Array based method and kit for determining copy number and genotype in pseudogenes
A kit and copy number technology, applied in the field of genetic analysis, can solve problems such as technical complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0242] Screening for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Carriers
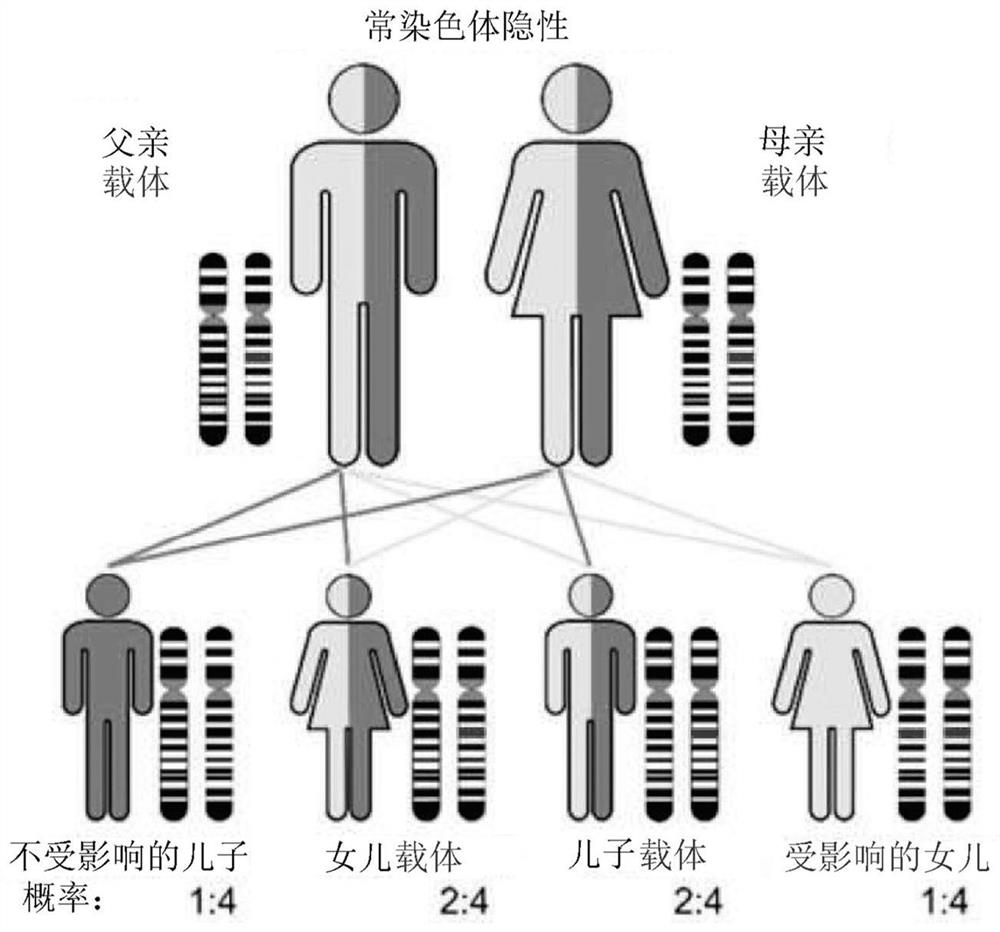
[0243] Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a rare but devastating disease with autosomal recessive inheritance. In some populations, 1 in 50 people carries a mutation in the SMN1 gene, which encodes a defective survival motor neuron (SMN) protein. Carrier screening requires accurate determination of the number of functional SMN1 genes in an individual. The presence of a highly homologous but largely non-functional SMN2 gene complicates carrier detection. Among the 28,081 bp of the SMN1 and SMN2 genes, only 27 positions differed (21 single-nucleotide substitutions and 6 small indels), accounting for only 38 nucleotides that differed between the SMN1 and SMN2 gene sequences.
[0244] In the examples provided herein, array-based analytical assays for genotyping and screening for SMA vectors according to some embodiments were designed and performed. Specifically, the arrays used herein have probe sets designed to differentiat...
