Bragg grating, preparation method thereof and distributed feedback laser
A Bragg grating and distributed feedback technology, applied in lasers, semiconductor lasers, phonon exciters, etc., can solve the problems of the coupling coefficient decreasing refractive index, small signal intensity modulation response bandwidth narrow, unfavorable high-speed direct modulation and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
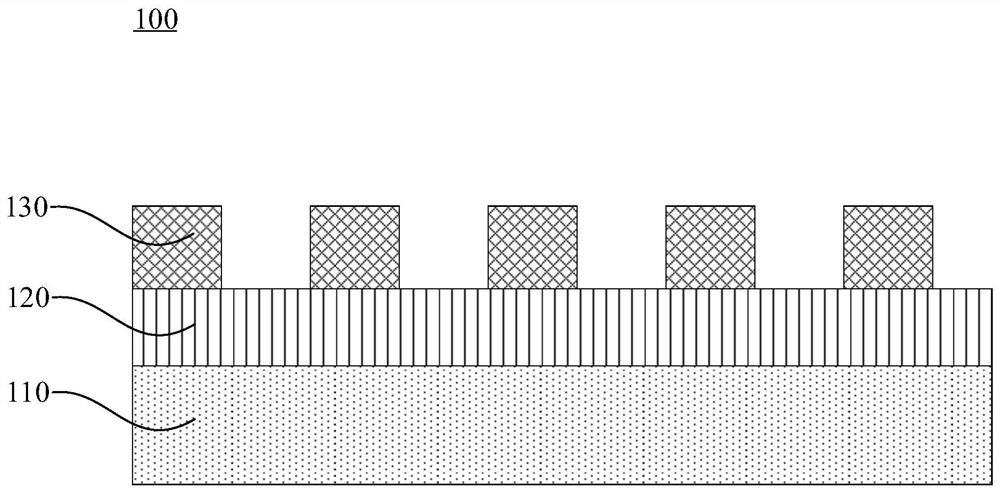
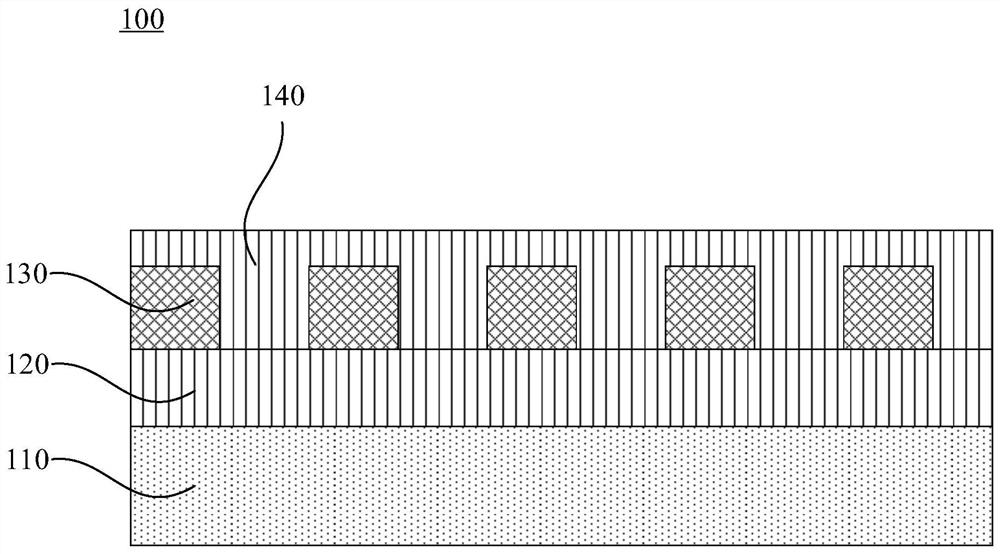
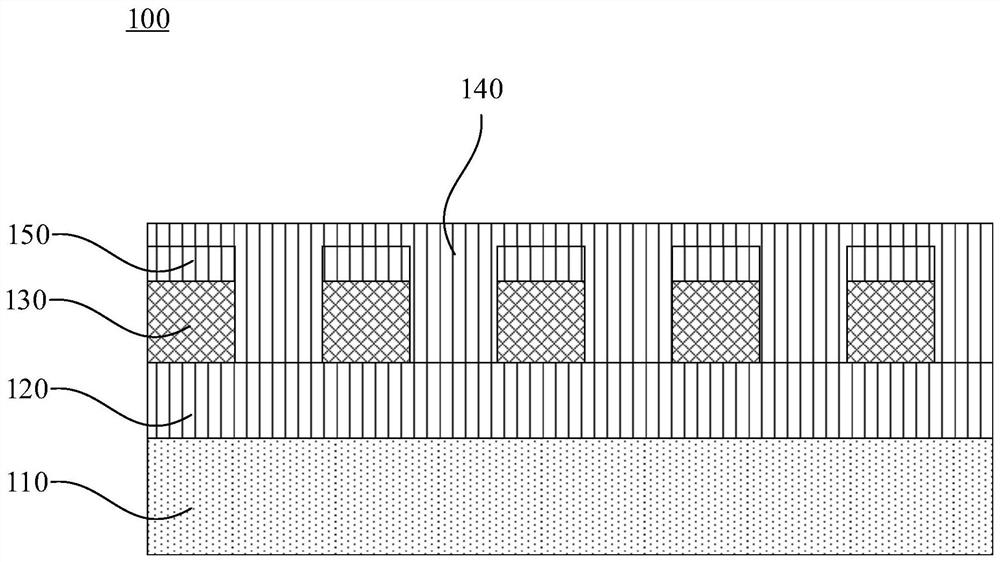
[0032] In order to make the purpose, technical solutions and advantages of the embodiments of the present invention clearer, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments It is a part of embodiments of the present invention, but not all embodiments. The components of the embodiments of the invention generally described and illustrated in the figures herein may be arranged and designed in a variety of different configurations.
[0033] Accordingly, the following detailed description of the embodiments of the invention provided in the accompanying drawings is not intended to limit the scope of the claimed invention, but merely represents selected embodiments of the invention. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art wi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com