Pavement depth information model construction method based on vehicle-mounted mobile laser point cloud
A technology of depth information and laser point cloud, applied in 3D modeling, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as blindness, inability to obtain road design status information, and large amount of calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
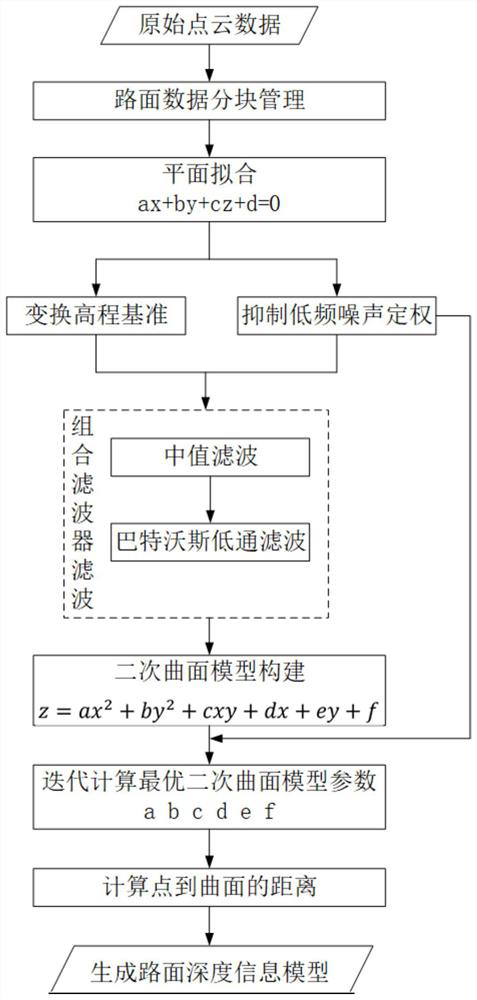
[0106] A road surface depth information model construction method based on vehicle-mounted mobile laser point cloud, such as Figure 1-6 shown, including the following steps:
[0107] a. Divide single-lane independent road sections, the overlapping area of two adjacent single-lane independent road sections is 4 / 5, and use single-lane independent road sections as data processing units for data processing;
[0108] The method of dividing single-lane independent road sections is as follows: in the direction of single-lane traffic, it is divided into several parts, and every 5 parts is a single-lane independent road section, and the overlapping area of two adjacent single-lane independent road sections is 4 / 5. The width is the width of a single lane, about 3.5m, and the length and width of each portion are equal.
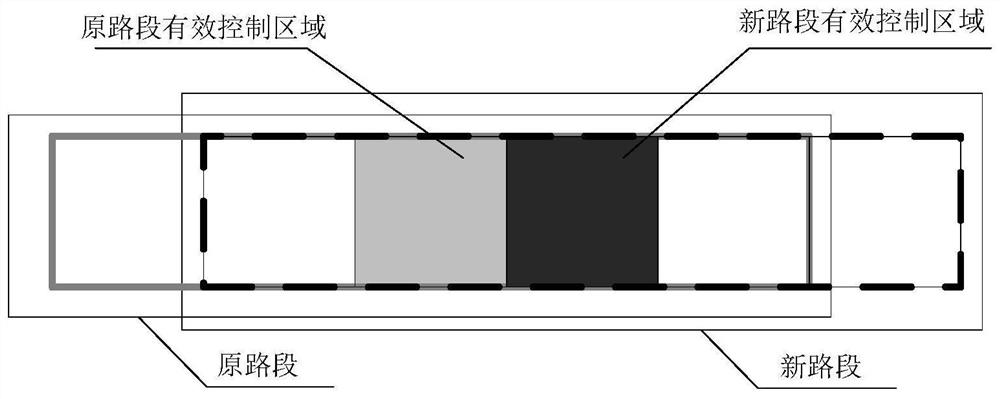
[0109] Such as figure 2 As shown, the adjacent two single-lane independent road sections are the original road section and the new road section respectively, and...
Embodiment 2
[0115] A method for building a road surface depth information model based on a vehicle-mounted mobile laser point cloud, as described in Embodiment 1, the difference is that step b includes the following sub-steps:
[0116] b1. Calculate the number of iterations according to the ratio relationship between the number n1 of points in the fitting plane and the number n of single-lane independent road section points and the success rate p:
[0117]
[0118] in, Interactive input in the form of a percentage, usually above 80%; p is the expected success rate of interactive input, usually above 90%, which can be determined according to the actual road conditions. The worse the road quality, the smaller the two input parameters, then k An estimate of the number of iterations required to achieve the above requirements;
[0119] Randomly select a three-point series of equations in the single-lane independent road section to solve the plane parameters, and then use the plane as a cons...
Embodiment 3
[0152] A method for building a road surface depth information model based on a vehicle-mounted mobile laser point cloud, as described in Embodiment 2, the difference is that step c includes the following sub-steps:
[0153] c1. Perform local median filtering on the road surface point cloud, specifically:
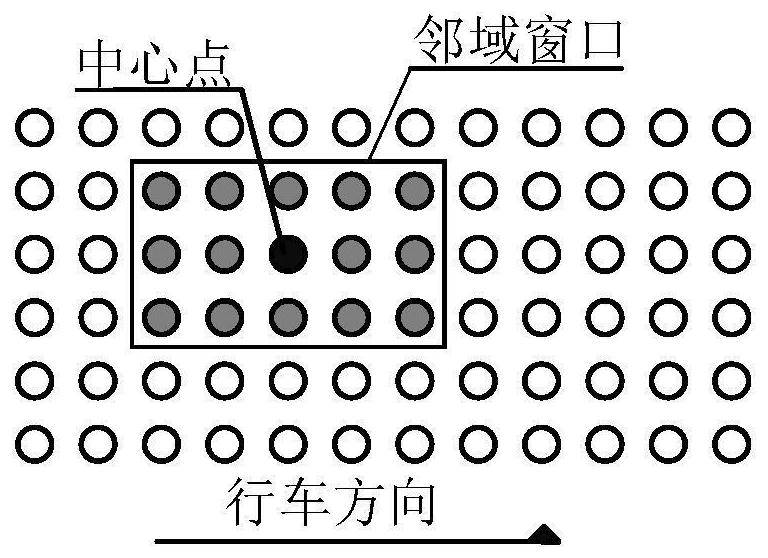
[0154] Use the K-D tree operator to search the neighborhood point set of the target point, and constrain the neighborhood range to a 5×3 long and narrow window distributed along the road direction, such as image 3 shown;
[0155] Sort the 15 points in the neighborhood window from small to large;
[0156] Replace the elevation value of the central point with the median elevation value of the 15 sorted points, and the local median filtering process of the single-lane segmented point cloud is as follows Figure 6 shown;
[0157] c2. Perform global Butterworth low-pass filtering on the point cloud after median filtering:
[0158] For the statistical distribution of the rela...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com