A commutation control method for ultrasonic transmission based on excitation phase difference modulation
A control method and a technology for modulating ultrasound, which is applied to conveyors, transportation and packaging, and non-mechanical conveyors. Simple, efficient effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
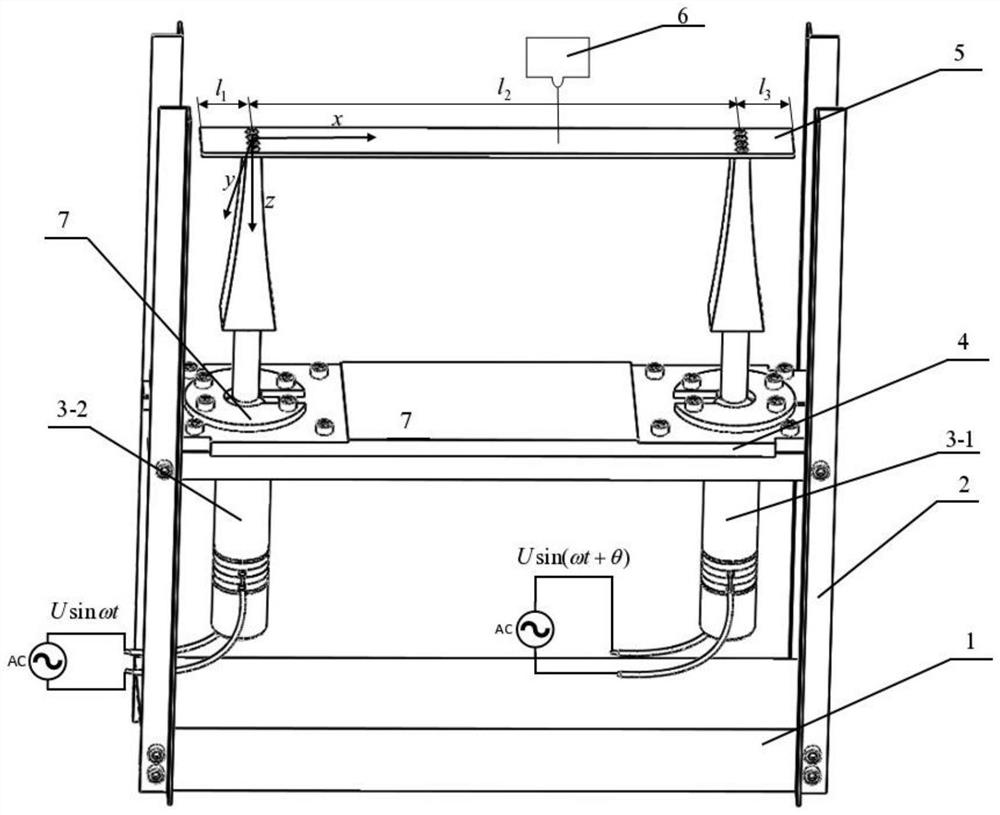
[0089] Combine below Figures 1 to 4 Illustrating this embodiment, a method for controlling the commutation of ultrasonic transmission based on excitation phase difference modulation, the method includes the following steps:
[0090] Step 1: Build an ultrasonic suspension drive device as required, and apply two excitation signals with the same amplitude and frequency to transducer one 3-1 and transducer two 3-2, but with a phase difference θ;
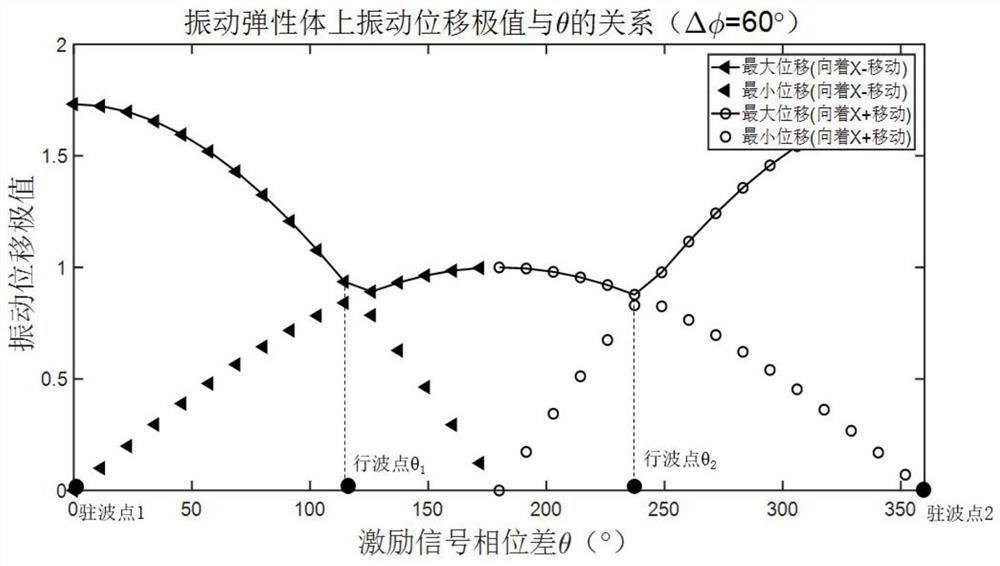
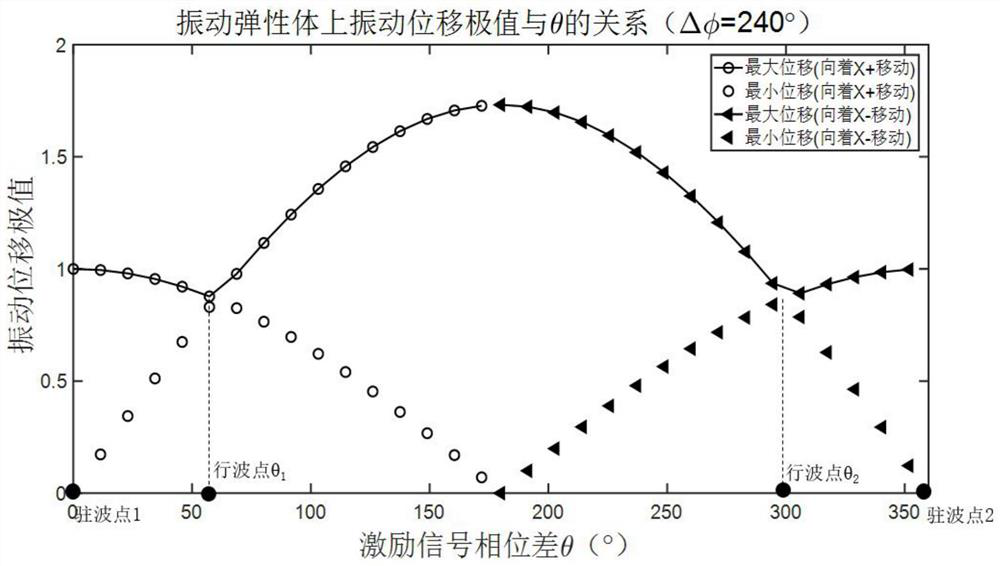
[0091] Step 2: Analyze the vibration displacement of the elastic vibration body 5, and set the equivalent spatial phase difference of the distance between the two support points of the elastic vibration body as Get the maximum amplitude of the elastic vibrating body and minimum amplitude solve get in In the case of constant, the theoretical formula of pure traveling wave θ value is formed; write down the vibration equation f(x, t) of the particle located at x on the elastic vibrating body 5 along the z direction at any time t; ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0096] Combine below Figures 1 to 4 This embodiment is described, and the first embodiment is further described in this embodiment. The excitation signal is the mechanical resonance frequency of the ultrasonic suspension drive device operating in the required longitudinal vibration mode; the long-distance