Power amplification module
A power amplifier module and power stage technology, applied in power amplifiers, amplifiers, radio frequency amplifiers, etc., can solve problems such as larger deviation of impedance conversion circuits, longer signal paths, and increased parasitic resistances.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0069] refer to Figure 1 to Figure 5 The accompanying drawings illustrate the power amplifying module of the first embodiment.
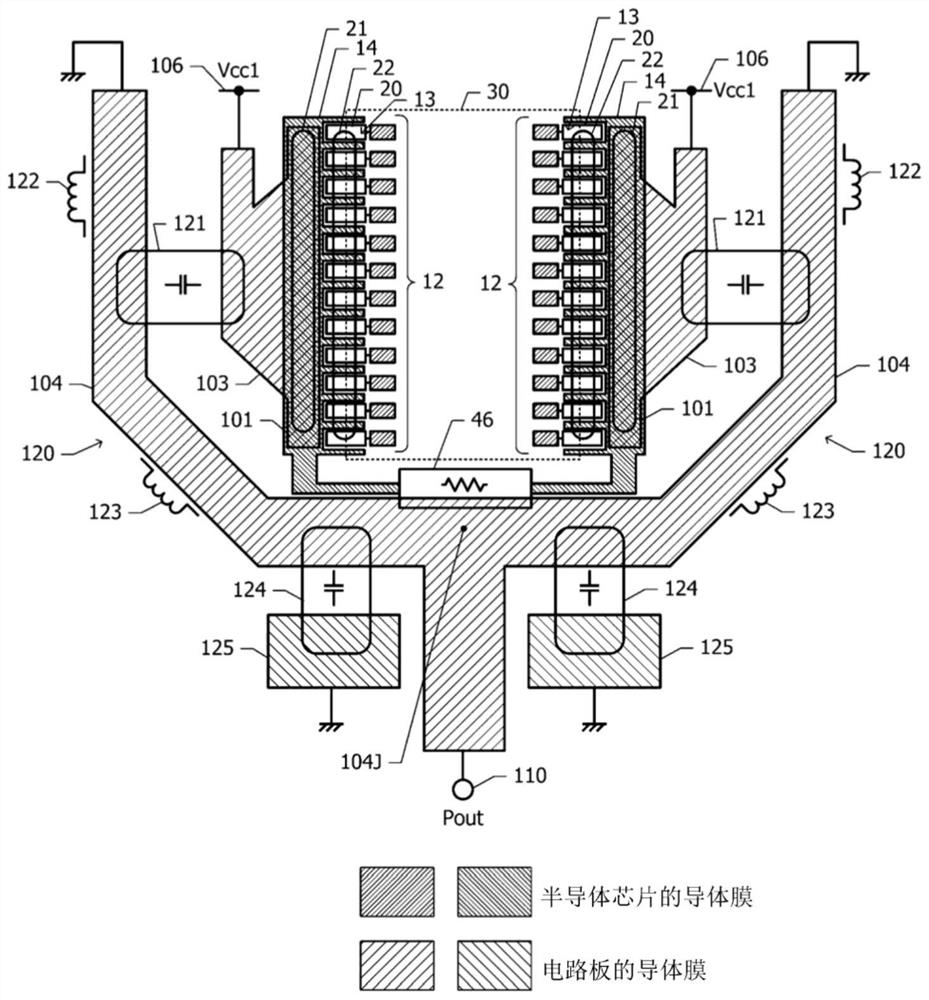
[0070] figure 1 It is a diagram showing the positional relationship in plan view of a plurality of constituent elements of the power stage amplifying circuit and the output impedance converting circuit of the power amplifying module of the first embodiment. The power amplifying module of the first embodiment has a semiconductor chip and a circuit board. exist figure 1 In this method, relatively thick shading is given to the conductor film formed on the semiconductor chip, and relatively light shading is given to the conductor film formed on the circuit board.
