Nucleic acid aptamer specifically binding to lipocalin-1, and application of nucleic acid aptamer
A technology of lipocalin and nucleic acid aptamer, applied in the field of ophthalmology, can solve problems such as difficulty in meeting early clinical diagnosis, and achieve the effects of easy preparation and modification, good stability and strong specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1. Immobilization of LCN 1 on the surface of magnetic beads
[0034] The LCN 1 protein is mainly immobilized on the surface of magnetic beads through the His tag at the C-terminus. The specific process is as follows: (a) Take 20 μL of Dynabeads TM His-Tag Isolation&Pulldown magnetic beads with 200μL selection buffer (1mM MgCl 2 in1xPBS, pH 7.2) and washed several times; (b) Dissolve 5 μg of LCN 1 protein in 200 μL of screening buffer, and add it to the 20 μL of the washed magnetic beads, and incubate at room temperature for 30 minutes; (c) incubate After finishing, rinse with screening buffer 3 times, resuspend in 20 μL of screening buffer, and store at 4°C.
Embodiment 2
[0035] Construction of embodiment 2.ssDNA library and its primers
[0036] Random ssDNA library: 5′-AGCAGCACAGAGGTCAGATG-N 40 -CCTATGCGTGCTACCGTGAA-3' (SEQID No.9), wherein, N represents any one of the bases A, T, C, G, N 40 Represents a random sequence of 40 nucleotides in length. Upstream primer: 5'-AGCAGCACAGAGGTCAGATG-3' (SEQ ID No.10); Downstream primer: 5'-TTCACGGTAGCACGCATAGG-3' (SEQ ID No.11); Modified downstream primer: 5'-poly(dA20)-Spacer18 -TTCA CGGTAGCACGCATAGG-3' (SEQ ID No. 12).
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3. Screening of LCN 1 nucleic acid adaptation
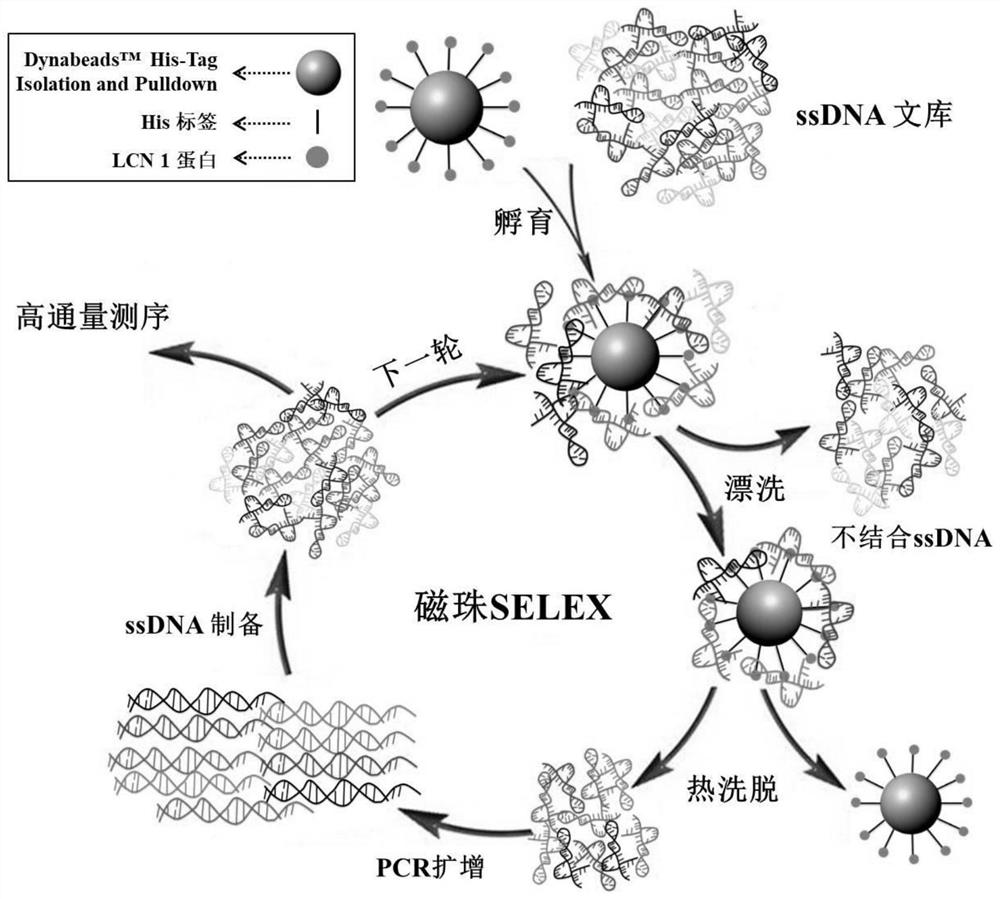
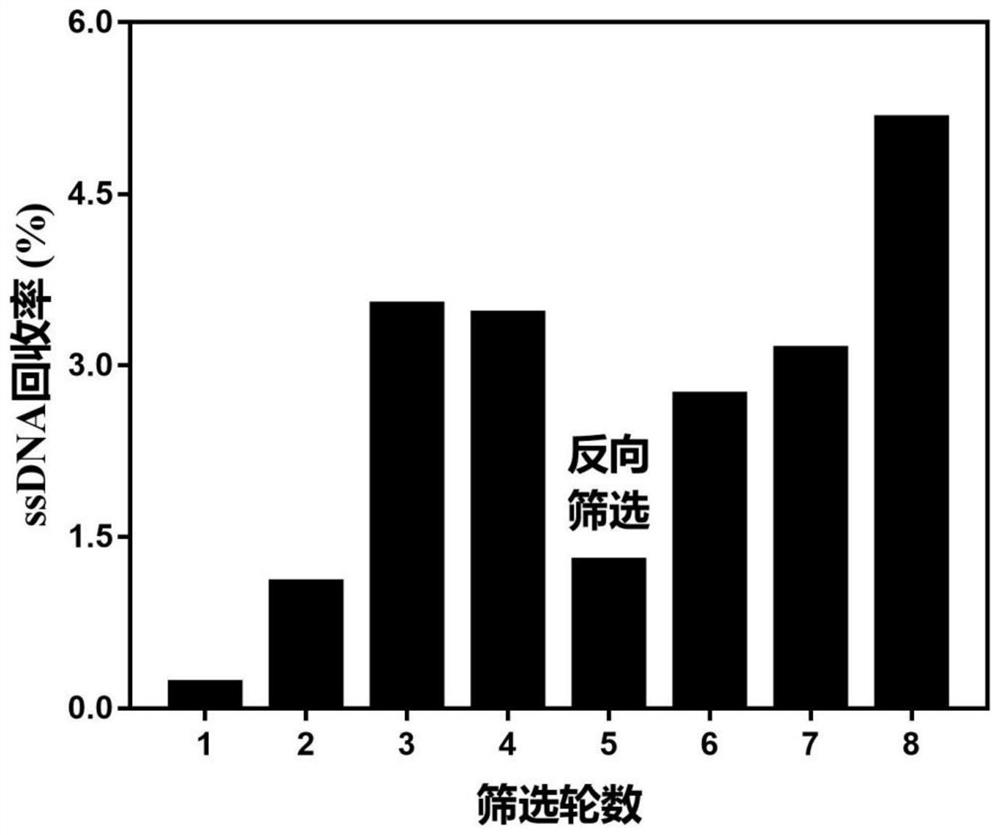
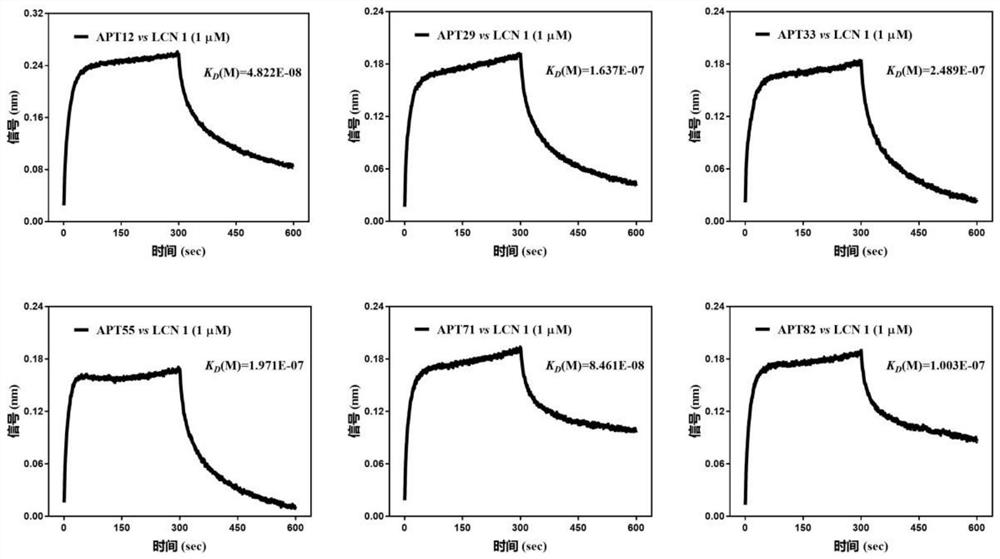
[0038] Such as figure 1As shown, in order to obtain high-affinity nucleic acid aptamers that specifically bind to LCN 1, a total of 8 rounds of screening were performed. The screening protocol is shown in Table 2. The specific screening process is as follows: (a) Take 20 μL LCN 1 magnetic beads, add blocking buffer (screening buffer containing 0.1 mg / ml yeast tRNA, 1 mg / mL BSA) and incubate at room temperature for 15 min Afterwards, rinse twice with screening buffer; (b) Put a certain amount of ssDNA library in a water bath at 95°C for 10 minutes, quench in an ice bath for 5 minutes, and place it at room temperature for 10 minutes, then add it to the blocked magnetic beads, and incubate with rotation at room temperature; (c) After incubation, rinse the magnetic beads with 200 μL of screening buffer several times, magnetically separate, remove unbound ssDNA, add 100 μL of sterile water, and bathe at 95°C for 10 min...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com