Waveguide structure linear polarization complementary source antenna based on 3D printing technology
A waveguide structure and 3D printing technology, which is applied in the structural form of radiation elements, antenna grounding switch structure connection, additive processing, etc., can solve the complex structure of complementary source antennas in the microwave frequency band, insufficient mechanical properties of metal waveguide structures, and sensitivity to processing errors, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of solving performance sensitivity problems, light weight, and stable gain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
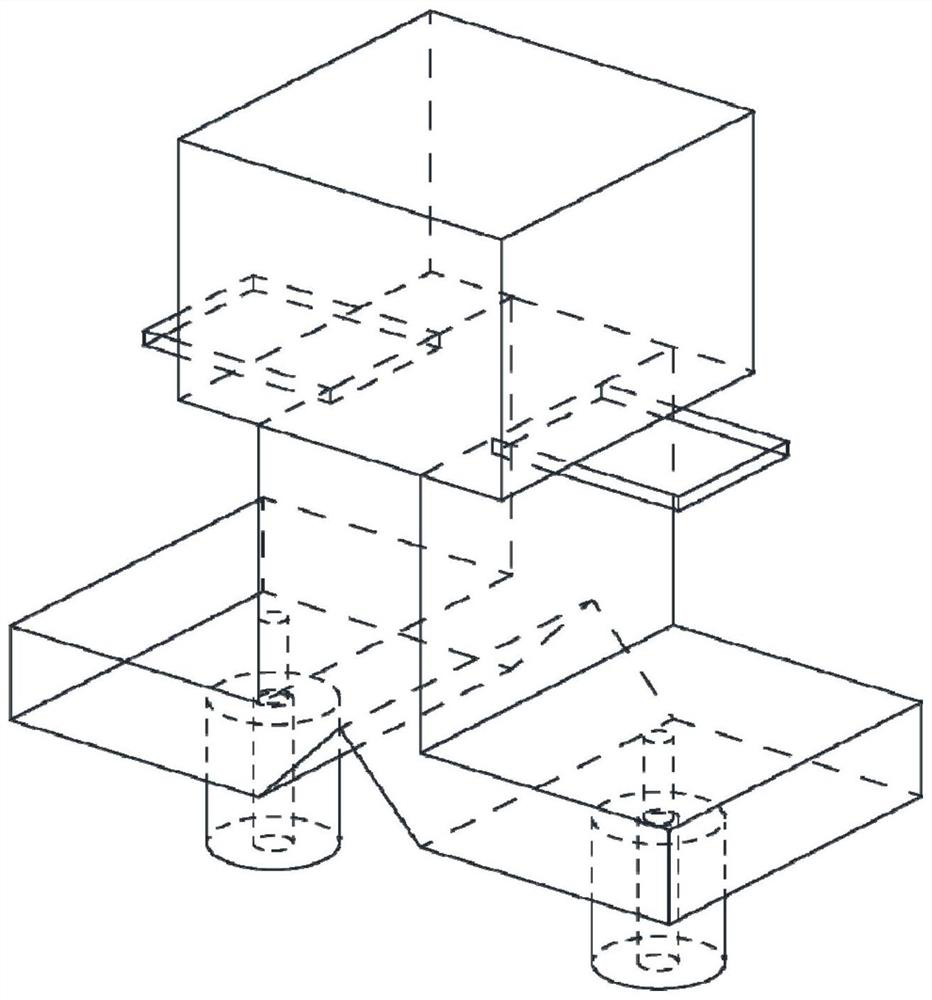
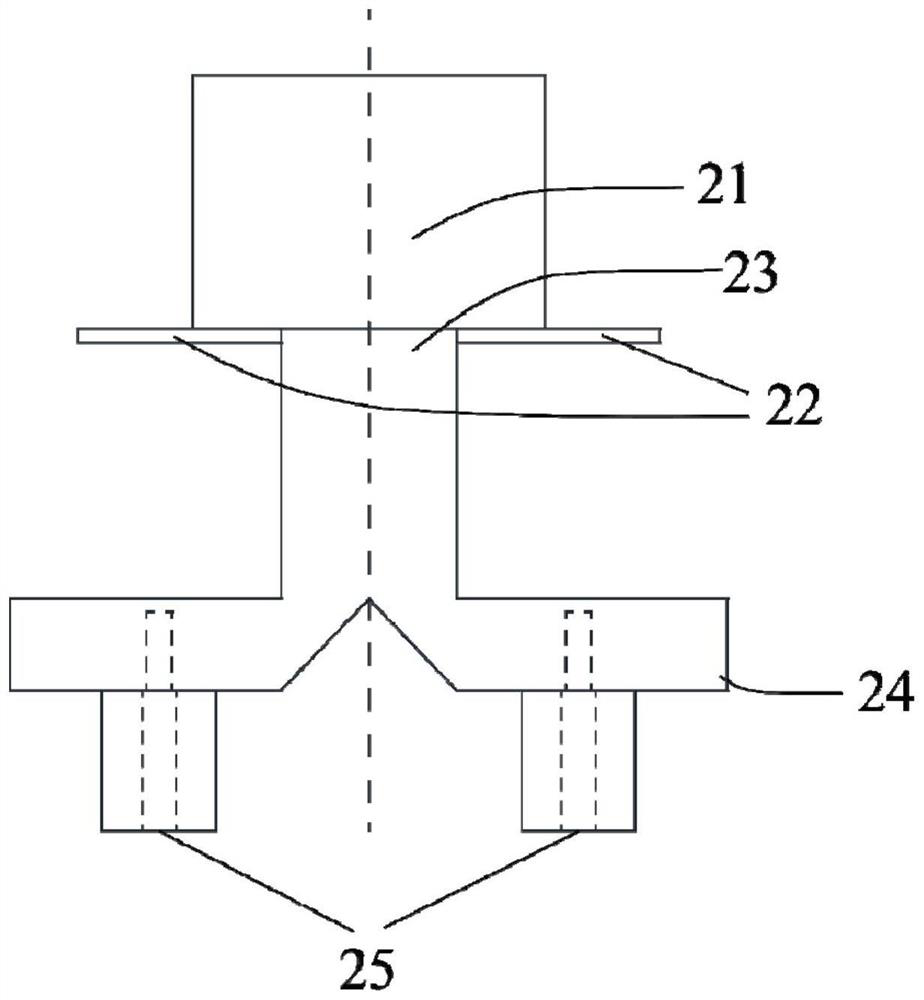
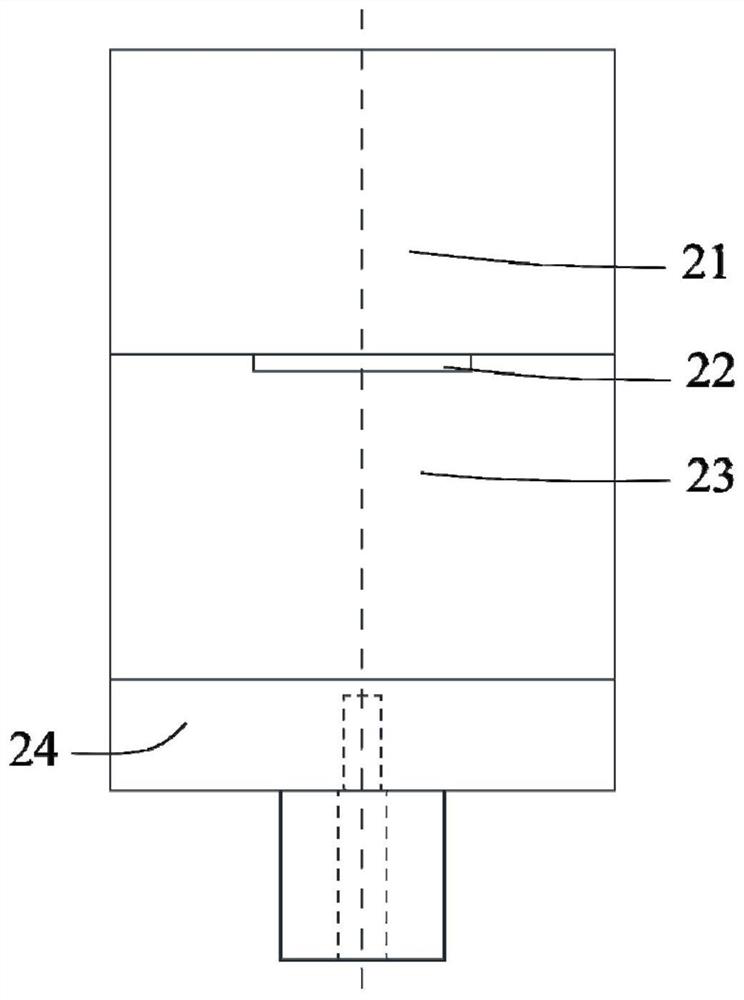
[0037] A waveguide structure linearly polarized complementary source antenna based on 3D printing technology, such as figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 As shown, it includes a rectangular dielectric block 21, two rectangular dielectric sheets 22, TE 10 Mode rectangular opening waveguide 23, E-plane T-junction waveguide power divider 24 and two coaxial connectors 25;
[0038] Among them, the rectangular dielectric block 21 is located at the top of the antenna, and TE 10 Mode rectangular opening waveguides 23 are connected; TE 10 The E-plane T-junction waveguide power divider 24 is connected to the bottom of the mode rectangular opening waveguide 23; the structural parameters of the two rectangular dielectric sheets 22 are exactly the same, and the TE 10 The wide side of the mode rectangular opening waveguide 23 cross-section is symmetrically placed at the opening connected to the rectangular dielectric block 21, and the TE 10 The mode rectangular opening waveguide 23 is conn...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com