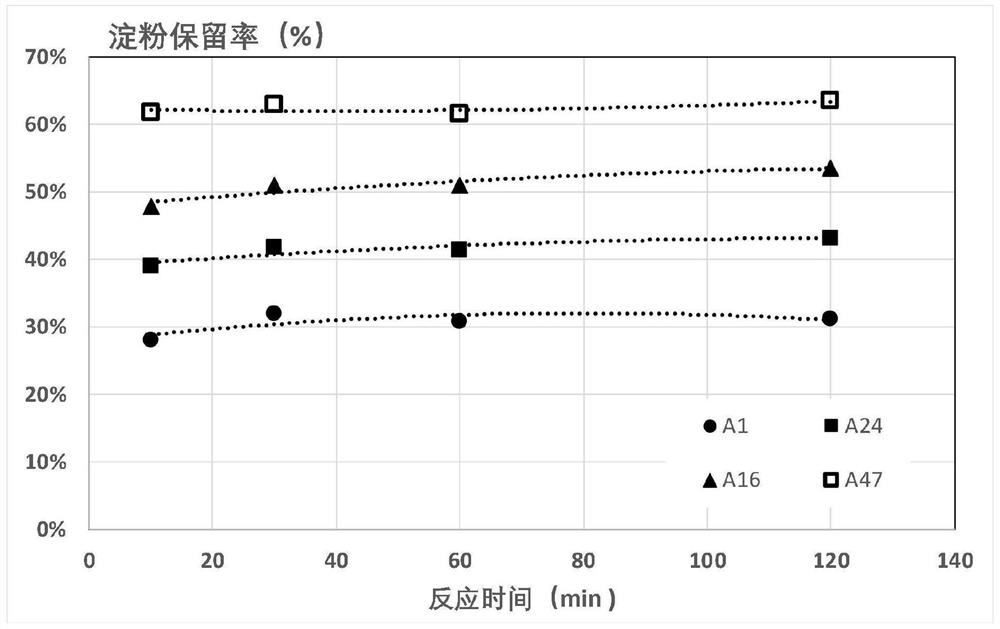
[0246] The impact of embodiment 2 reaction time on starch binding reaction
[0247] In this example, the effect of the reaction time of the starch binder and starch on the modified starch was investigated.
[0248] Experimental steps: (1) take a cornstarch sample and prepare 7% "standard starch solution"; (2) take an appropriate amount of standard starch solution and dilute it with deionized water until the starch concentration is 1800 mg / L (or other required concentration); (3 ) Take 500mL of the prepared starch solution or OCC white water, put it in a beaker, and put it in a 45°C constant temperature water bath, and equilibrate to the specified temperature; (4) Add 30mg / L starch binder as required, and when the reaction reaches 10 , 30, 60 and 120 minutes, the sample was centrifuged (4000x g) for 5 minutes, and the supernatant was taken to test the starch content and the COD concentration.
[0249] This embodiment tests multiple anionic starch complexing agents, and their r...
