Method for simulating gas-liquid two-phase seepage characteristics in shale natural fractures
A technology of natural fractures and medium gas, which is applied in earth-moving drilling, special data processing applications, wellbore/well components, etc. Control problems such as low accuracy to achieve the effect of saving experimental material funds, saving experimental time, and improving recognition accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
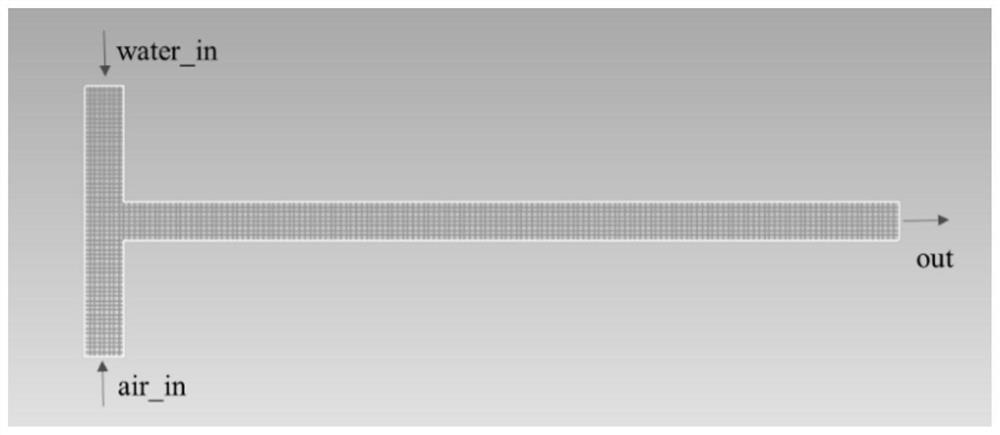
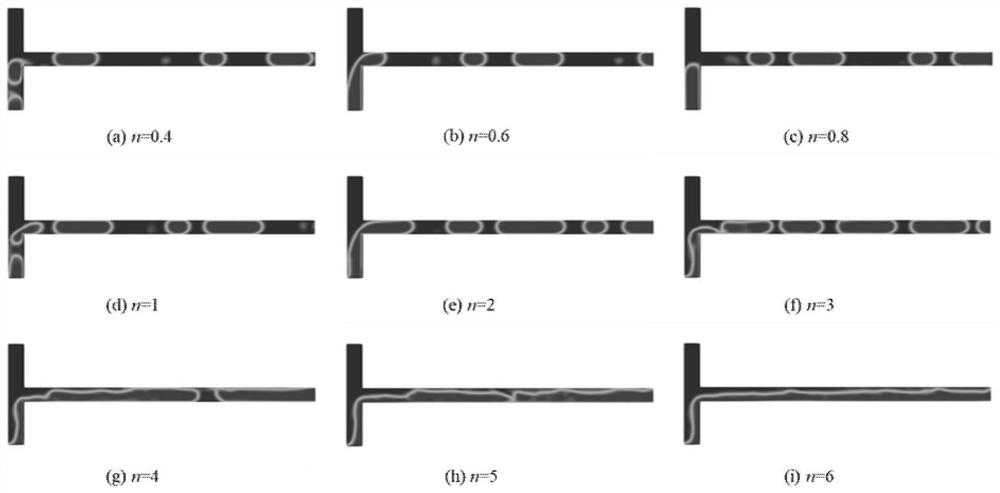
[0043] Step 1. Based on the ANSYS DesignModeler module, establish a T-shaped pipe model. The vertical pipe of the T-shaped pipe model is the gas-liquid two-phase outlet, the upper end of the vertical pipe is the liquid phase inlet, the lower end is the gas phase inlet, and the horizontal pipe is the two-phase outflow.
[0044] Create a three-dimensional T-shaped pipe model in the ANSYS DesignModeler module. The upper part of the vertical pipe of the T-shaped pipe is the liquid phase inlet, the lower part is the gas phase inlet, the horizontal pipe is the gas-liquid two-phase outlet, and the outlet pressure is set to 0MPa (the outlet pressure setting can be adjusted according to the needs, this embodiment only gives a setting possibility sex, the model is attached figure 1 shown). The positions of the gas-liquid two-phase inlet and outlet can be adjusted according to actual needs, and are not limited to the above expressions, which are just an inlet and outlet method given in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com