Piezoelectric MEMS actuator for compensating unwanted movements and manufacturing process thereof
A technology of actuators, elastic elements, applied in the manufacture/assembly of piezoelectric/electrostrictive devices, processes for producing decorative surface effects, piezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devices, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
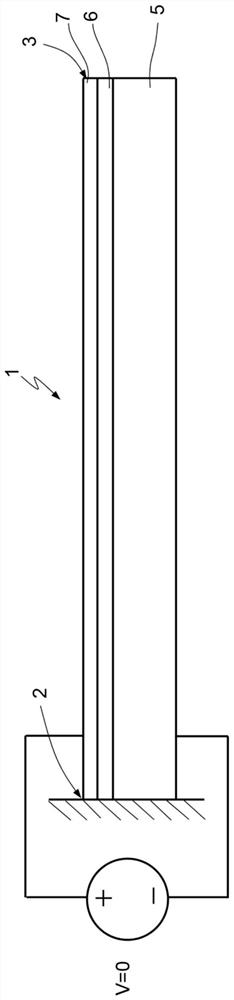
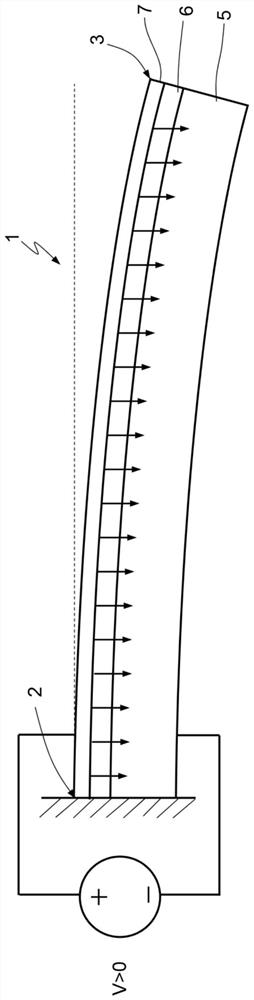
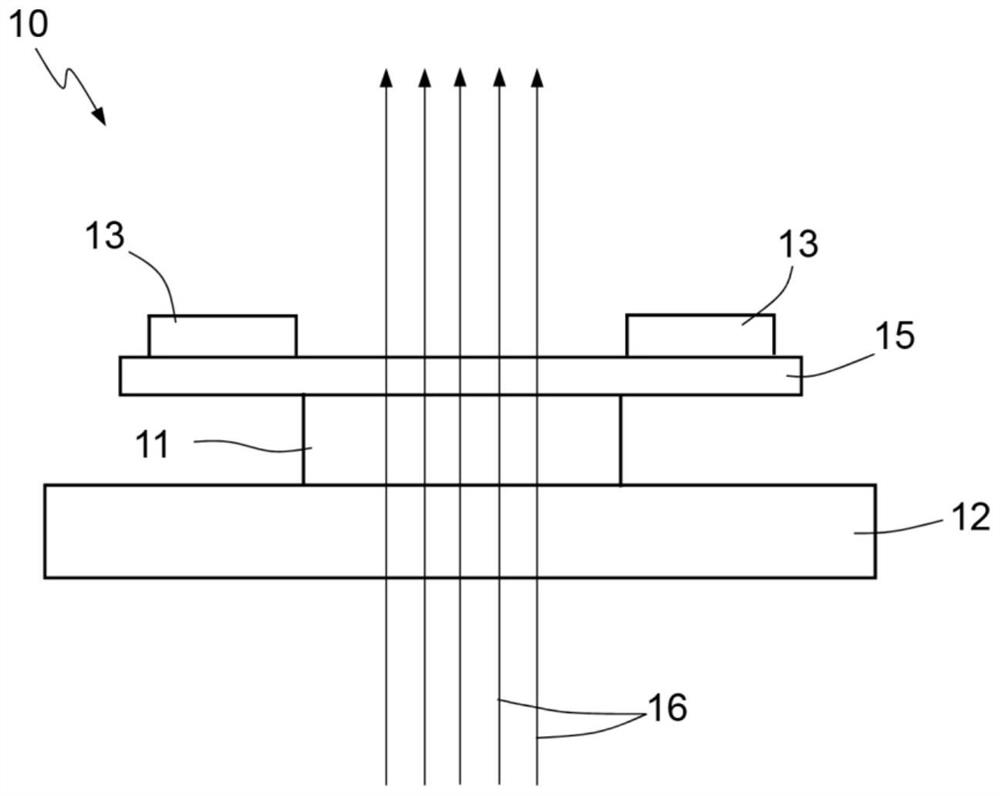
[0058] Figure 4 to Figure 6 A piezoelectric MEMS actuator 100 is schematically shown. In particular, the MEMS actuator 100 is configured to integrate optics, eg for autofocus, and to allow compensation of undesired movements.
[0059] The MEMS actuator 100 is formed from a monolithic body of semiconductor material (e.g., polysilicon) 101 having a generally parallel hexahedral shape with a first larger surface 100A and a second larger surface 100B and a reduced thickness ( in a direction parallel to the Cartesian Z axis in the Cartesian reference frame XYZ). exist Figure 4 to Figure 6 In an embodiment of the MEMS actuator 100 has a square shape (in top view) with a side length of eg 7 mm x 7 mm and a depth (in the Z direction) of eg 710 μm.
[0060] The main body 101 of the MEMS actuator 100 includes: a support portion 102, which is viewed from above ( Figure 4 ) has a quadrilateral shape (for example, a square); the first frame 104, which surrounds the support part 102,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com