example 1
[0245] Example 1 - Design of Probe Sets
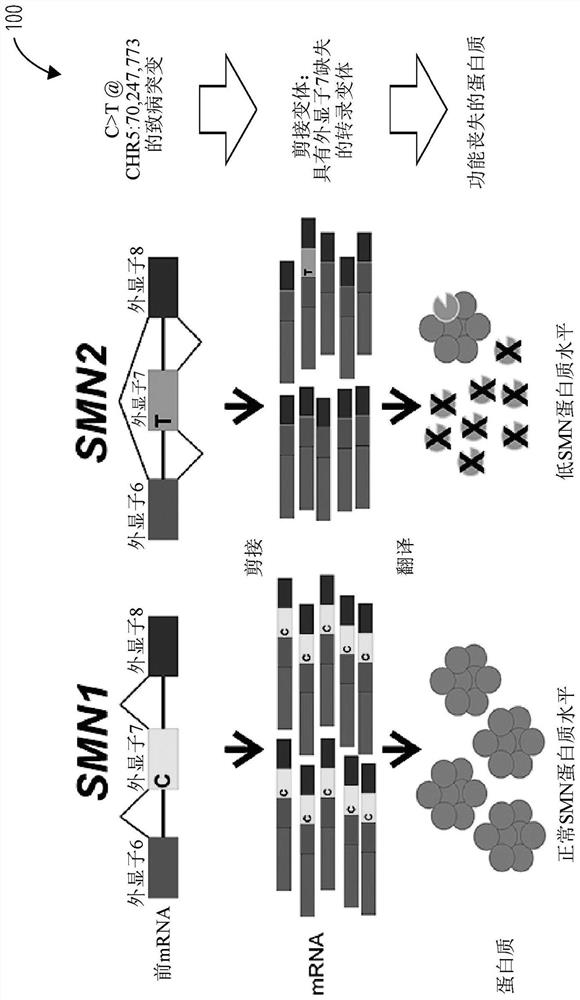
[0246] Comparison of the SMN1 gene and SMN2 genomic DNA sequences identified 27 locations where there were sequence differences between these two genes. These differences were used to design gene-specific probe sets. Most of these positions are intronic, but one is within exon 7 and one is within exon 8. (see Figure 5 ) exon 7 positioning is both a sequence difference between SMN1 and SMN2 and the site of a mutation that converts SMN1 into a non-functional SMN2 gene. This mutation interferes with exon splice junctions and results in transcripts that do not contain exon 7. The most common type of carrier is an exon 7 deletion mutation, but gene conversion mutations can also occur. figure 2 Four genomic locations are shown with probe sets used to detect relative copy numbers of SMN1 and SMN2.
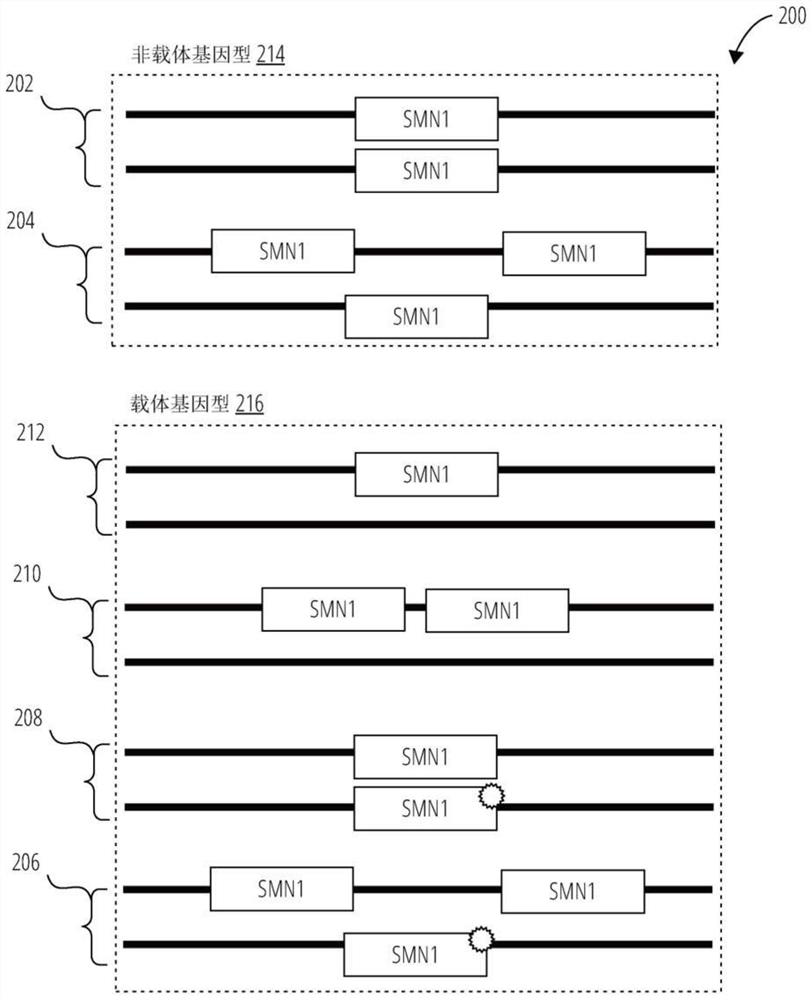
[0247] Carrier determination requires an accurate assessment of the total copy number of SMN1 and SMN2. The 1,181 copy number probe set h...
example 2
[0248] Example 2 - Sample Preparation
[0249] Example 2.1 - During Genome Amplification and Target Amplification
[0250] Usually by following the Thermo Fisher Scientific CarrierScan TM Protocols are available for the Analytical Assay Kit (Catalog # 931931 ) and the GeneTitan Instrument (supra) to prepare and process nucleic acid samples for genotyping and carrier screening for SMA. Briefly, a biological sample obtained from an individual (eg, whole blood, saliva, or cells) and genomic DNA (gDNA) are isolated from the biological sample. Isolated gDNA diluted to 5 μg / μL was used to amplify gDNA and multiplex PCR for amplification of target polynucleotides was also performed. For amplification of gDNA samples, 20 μL of diluted gDNA and 20 μL of control DNA were aliquoted separately into plates (eg, Applied Bioscience Genetic 96 square well plates). After the plate was sealed and spun, PCR reactions were performed with reagents as indicated in the manufacturer's protocol. F...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com