Embodiment 3
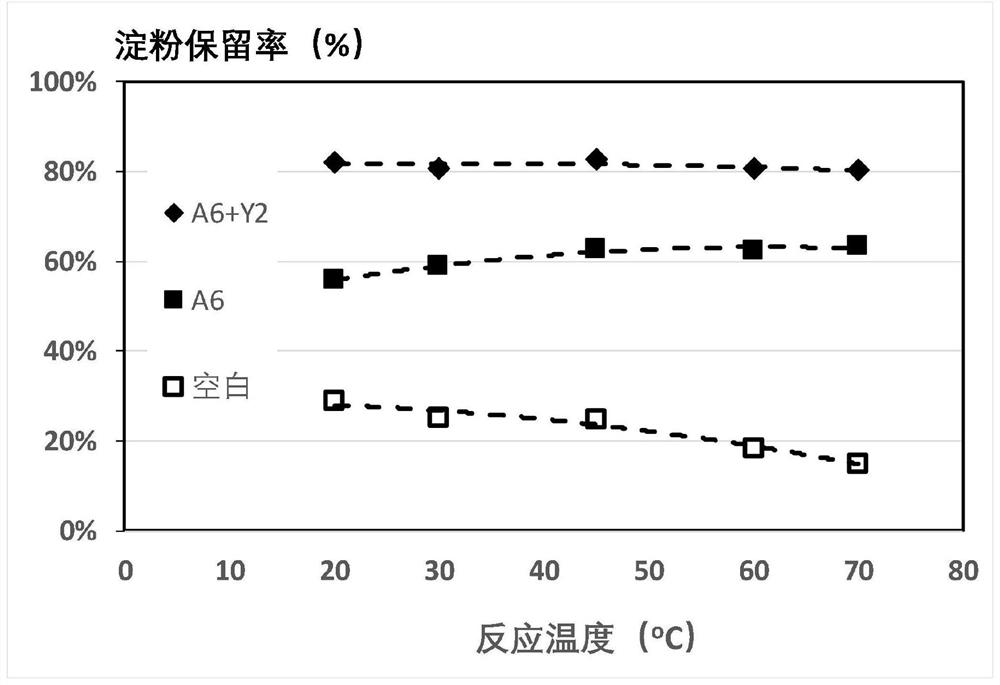
[0250] Embodiment 3 Reaction temperature is to the influence of starch binding reaction and the adsorption effect of modified starch
[0251] This embodiment examines the influence of reaction temperature on the reaction between starch binder and starch and the performance of modified starch (reaction product)
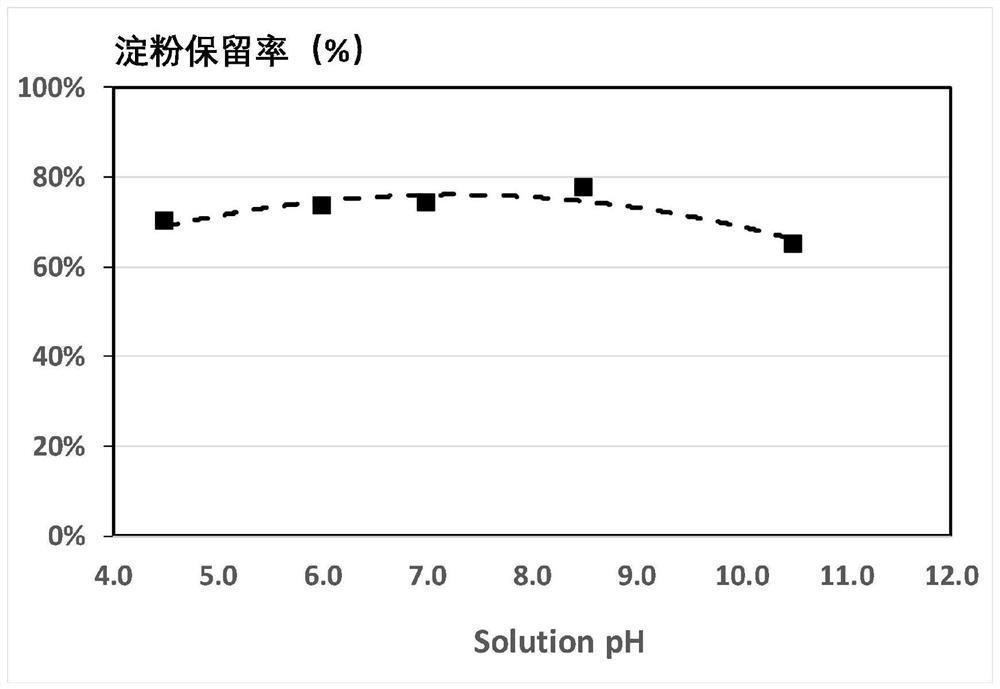
[0252] Experimental steps: (1) Take a cornstarch sample to prepare a 7% "standard starch solution"; (2) Take an appropriate amount of standard starch solution and dilute it with deionized water until the starch concentration is 600 mg / L; (3) Take the prepared starch solution 500mL, placed in a beaker, and placed in a constant temperature water bath with the required test temperature set in advance, and equilibrated to the specified temperature; (4) According to the test requirements, add 30mg / L anionic starch complexing agent A6, react for 60 minutes, Obtain the modified starch solution; (5) sample and centrifuge (4000x g) for 5 minutes, take the supernatant to test th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com