Speech coding
A coding and speech signal technology, which is applied in the field of speech coding, can solve the problems of large changes in gain correction factors and poor prediction values, and achieve the effect of improving quantization accuracy and accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
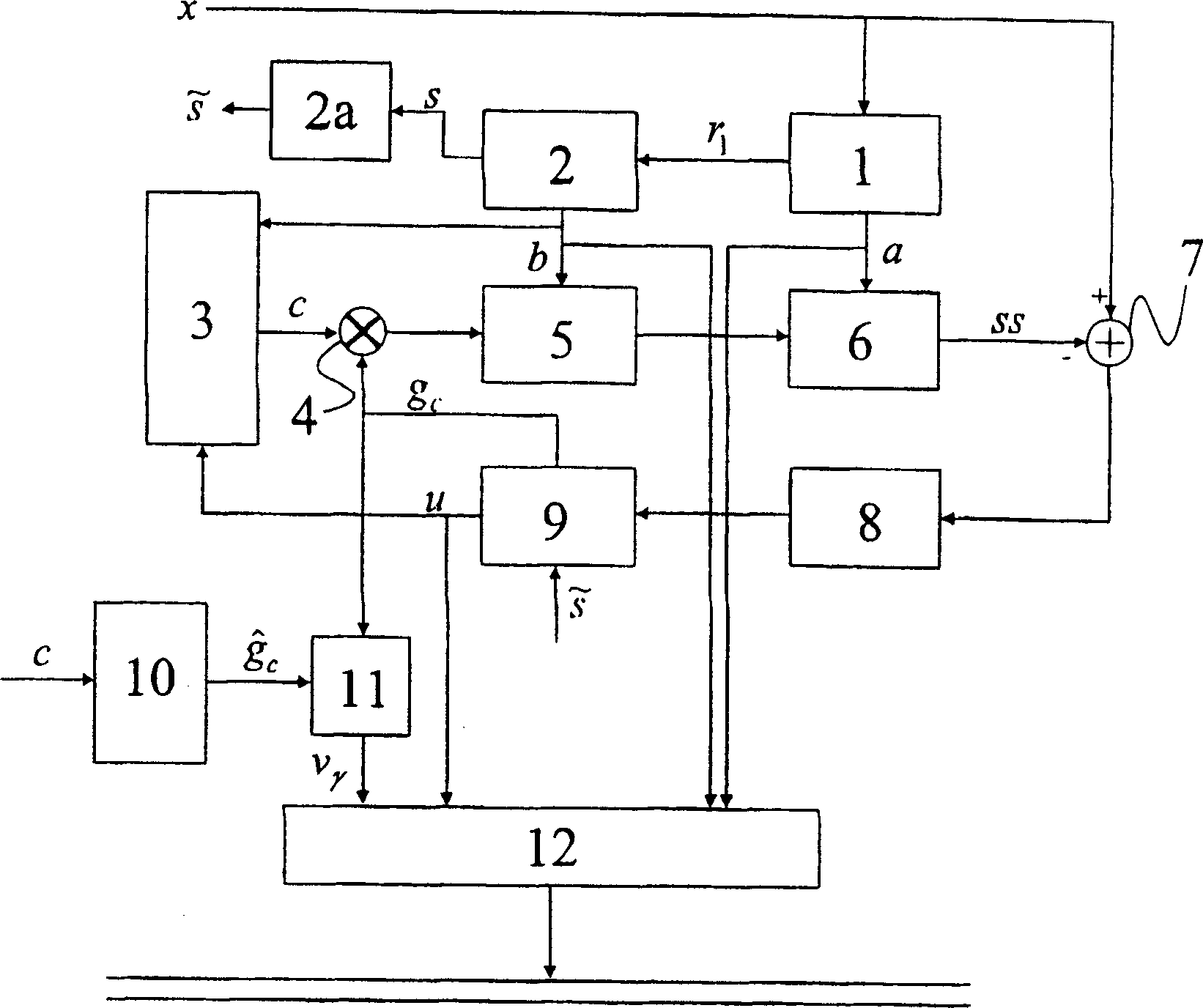
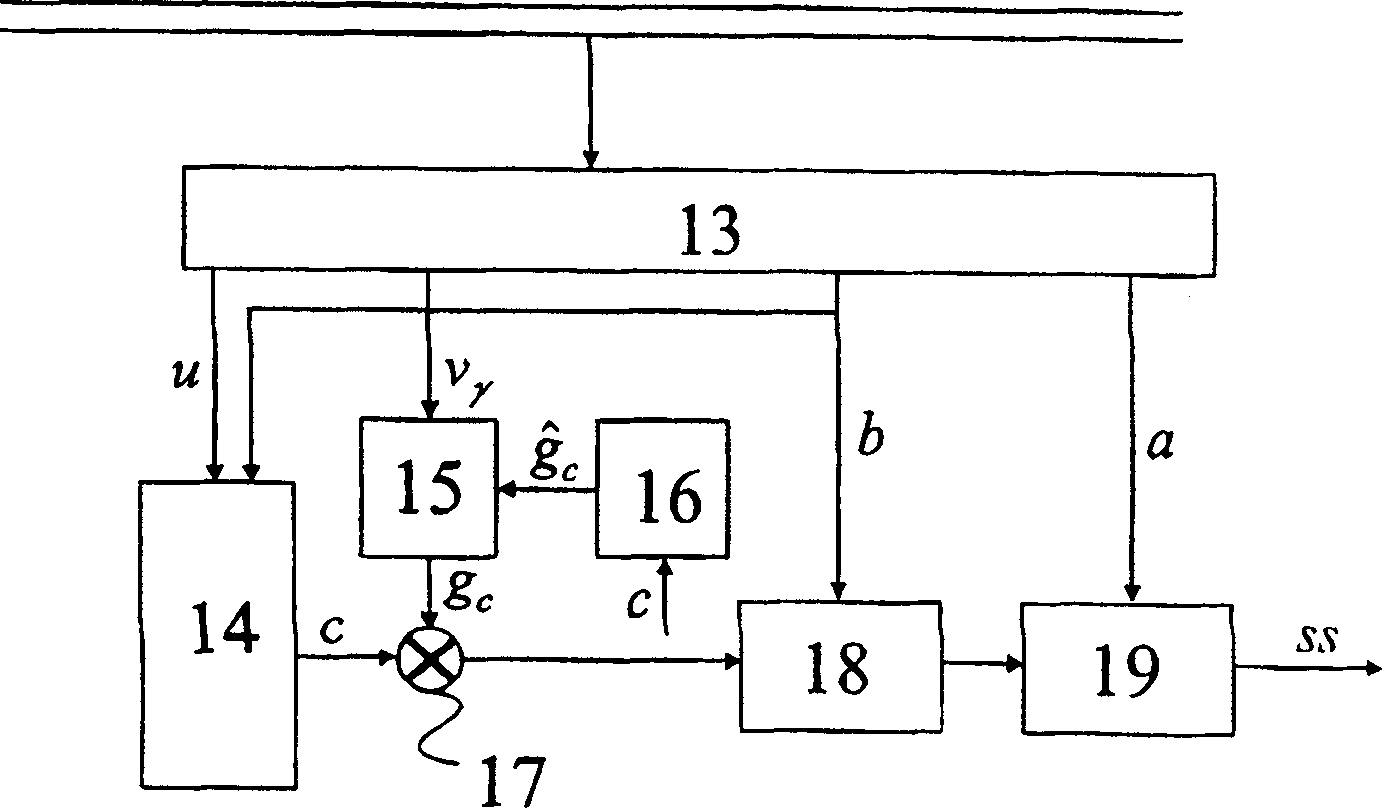
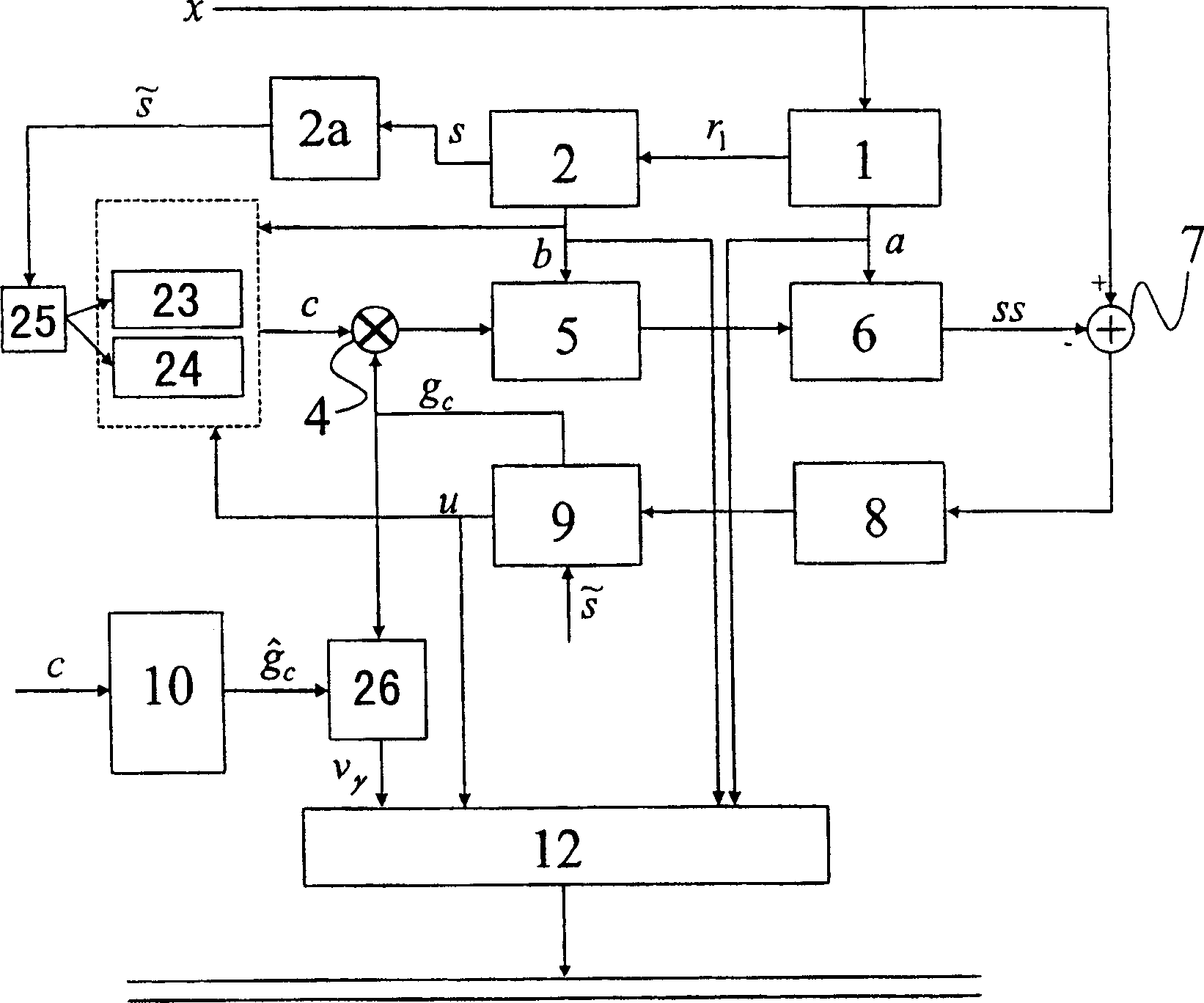
[0072] already referenced above figure 1 and 2 A speech codec similar to the ACELP proposed for GSM2 is briefly described. image 3 A modified ACELP speech coder suitable for variable bit-rate coding of digitized sampled speech signals is described, the functional blocks of which have been referenced figure 1 described, these functional blocks are labeled with like reference numerals.
[0073] exist image 3 in the encoder, figure 1 The single algebraic codebook 3 is replaced by a pair of algebraic codebooks 23,24. The first codebook 23 is used to generate the excitation vector c(i) based on the code vector d(i) containing two pulses, while the second codebook 24 is used to generate the excitation vector c(i) based on the codebook vector d(i) containing 10 pulses ) to generate the excitation vector c(i). For a given subframe, the codebook selection unit 25 gives the weighted residual signal according to LTP2 The energy in the selected codebook 23,24. If the energy in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com