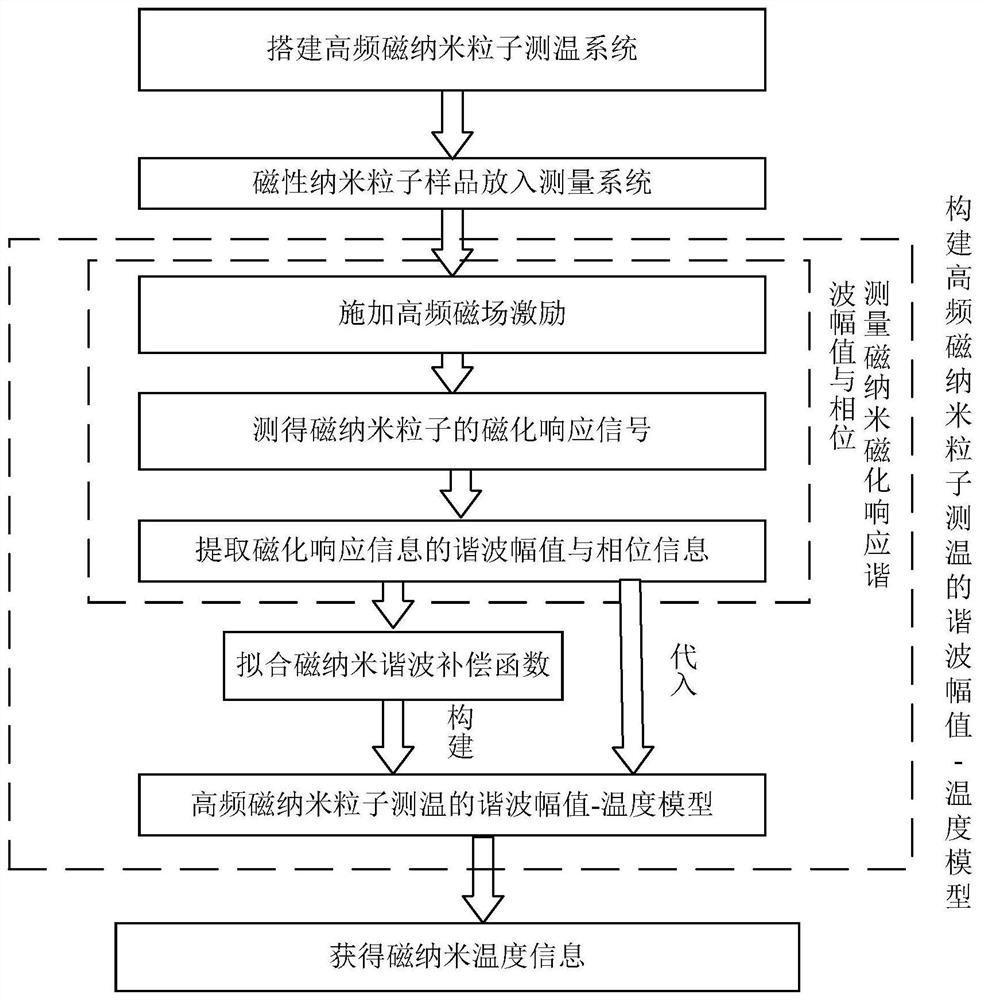
Harmonic amplitude-temperature method for magnetic nanoparticle temperature measurement in high-frequency excitation magnetic field
A technology of magnetic nanoparticles and harmonic amplitude, which is applied in the field of non-invasive temperature measurement, can solve the problems of not being suitable for high-frequency excitation magnetic fields, and being unable to build harmonic models
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
[0102] 1. Experimental conditions
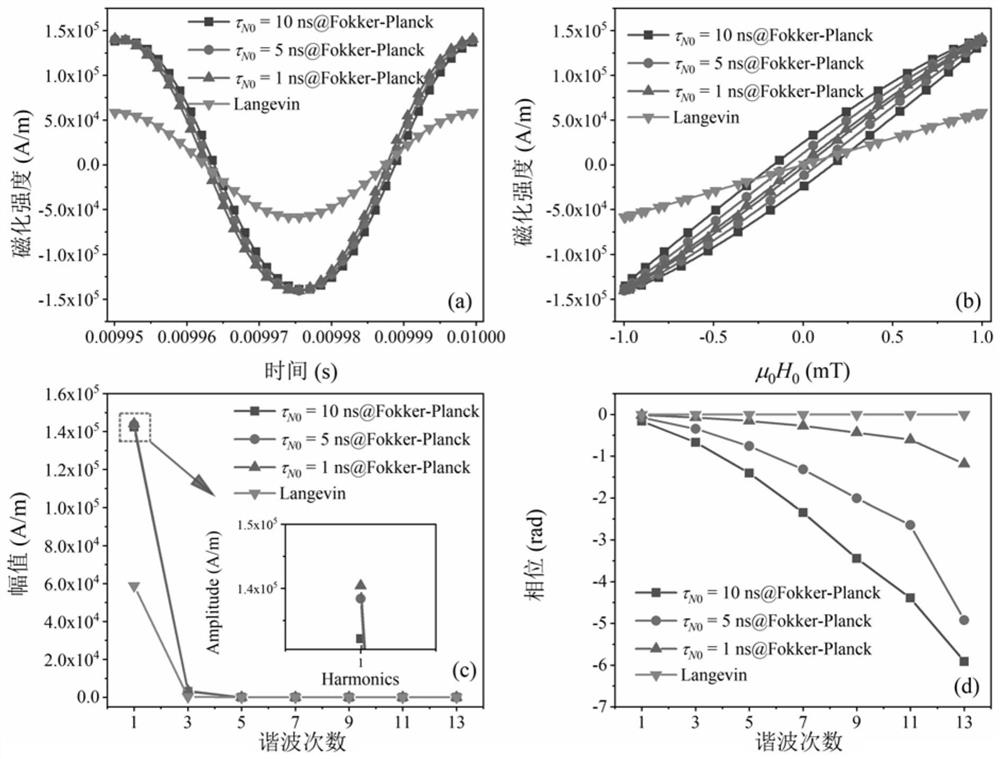
[0103] In order to study the effectiveness and feasibility of the present invention, the dependence of the harmonic and phase lag of the magnetization response information affected by Neel relaxation on the excitation magnetic field strength was studied. In the experiment, a commercially available magnetic nanoparticle sample SHP-20 (Ocean Nanotechnology, Inc., USA) was used. SHP-20 is an iron oxide nanoparticle having a carboxylic acid group, and the iron concentration of SHP-20 is 5 mg(Fe) / mL. The magnetic nanoparticle samples were fixed with epoxy resin to avoid the influence of Brownian relaxation. During the fixation process, the magnetic nanoparticle samples were placed on a DC excitation magnetic field with a strength of 50 mT to ensure that the easy magnetization axes of all magnetic nanoparticles were along the same direction.
