Directional coupler and beam splitter thereof
A technology of directional coupler and coupled waveguide, which is applied to instruments, light guides, optics, etc., and can solve problems such as unfavorable processing, reduced bandwidth of directional couplers, and large insertion loss.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
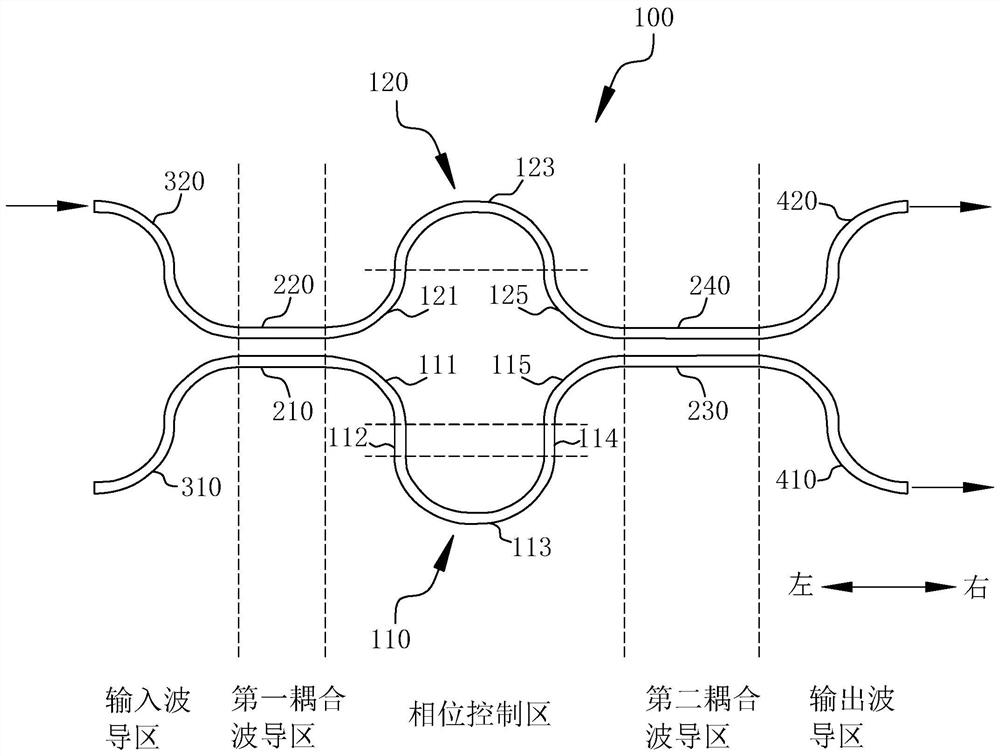
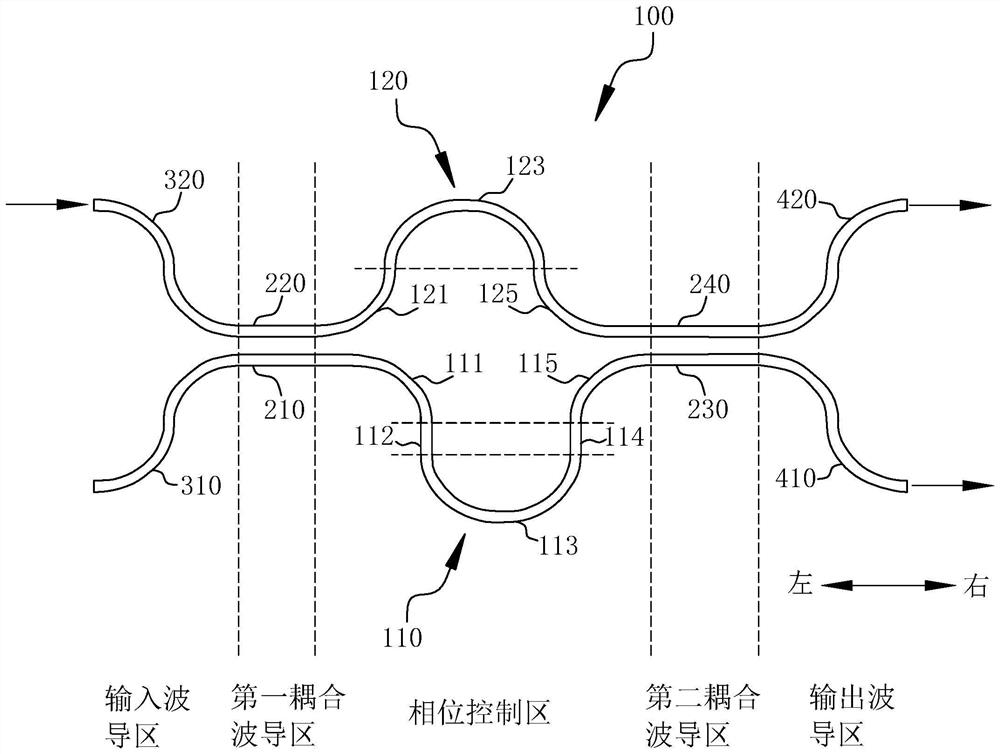
[0055] based on figure 1 In the shown structure, the input optical signal is input into the directional coupler 100 from the second input waveguide 320. When the input optical signal is transmitted to the first coupling waveguide region, the input optical signal will be divided into The through optical signal and the coupled optical signal transmitted in the first coupling waveguide 210, and subsequently, the through optical signal and the coupled optical signal respectively go through different optical paths in the corresponding first phase shifting arm 110 and the second phase shifting arm 120, Therefore, a specific phase difference is generated, and then, the through optical signal and the coupled optical signal with a phase difference between them will be coupled twice in the second coupling waveguide region, and then the first output waveguide 410 and the second output waveguide 420 are respectively Outputs two optical signals with a specific split ratio and has wide band...
example 2
[0058] based on figure 1 In the shown structure, the input optical signal is input into the directional coupler 100 from the second input waveguide 320. When the input optical signal is transmitted to the first coupling waveguide region, the input optical signal will be divided into The through optical signal and the coupled optical signal transmitted in the first coupling waveguide 210, and subsequently, the through optical signal and the coupled optical signal respectively go through different optical paths in the corresponding first phase shifting arm 110 and the second phase shifting arm 120, Therefore, a specific phase difference is generated, and then, the through optical signal and the coupled optical signal with a phase difference between them will be coupled twice in the second coupling waveguide region, and then the first output waveguide 410 and the second output waveguide 420 are respectively Outputs two optical signals with a specific split ratio and has wide band...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com