Non-dairy analogs with succinylated plant proteins and methods using such products
A technology for succinylation, analogues, used in the field of food products to address issues of taste, health and/or nutritional impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0178] Example 1: Preparation of succinylated refined protein from pea flour.
[0179] This example illustrates a method for preparing a succinylated refined protein that can be used in the compositions (compositions), formulations (formulations) and methods of the present disclosure.
[0180] Materials and methods: Pea flour (Ingredion, Westchester, IL) was added to distilled water adjusted to pH 8.5 with 6N sodium hydroxide while stirring for about 30 to 60 min to achieve a final solids concentration of 20% w / w. The pea flour extract was isolated by centrifugation at between 5,000 to 15,000 g for about 10 minutes. The supernatant was kept as an extract, while the pellet was discarded. The supernatant was centrifuged again to remove (or substantially remove) solids from it. Succinic anhydride (0.5 g succinic anhydride / g protein) was slowly added to the supernatant while stirring. Throughout the addition, 6N sodium hydroxide was added to maintain the pH of the mixture aro...
Embodiment 2
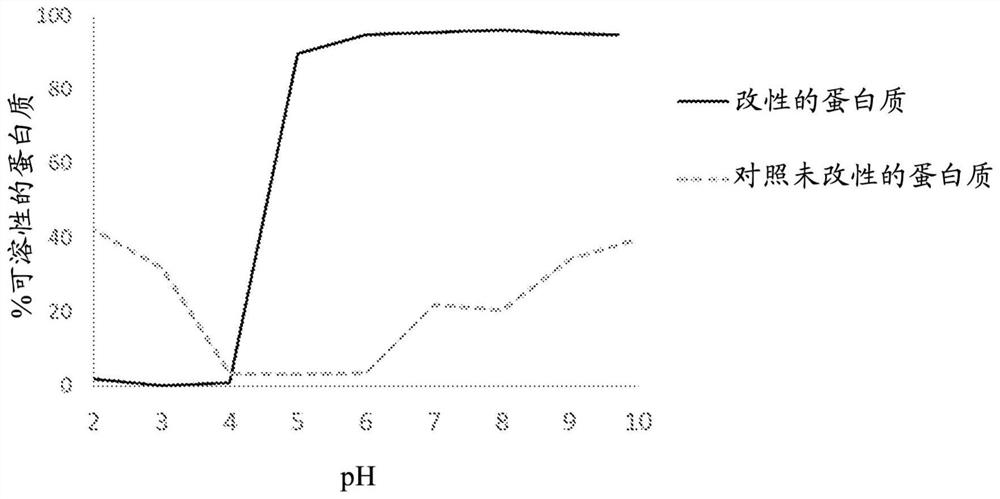
[0181] Example 2: Isoelectric point and increased solubility curve of succinylated refined protein from pea flour.
[0182] This example illustrates the characterization of the effect of succinylation on the isoelectric point and protein solubility profile of refined pea proteins.
[0183] Materials and methods: An unmodified refined pea protein paste (control) was prepared as in Example 1, but without the addition of any succinic anhydride and the precipitation pH was adjusted to pH 5.5. A succinylated refined protein paste was prepared as in Example 1. Both the control and succinylated protein pastes were dissolved at 10% by weight in ~150 mL of separate aqueous solutions. Aliquots (5 mL) of each solution were removed and total protein content was checked using a protein combustion assay on a Leco CN828 (Leco Corporation, St. Joseph, MI, USA). Titration of each solution was performed with 1N hydrochloric acid and 1N sodium hydroxide. Aliquots (5 mL) of each solution at ...
Embodiment 3
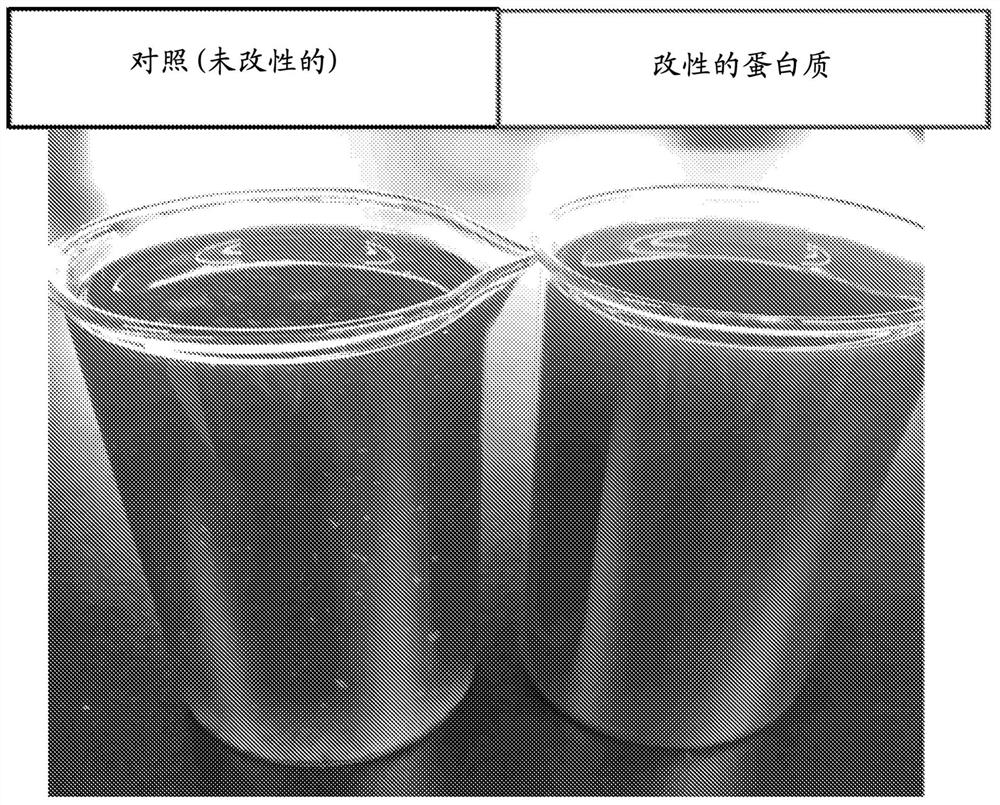
[0185] Example 3: Comparison of feathering in coffee with non-dairy analogues made using unmodified or succinylated refined pea protein.
[0186] This example illustrates the measurement and comparison of the coffee Experiments with the feathering properties in .
[0187] Materials and methods: Succinylated refined pea protein was prepared as provided in Example 1 (50% by weight succinic anhydride for protein). An unmodified refined pea protein paste (control) was prepared as in Example 1, but without the addition of any succinic anhydride and the precipitation pH was adjusted to pH 5.5. Sweetener-free non-dairy analogs were formulated and prepared as described in Example 5 using 100% unmodified refined pea protein or 50% unmodified to 50% succinylated refined pea protein. The protein content of both non-dairy analog compositions was about 3.3% by weight. The coffee was heated to a temperature between 65-70°C before being mixed with the non-dairy analogue. The non-dairy ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com