Verification of type 2 diabetes mellitus preventing application of semaglutide oral preparation by Mendelian randomization method
A technology of diabetes and oral dosage, which is applied in the Mendelian randomization method to observe drug effects, in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of less access to concomitant diseases and concomitant treatments, obstacles, adverse reactions, etc., to avoid ethical problems and improve statistical power Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
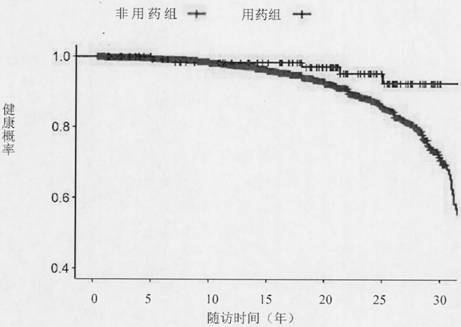
[0057] Embodiment 1 in the whole study object the risk comparison of medication group and non-medication group
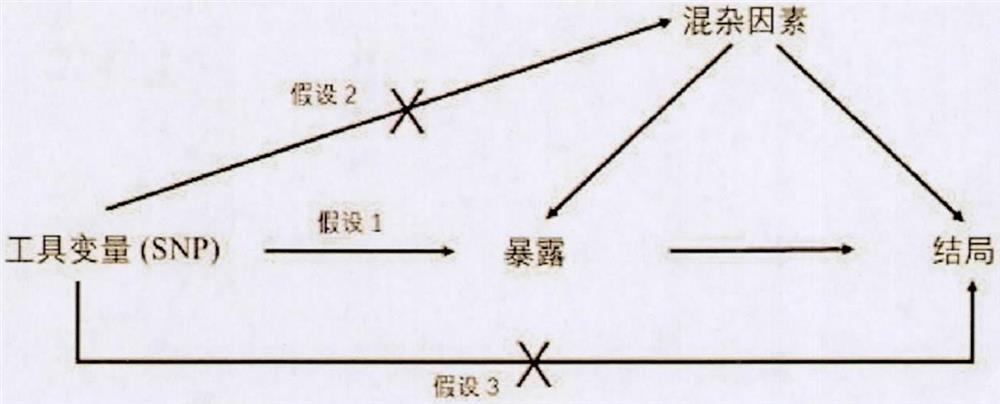
[0058] Background: GLP-1 is a short peptide, which is mainly secreted by intestinal epithelial cells. The secreted GLP-1 can bind to GLP-1 receptors, thereby activating the downstream biological pathways of hypoglycemia. Oral preparations of GLP-1 receptor agonist semaglutide can activate GLP-1 receptors, allowing the body to receive GLP-1 signals, thereby exerting the same biological function as GLP-1. In the population, some people carry a genetic variation related to the GLP-1 receptor. People with this kind of variation have a long-term activation of the GLP-1 receptor, that is, the blood sugar lowering pathway in their body is more active than normal people. To be active, thereby lowering its blood sugar. According to biological data, the genetic variation rs10305492-A is located on the fifth transmembrane domain of the GLP-1 receptor. 1 receptors are always ...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Example 2 Risk comparison between medication group and non-medication group in high-risk type 2 diabetes population
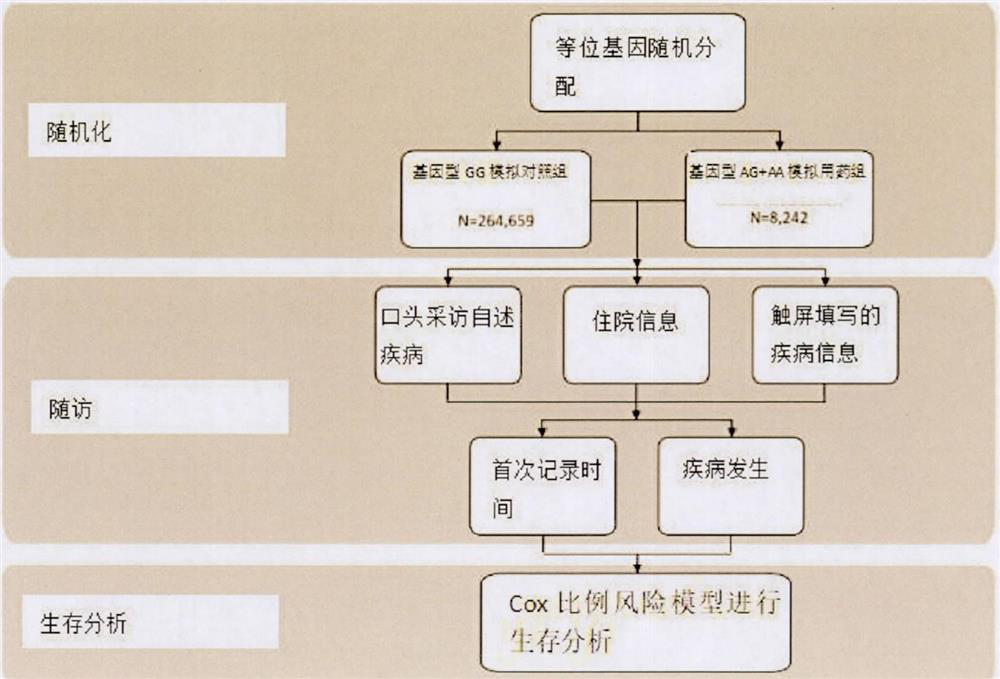
[0077] Methods: The population was divided into high-risk type 2 diabetes population and low-risk type 2 diabetes population according to the polygenic risk score. The polygenic risk score uses 266 SNPs that are strongly associated with type 2 diabetes (P value is less than 5e-5, significant in the whole genome), and is calculated by the formula: PRS = effect value 1 *SNP 1 Quantity +... + Effect Size i *SNP i Quantity to obtain polygenic risk score values for the entire population. The high-risk type 2 diabetes population was selected, and the population was divided into a medication group and a non-medication group according to whether they contained the rs10305492-A allele. The same Cox proportional hazards model regression as in Example 1 was carried out on the high-risk population to determine whether the population could reduce their risk of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com