Motor capable of quickly stopping
A fast, chassis-based technology, applied in the direction of electromechanical devices, electrical components, and electric components, can solve the problems of low motor operation efficiency, affecting the normal use of the motor, and reducing the damping torque, so as to avoid the load slipping or slipping, and meet the long-term requirements. The effect of stable operation over time and stable output damping torque
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
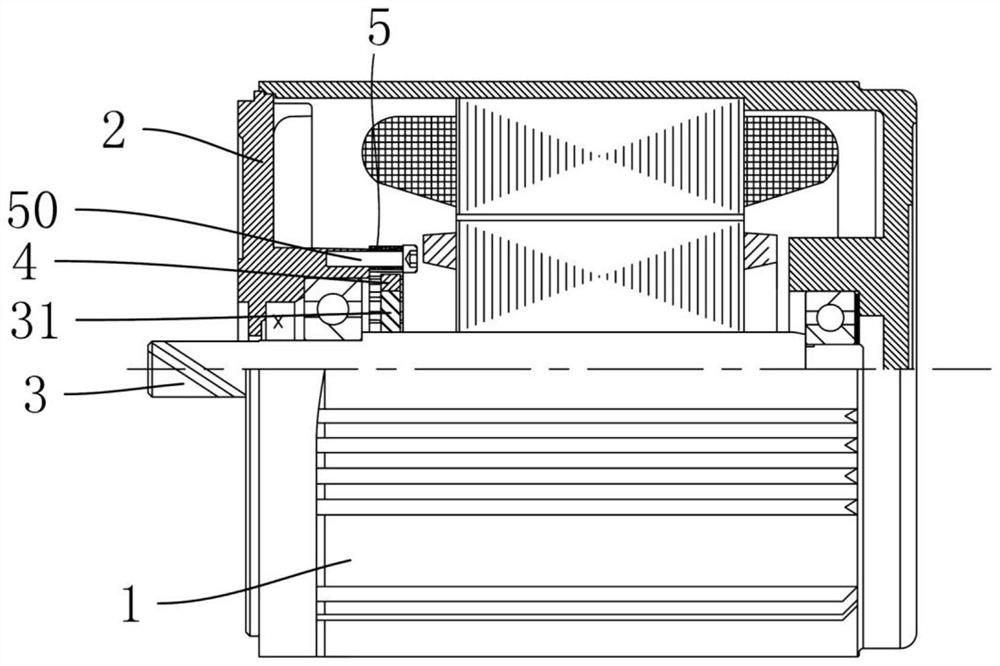
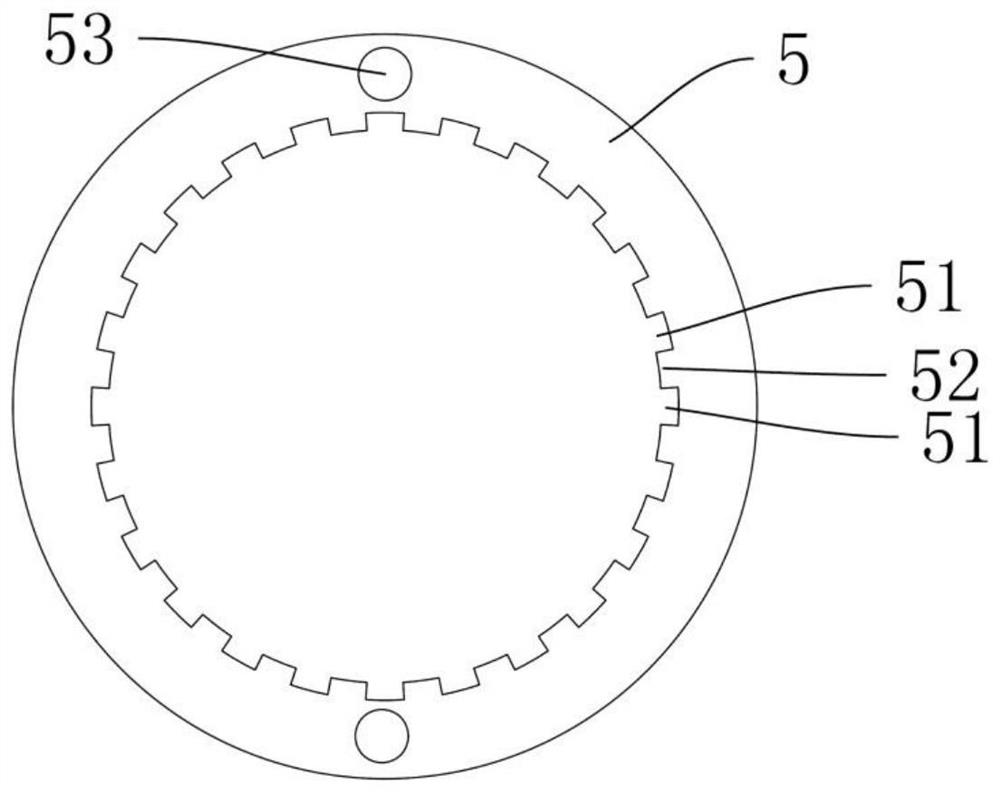
[0027] Depend on figure 1 with figure 2 As shown, a motor that can be stopped quickly includes a casing 1, an end cover 2, a rotor, a magnetic ring 4 and a metal ring 5, the metal ring 5 is made of magnetically conductive material, the magnetic ring 4 is a permanent magnet, and the magnetic ring 4 The metal ring 5 is adjacent to each other and can interact with each other with magnetic force. The metal ring 5 is provided with a plurality of grooves 51 on the end surface or the circumferential surface adjacent to the magnetic ring 4. The plurality of grooves 51 are arranged at uniform intervals in a circular shape in the circumferential direction of the metal ring. A number of magnetic poles are formed on the end face or circumferential surface adjacent to the ring 4 and the metal ring 5. The number of grooves 51 is the same as the number of magnetic poles of the magnetic ring 4, and the magnetic poles are alternately arranged in N poles and S poles in the circumferential dire...