ultrasonic suspension transmission is determined in the finite element simulation software. The dynamic model of the device is analyzed by modal simulation analysis, and the mechanical resonance frequency of the two ultrasonic transducers 3-1 and 3-2 in the suspension transmission device working in the longitudinal vibration mode is obtained. The model includes two ultrasonic transducers - 3-1 and 3-2, elastic vibration body 5, and the support structure of the transducer, etc., focusing on the placement of the piezoelectric ceramics of the ultrasonic transducer, the horn and the elastic vibration The structure of body 5 is modeled. The elastic vibrating body 5 is an ultraso...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0097] Combine below Figures 1 to 4This embodiment will be described. This embodiment will further describe Embodiment 2. The ultrasonic suspension driving device includes a transducer one 3-1, a transducer two 3-2, an elastic vibrating body 5 and a laser vibrometer 6, An elastic vibrating body 5 is detachably and fixedly connected between the vibration output ends of the transducer one 3-1 and the transducer two 3-2, and the laser vibrometer 6 conducts a vibration velocity scanning experiment on the radiation surface of the entire elastic vibrating body 5; Among them, transducer one 3-1 and transducer two 3-2 are installed opposite to each other, and the structural dimensions and electrical parameters of the two transducers are the same, and Langevin piezoelectric ceramic transducers can be used as transducers. Both ends of the elastic vibrating body 5 are respectively fixedly connected to the vibration output ends of the two transducers 1 3-1 and the second transducer 3-2, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com