Single-hop broadcast control beam pointing method
A beam pointing and beam pointing technology, which is applied in the field of fast single-hop broadcast control beam pointing, can solve the problems of poor network scalability, power reduction, and consumption, achieve low software and hardware resource requirements, improve receiving signal-to-noise ratio, and increase scalability sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
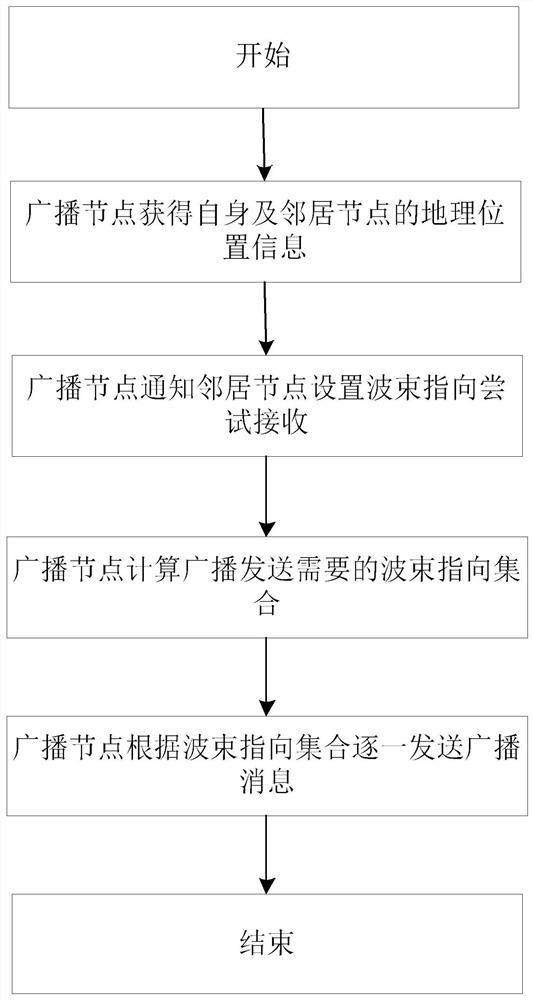
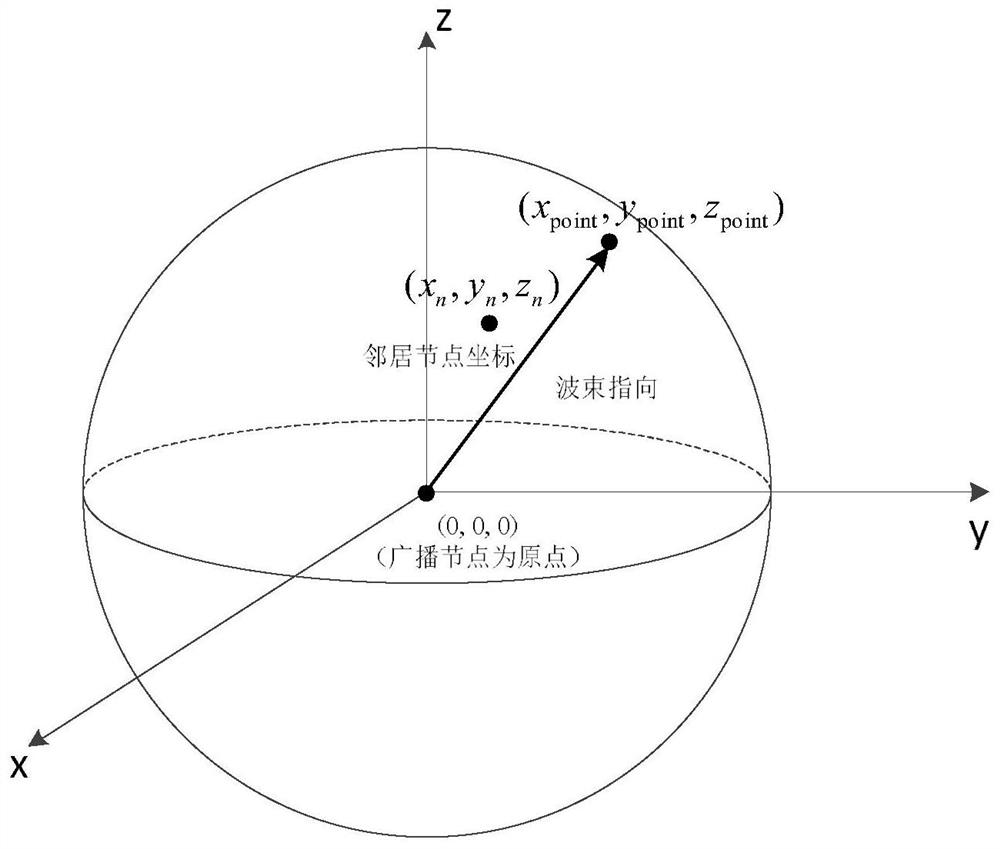
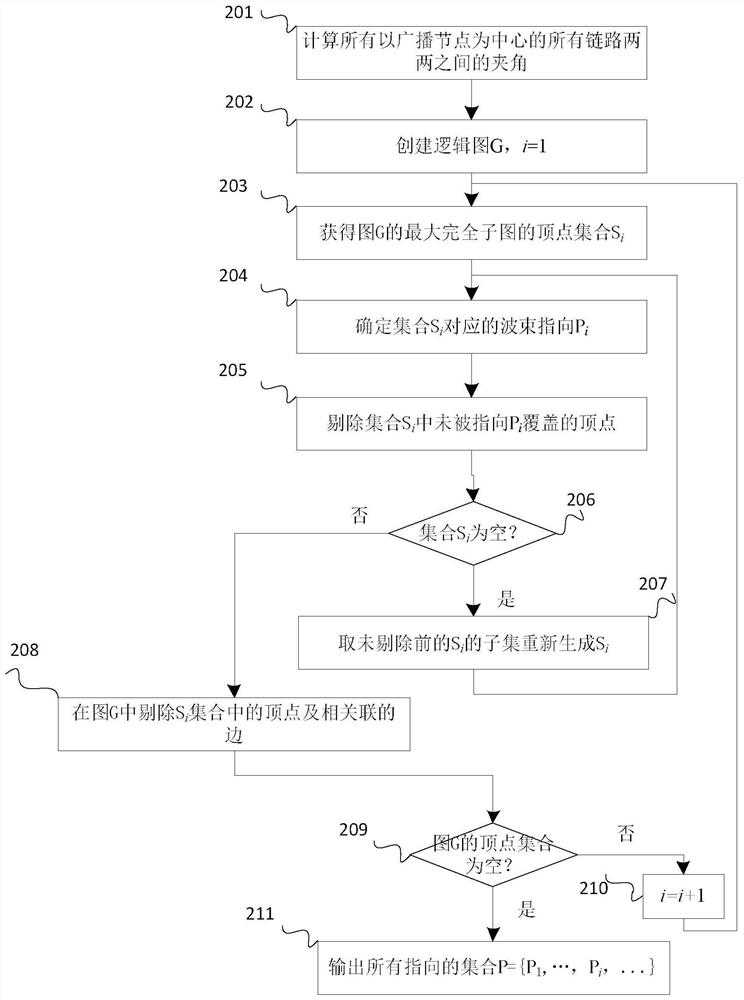
[0023] see figure 1 . According to the present invention, a single-hop broadcast control beam pointing method has the following technical features: in the directional network, in the directional network, the broadcast node obtains the geographic location information of itself and each neighbor node through GPS, and uses Send data with a single beam, notify all neighbor nodes to set the beam pointing and try to receive, and all other nodes schedule beam resources to point to the broadcast node to receive data; then, the broadcast node uses all geographical location information to calculate the beam pointing set required for broadcast transmission, and calculates Find the included angles between all pairs of links, create a logical graph G, and find the largest complete subgraph in the logical graph G to calculate the beam pointing, and use the largest complete subgraph to determine the beam pointing P i ; During a single beamforming transmission process, broadcast messages ar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com