A positive pole piece and its preparation method, a lithium ion battery containing the positive pole piece and its application
A lithium-ion battery and positive pole piece technology, which is applied in the field of lithium-ion batteries, can solve the problems of the battery’s small adaptable temperature range, inability to guarantee battery power, and various preparation processes, so as to achieve both high-temperature storage performance, improved battery efficiency, and reduced The effect of side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
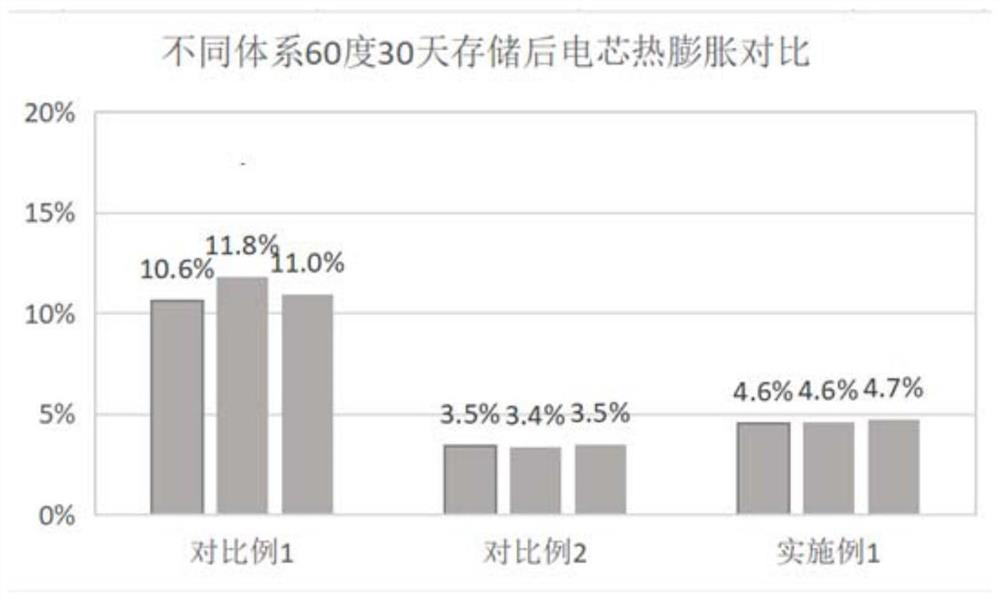
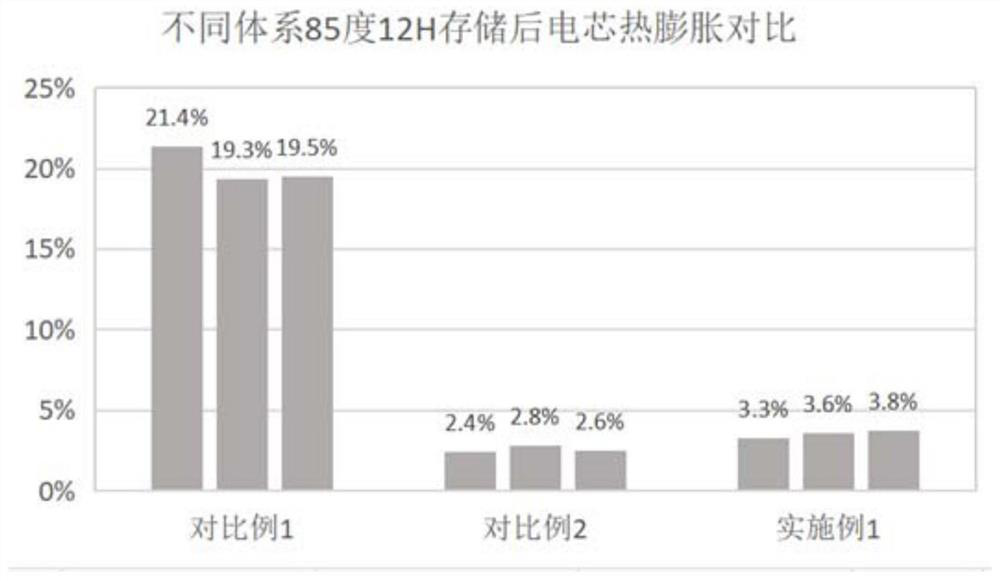
Embodiment 1
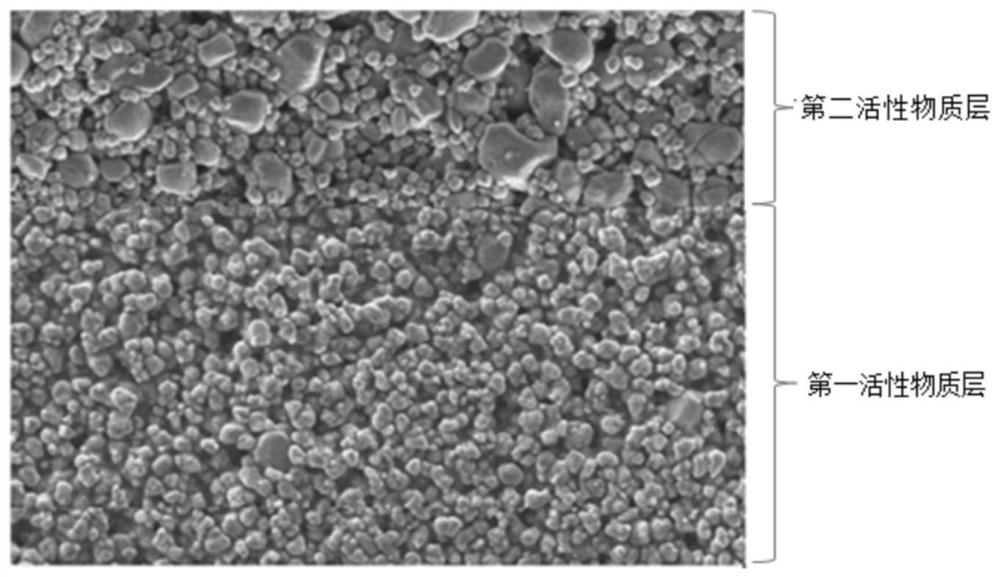
[0067] This embodiment provides a positive electrode sheet, including a current collector, a first active material layer, and a second active material layer, the first active material layer is located between the current collector and the second active material layer, and the first active material layer is located between the current collector and the second active material layer. Both the first active material layer and the second active material layer include a positive electrode active material, a conductive agent and a binding agent. The current collector adopts aluminum foil, the positive electrode active material is lithium cobaltate, and the binding agent is polyvinylidene fluoride (polyvinylidene fluoride, PVDF), the conductive agent is a composite conductive agent of carbon black and carbon nanotubes, and the compounding ratio of the carbon black and carbon nanotubes is 1:1;
[0068] Wherein, in the first active material layer, the particle size D50 of lithium cobaltat...
Embodiment 2
[0079]The difference between this example and Example 1 is that the D50 of the lithium cobaltate particles used in the first active material layer of the positive electrode sheet is 5.0 μm, the D90 is 11 μm, and the D10 is 3.5 μm. The second active material layer uses Among the lithium cobaltate particles, the D50 of the lithium cobaltate particles with the first particle size is 5 μm, the D90 is 11 μm, and the D10 is 3.5 μm; the D50 of the lithium cobaltate particles with the second particle size is 14 μm, the D90 is 24 μm, and the D10 is 8 μm. Other parameters and conditions are exactly the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0081] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that, based on the sum of the mass of the first active material layer and the second active material layer as 100%, the mass of the first active material layer accounts for 85wt.%. , the second active material layer accounts for 15wt.%. Other parameters and conditions are exactly the same as in Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com