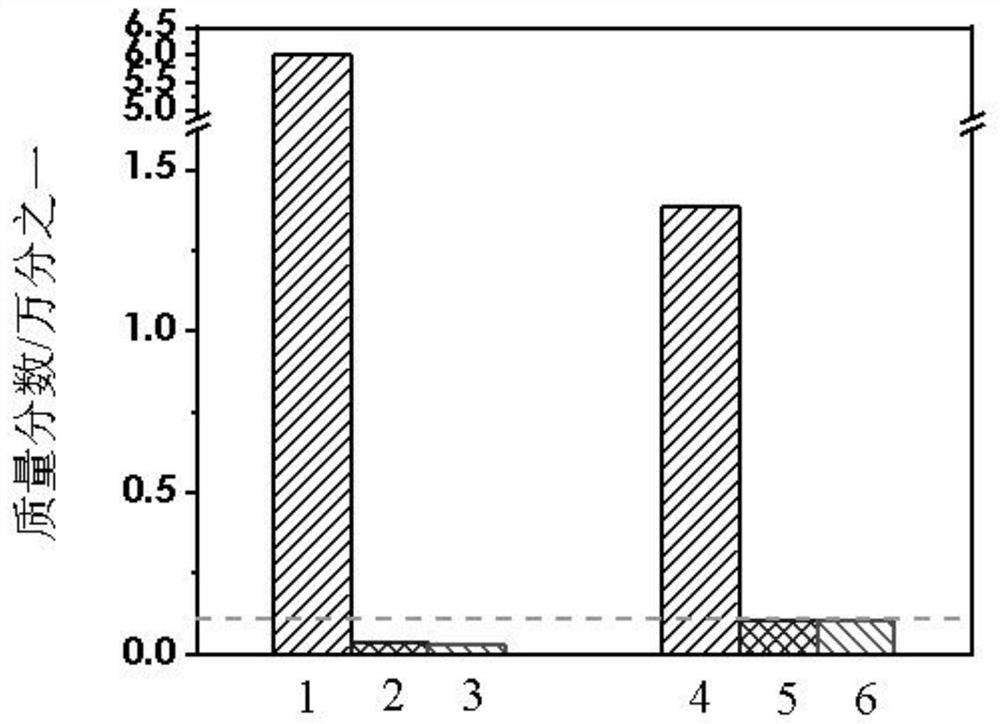
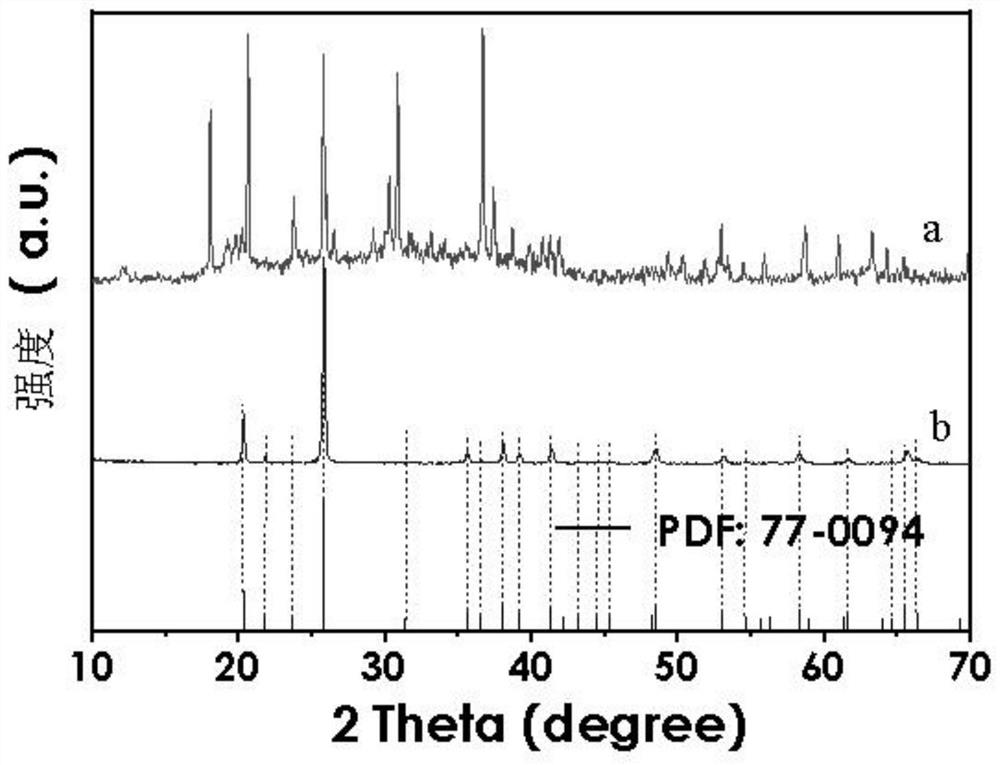
Method for recovering battery-grade iron phosphate from waste iron phosphate slag
A technology of iron phosphate slag and iron phosphate, which is applied in waste collector recycling, battery recycling, recycling technology, etc., can solve the problems of high content of Cu and Ni impurity metals and disordered crystal forms, and achieve low acid concentration and good morphology Regular, to achieve the effect of closed-loop regeneration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0018] Specific implementation mode 1: This implementation mode is a method for recycling battery-grade iron phosphate from waste iron phosphate slag, specifically according to the following steps:
[0019] 1. Pour the iron phosphate slag to be treated into a single-necked flask, add an inorganic acid solution to immerse the iron phosphate slag to be treated, and then seal it; iron phosphate slag;
[0020] 2. Fix the single-necked flask in a constant temperature oil bath, keep it warm for 1h-10h at a temperature of 40°C-180°C and stirring. After heating, take out the single-necked flask and let it cool down to room temperature naturally. Separate and dry the solid residue;
[0021] 3. Put the sample obtained after drying in step 2 into a quartz crucible, place it in a tube furnace, and heat it at a temperature of 200° C. to 1200° C. for 1 h to 10 h to obtain battery-grade iron phosphate.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0022] Embodiment 2: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that the inorganic acid solution described in step 1 is a mixture of one or more of sulfuric acid aqueous solution, hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, nitric acid aqueous solution and phosphoric acid aqueous solution. Others are the same as the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0023] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is different from Embodiment 2 in that: the concentration of the inorganic acid solution described in step 1 is 1 mol / L˜6 mol / L. Others are the same as in the second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap