Reduction of black silicon in semiconductor manufacture
A semiconductor and black silicon technology, applied in the field of reducing the formation of black silicon, can solve problems such as affecting the resolution or reliability and corrosion uniformity of lithography, and reducing the yield of chips
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
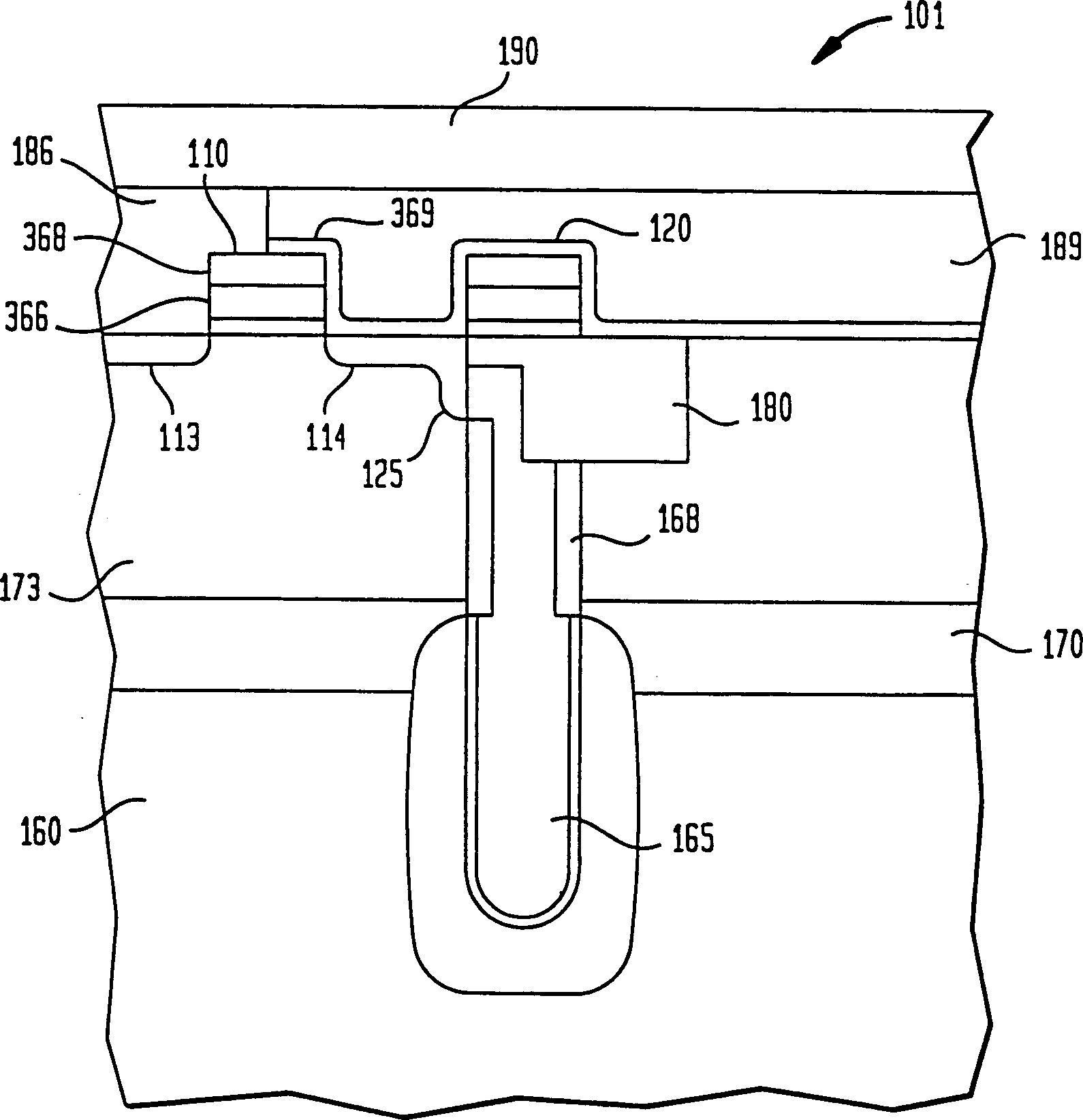
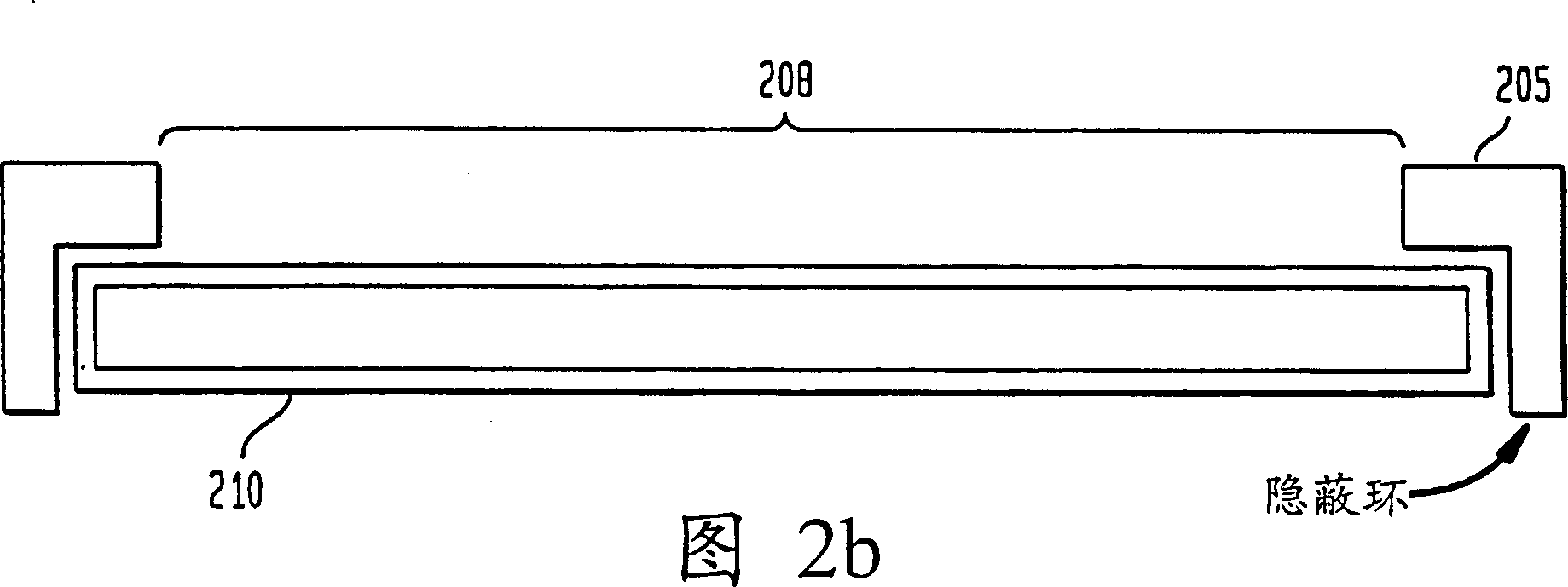
[0020] The present invention relates to preventing the formation of black silicon during the manufacture of integrated circuits (ICs). ICs, for example, include memory circuits such as random access memories (RAMs), dynamic RAMs (DRAMs), synchronous DRAMs (SDRAMs), static RAMs (SRAMs), or read only memories (ROMs). Furthermore, ICs may also include logic devices such as programmable logic arrays (PLAs), application specific ICs (ASICs), merged DRAM-logic ICs (embedded DRAMs), or any other circuit devices.
[0021] Typically, many parallel ICs are fabricated on a substrate such as a silicon wafer. After processing, the wafer is diced in order to separate the ICs into individual chips. The chips are then packaged into final products that are used, for example, in consumer products such as computer systems, cellular telephones, personal digital assistant devices (PADs) and other products.
[0022] For purposes of discussion, a conventional DRAM cell will first be described. re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com