Micro-grid protection method based on zero-sequence characteristic signal injection
A characteristic signal and micro-grid technology, applied in the direction of emergency protection circuit devices, electrical components, circuit devices, etc., can solve the problems of protection malfunction or refusal to operate, and cannot be applied at the same time, so as to avoid risks, delays, and fault characteristics Obvious, highly economical effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
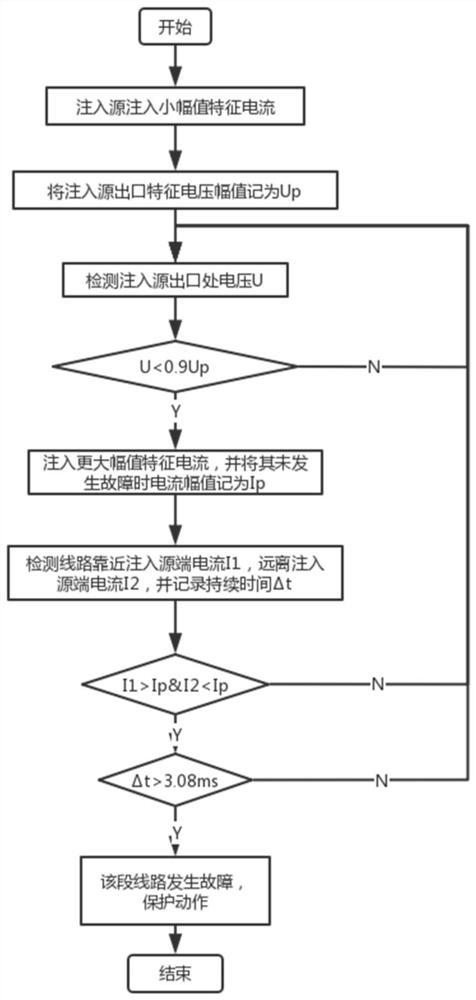
[0038] This embodiment provides a microgrid protection method based on injecting zero-sequence characteristic signals, including the following steps:
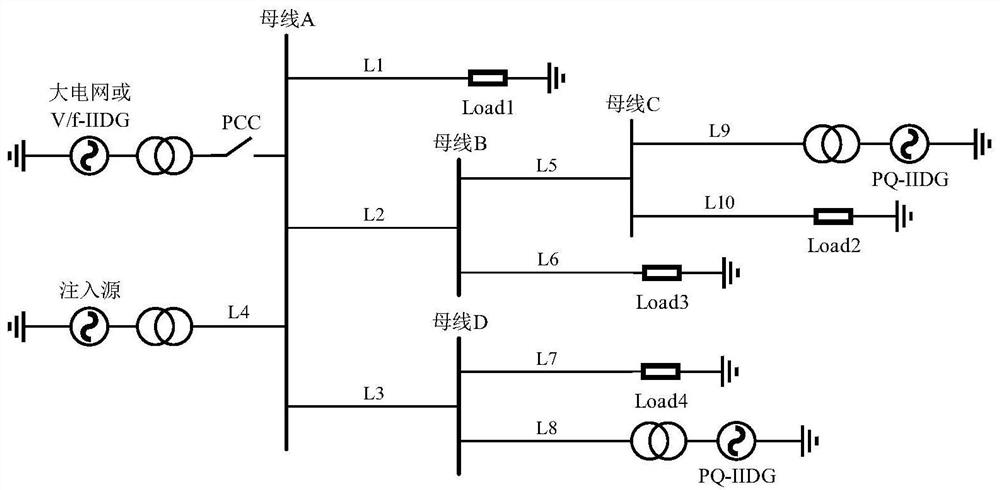
[0039] An inverter micro power source in the microgrid is selected as the injection source. When the microgrid is working normally, the injection source continuously injects a small-amplitude characteristic signal while outputting the power frequency current. The characteristic signal is the zero-sequence characteristic Signal;
[0040] The injection source continuously monitors the characteristic signal amplitude at its outlet, and if the characteristic signal amplitude of any phase at the outlet drops below the first multiple of its first rated value, it is judged that there is a risk of failure, and the microcomputer is started. Power grid protection; the first rated value is the characteristic signal amplitude generated by the characteristic signal at the outlet of the injection source when no fault occurs in the power grid...
Embodiment approach
[0053] As a preferred embodiment, the microgrid protection method also includes a backup protection step:
[0054] The injection source continuously monitors the characteristic signal amplitude of each phase of each line. If the characteristic signal amplitude of a certain phase of a certain line exceeds the second multiple of its second rated value, it is judged that a fault has occurred. If the fault continues to reach At the preset second time, the corresponding phase of the line is cut off, and the injection of the characteristic signal is finished, otherwise the power grid does not have a fault.
[0055] An optimum implementation manner can be obtained by combining the above preferred implementation manners, and the scheme of the optimum implementation manner will be described in detail below.
[0056] 1. Start-up criterion for characteristic signal injection
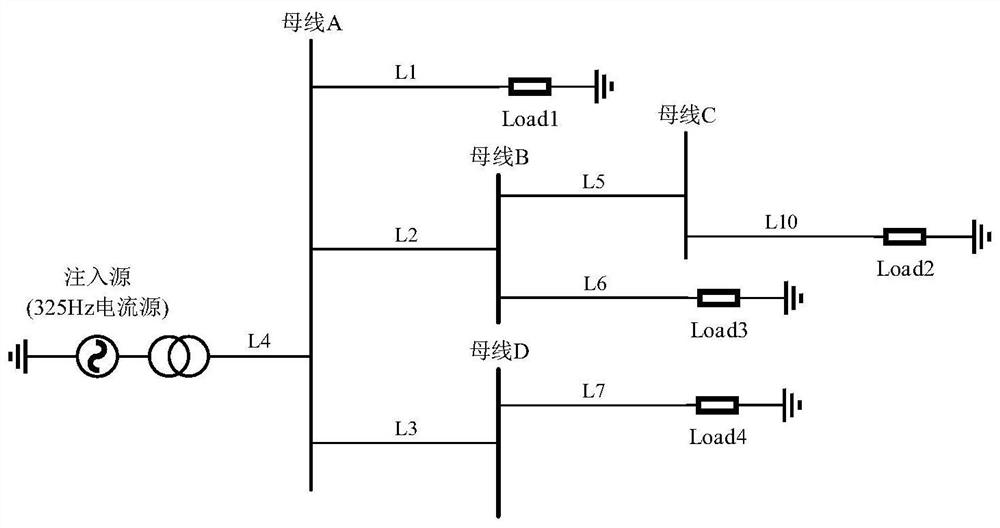
[0057] by figure 1 The microgrid with the general structure shown is taken as an example. In the microgrid, it...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com