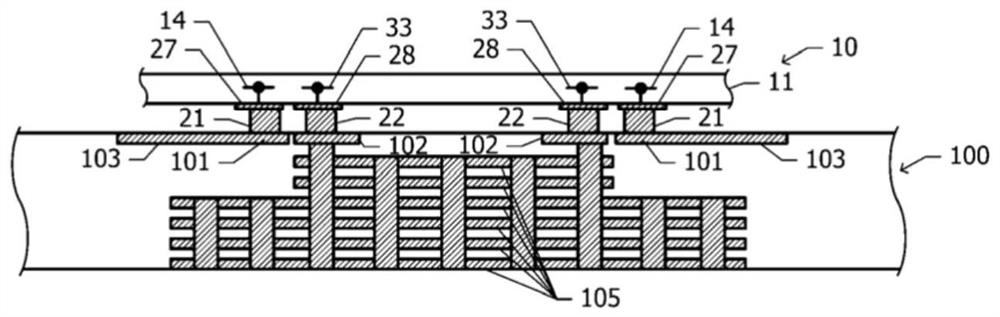
[0071] First, the structure of a semiconductor chip will be described. The semiconductor chip includes a substrate made of a semiconductor, and two transistor columns 12 arranged on the substrate. Each of the two transistor columns 12 includes a plurality (for example, 12) of power stage ...
no. 2 example
[0123] Next, refer to Figure 10 as well as Figure 11 , to describe the power amplifying module of the second embodiment. Hereinafter, for the power amplifying module ( Figure 1 to Figure 5 Accompanying drawing) common structure, omit description.
[0124] Figure 10 It is a diagram showing the positional relationship in plan view of a plurality of constituent elements of the power stage amplifying circuit and the output impedance converting circuit of the power amplifying module of the second embodiment. exist Figure 10 in, also with figure 1 Similarly, relatively thick shadows are added to the conductor film provided on the semiconductor chip 10, and relatively thick shadows are applied to the conductor film provided on the circuit board 100 ( figure 2 ) is shaded relatively lightly.
[0125] In the first embodiment, the first bump 21 and the collector wiring 14 ( figure 1 ) are connected in a direct current manner. In contrast, in the second embodiment, the fir...
no. 3 example
[0135] Next, refer to Figure 12 , to describe the power amplifying module of the third embodiment. Below, for Figure 1 to Figure 5 The common structure of the power amplifying module of the first embodiment shown in the accompanying drawings is omitted.
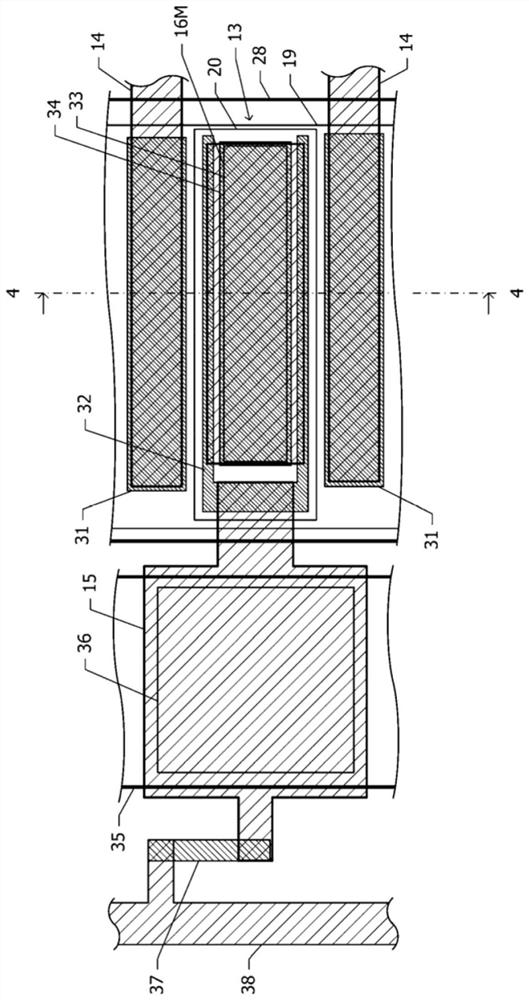
[0136] Figure 12 It is a diagram showing the positional relationship in plan view of a plurality of constituent elements of the power stage amplifying circuit and the output impedance converting circuit of the power amplifying module of the third embodiment. In the first embodiment, the two transistor columns 12 are arranged along two opposing sides of the rectangular convex polygon 30 . In contrast, in the third embodiment, two transistor columns 12 are arranged along two sides of a square convex polygon 30 adjacent to each other.
[0137] The respective collector mesas 20 of the power stage transistors 13 have a long shape in a direction forming 45° with respect to the sides of the convex polygon 30 in plan view. Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com