[0104] The saturation magnetization (211kA / m) of the magnetic nanoparticle sample was measured under a ...
experiment example 2
[0108] 1. Experimental conditions
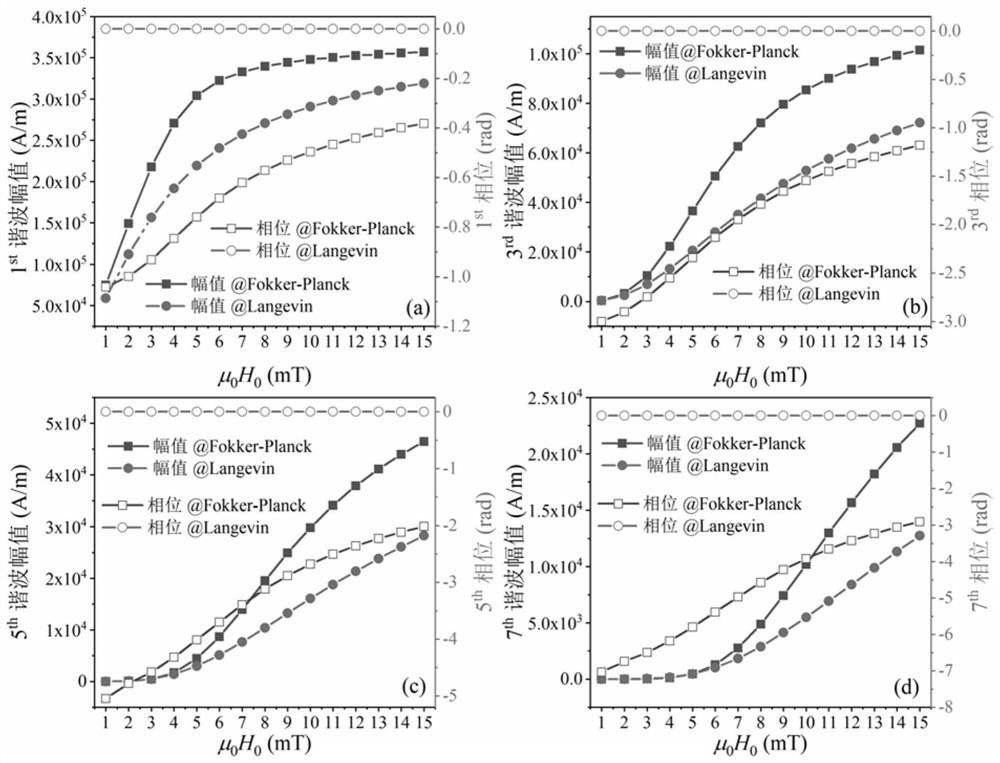
[0109] The magnetization of the magnetic nanoparticle sample was calculated using the Langevin equation and the harmonic amplitude A was obtained using DPSD 2j-1 . The experimental conditions are the same as the experimental case one. Therefore, G associated with the strength of the excited magnetic field can be obtained 2j-1 =C 2j-1 / A 2j-1 .
[0110] 2. Experimental test results
[0111] Figure 8 Representing the compensation function G of different harmonics of the magnetic nanoparticle sample SHP-20 2j-1 , the symbol is G 2j-1 The experimental data of , the solid line represents G 2j-1 Polynomial fit results. For the SHP-20 sample, the compensation function G for different harmonics 2j-1 The dependence on the excitation magnetic field is different. The first harmonic and the third harmonic decrease with the increase of the excitation magnetic field strength; the third harmonic shows a rapid decrease with the increase of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com