Non-Gaussian load damage equivalent test spectrum optimization method
An optimization method and technology of test spectrum, applied in the formulation and optimization of effective test spectrum, can solve problems such as product over-test, under-test, and equivalent test spectrum error, so as to improve economic benefits, improve evaluation accuracy, and improve damage, etc. The effect of test spectrum accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] A damage equivalent test spectrum optimization method for non-Gaussian loads, comprising the following steps:
[0067] (1) Calculate the FDS of the measured signal in the time domain according to formula (1) to formula (6) in the prior art and combined with formula (7), where Q=10, b=4,
[0068] (7);
[0069] (2) Determine the equivalent test time, and use the FDS obtained in step (1) and formula (13) to calculate the initial PSD value,
[0070] (13), where for the input acceleration A resonant frequency at , is the frequency-domain damage index, is the gamma distribution, is the load duration, where Q=10, b=4;
[0071] (3) Use the PSD and the frequency domain method to calculate FDS in the frequency domain, where the frequency domain method assumes that the response stress peak value obeys the Rayleigh distribution:
[0072] (8)
[0073] in, is the peak stress, is the root mean square value of the stress.
[0074] frequency domain impairment ...
Embodiment 2
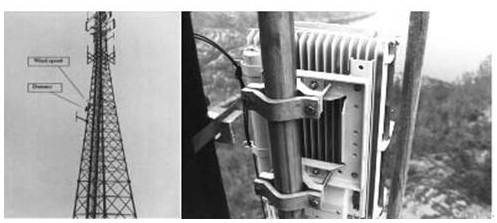
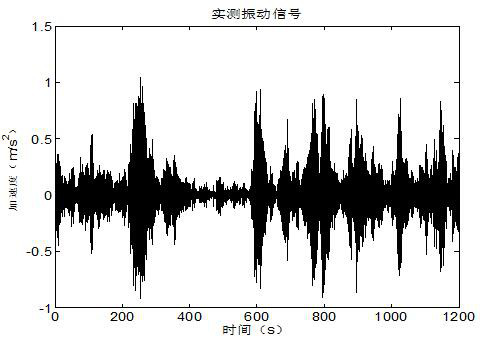
[0087] This case utilizes measured non-Gaussian wind load verification method that the present invention proposes, test object and measured load such as figure 1 and figure 2 shown.
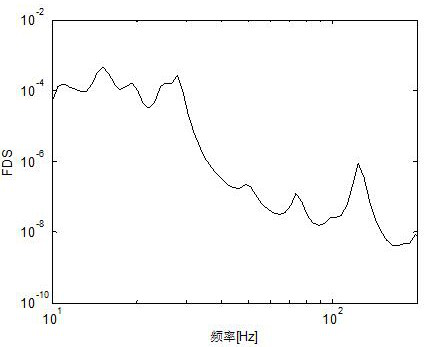
[0088] The load is a non-Gaussian random wind load with a kurtosis of 9.4, the acquisition time is 1200s, and the sampling frequency is 2000Hz. Since the Q value has no effect on the synthesis of the equivalent test spectrum, and when the test time is shorter than the measured signal time, the smaller the b value is, the larger the value of the synthesized equivalent Gaussian signal is. In order to avoid under-testing, Q=10 and b=4 are used to calculate the pseudo-velocity FDS of the measured signal, and the results are as follows image 3 shown.
[0089] In order to shorten the test time and avoid excessive acceleration, the test time is shortened to 120s in this example, and the damage equivalent test spectrum is calculated by using the measured non-Gaussian load FDS and formula (13). The r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com