Embodiment 2
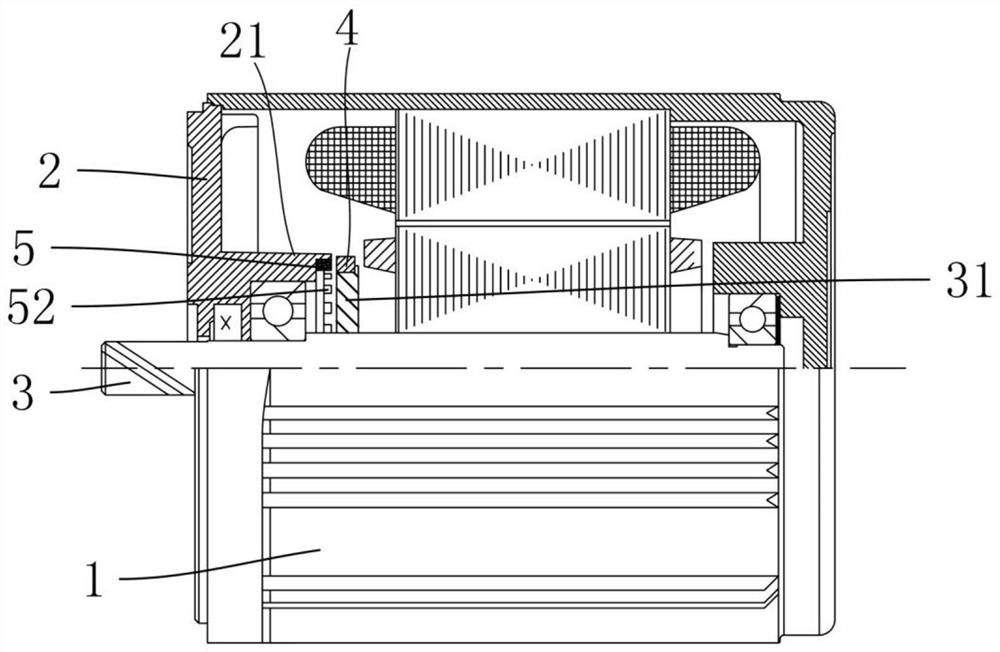
[0032] Depend on image 3 with Figure 4 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that: the magnetic ring 4 and the metal ring 5 are arranged at intervals along the axial direction of the rotor, the magnetic poles are formed on the end surface of the magnetic ring 4, and the metal ring is provided with The groove 51 on the surface, the end surface of the magnetic ring 4 and the end surface of the metal ring 5 have a ring-shaped overlapping surface along the rotor axial direction. The inner side of the end cover 2 is formed with a fixing groove, the metal ring 5 is fixed in the fixing groove, the fixing groove is located at the opening of the bearing bracket 21 of the end cover 2, and the metal ring 5 is fixed in the fixing groove by die-casting.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Depend on Figure 5 with Image 6 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the axis of the metal ring 5 deviates from the axis of the magnetic ring 4 . Wherein, the connecting ring 31 has a stepped structure, the rotor shaft 3 has a stepped protrusion 30 for limiting the connecting ring 31 , the connecting ring 31 is tightly fitted on the rotor shaft, and the magnetic ring 4 is tightly fitted on the connecting ring 31 . The inner side of the end cover 2 is formed with a fixing groove, the metal ring 5 is fixed in the fixing groove, the fixing groove is located at the opening of the bearing bracket 21 of the end cover 2, and the metal ring 5 is fixed in the fixing groove by die-casting.
[0035] When the motor of the present invention is in normal use, the damping torque between the metal ring and the magnetic ring alternates between positive and negative at different times, so that the rotor is continuously subjected to alternate pullin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com