Electric imaging logging fracture-cavity recognition method and system and pore structure characterization method
An identification method and technology of pore structure, applied in surveying, earthwork drilling, wellbore/well components, etc., can solve the problem of difficult to achieve high-precision automatic identification and separation of fractures and caves, and difficult to eliminate stratigraphic bedding and muddy strips. , the denoising effect is not ideal, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
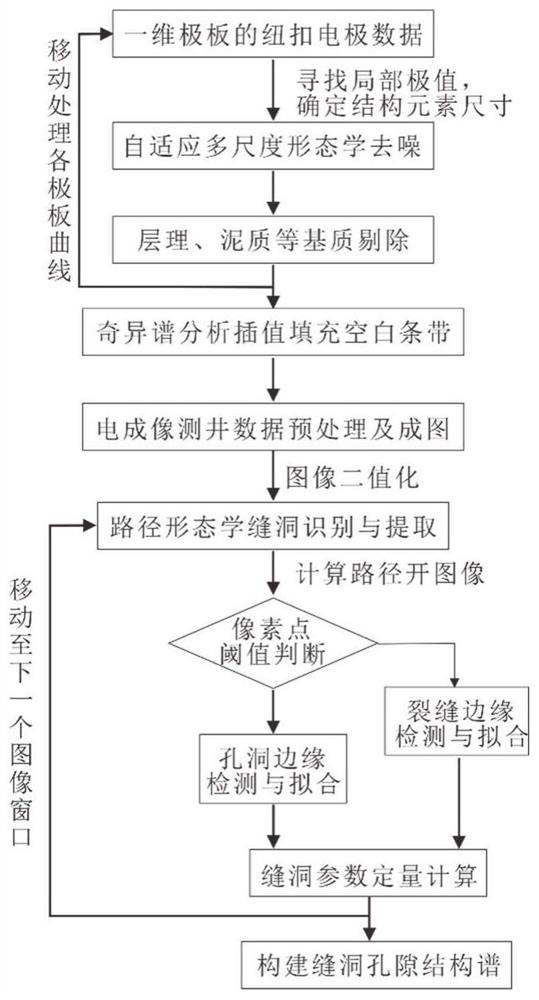
[0102] One-dimensional electrode plate data noise suppression and formation matrix low-frequency components (stratum bedding and muddy bands, etc.) are eliminated based on an adaptive morphological algorithm.
[0103] 1. Construction of adaptive multi-scale structural elements
[0104] Morphological operators and structural elements determine the operational characteristics of morphology. The key to morphological operations is how to select structural elements, especially the length and height of structural elements. Therefore, adaptively selecting structural elements to enable multi-scale morphological processing functions plays an important role in effectively extracting morphological features of different scales in the signal.
[0105] The composition of structural elements has aspects such as amplitude, shape and size. Among them, there are many shapes, and the commonly used ones are flat, triangular and semicircular. It is necessary to carry out experimental analysis of...
Embodiment 2
[0124] Example 2: The method of reconstructing the two-dimensional conductivity data of the whole borehole by the interpolation method of singular spectrum analysis
[0125] 1. Blank band interpolation method for singular spectrum analysis
[0126] During the measurement process, the plates of the electrical imaging logging tool did not cover the entire borehole, which resulted in the lack of conductivity data in the image and the phenomenon of blank strips. In this embodiment, a singular spectrum analysis interpolation method is introduced to reconstruct the two-dimensional conductivity data of the whole borehole.
[0127] (1) Apply Fourier transform to the two-dimensional imaging conductivity data to obtain two-dimensional conductivity data in the frequency domain;
[0128] (2) Applying a singular spectrum interpolation method to each frequency slice of the two-dimensional conductivity data in the frequency domain;
[0129] For each frequency slice S={s 1 ,s 2 ,...,s N}...
Embodiment 3
[0138] Example 3: An automatic identification and extraction of cracks and holes based on path morphology algorithm
[0139] 1. Basic principles of path morphology
[0140] 1.1 Adjacency
[0141] It is known that the discrete two-dimensional image domain E is a set of pixel points, and a is used to represent the directional relationship between each pixel point in E, which is called the adjacency relationship of pixel points. The set E and the adjacency relations it satisfies form a directed graph, namely the adjacency graph.
[0142] x a y means that there is a path from x to y, and y is called the successor point of x, and x is the predecessor point of y. Knowing the adjacency relationship "a", for any subset X(x∈X) in the image domain set E:
[0143] δ(X)={y∈E|x a y} (7)
[0144] In the formula, δ(X) is all subsequent point sets corresponding to the previous point of X set.
[0145] 1.2 Path opening operation
[0146] If set a={a 1 ,a 2 ,...,a L} satisfy a k a a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com