Preparation method and application of pancreatic progenitor cells
A technology of pancreatic progenitor cells and cells, which is applied in the field of preparation of pancreatic progenitor cells, can solve problems such as the inability to elucidate the complexity of the molecular network of pancreatic organs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0021] First, an embodiment of the present invention provides a method for preparing pancreatic progenitor cells, which includes: using a differentiation inducer to induce the differentiation of hindgut cells into pancreatic progenitor cells;
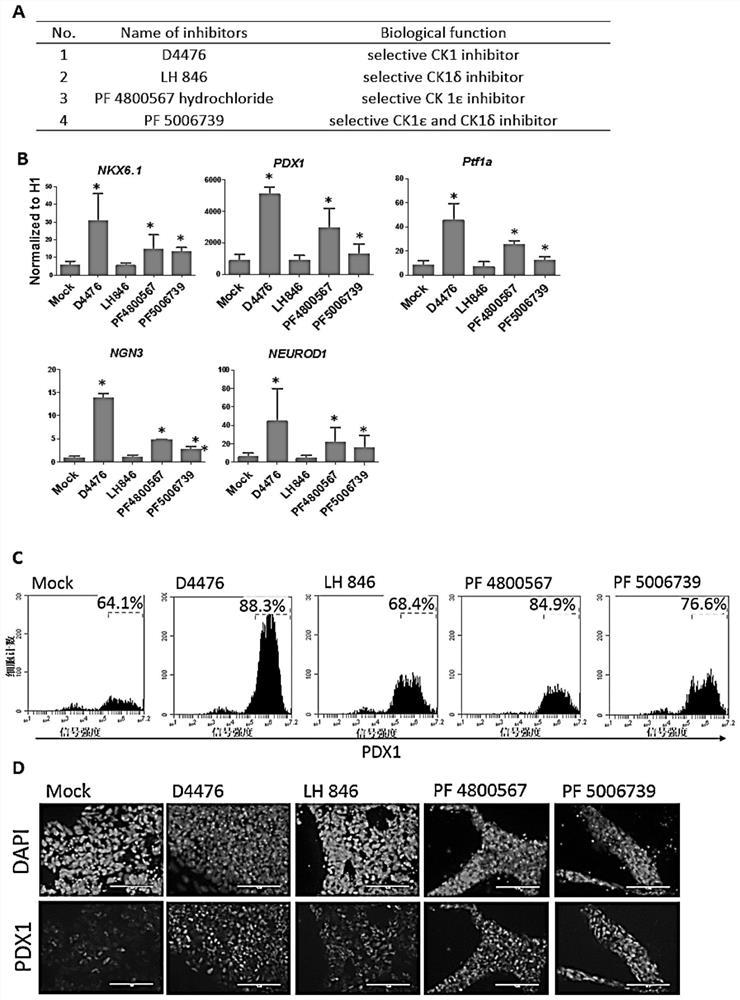
[0022] Such differentiation-inducing agents include casein kinase 1 inhibitors.
[0023] The "posterior hindgut cell" in this article is the same as the posterior foregut cell.
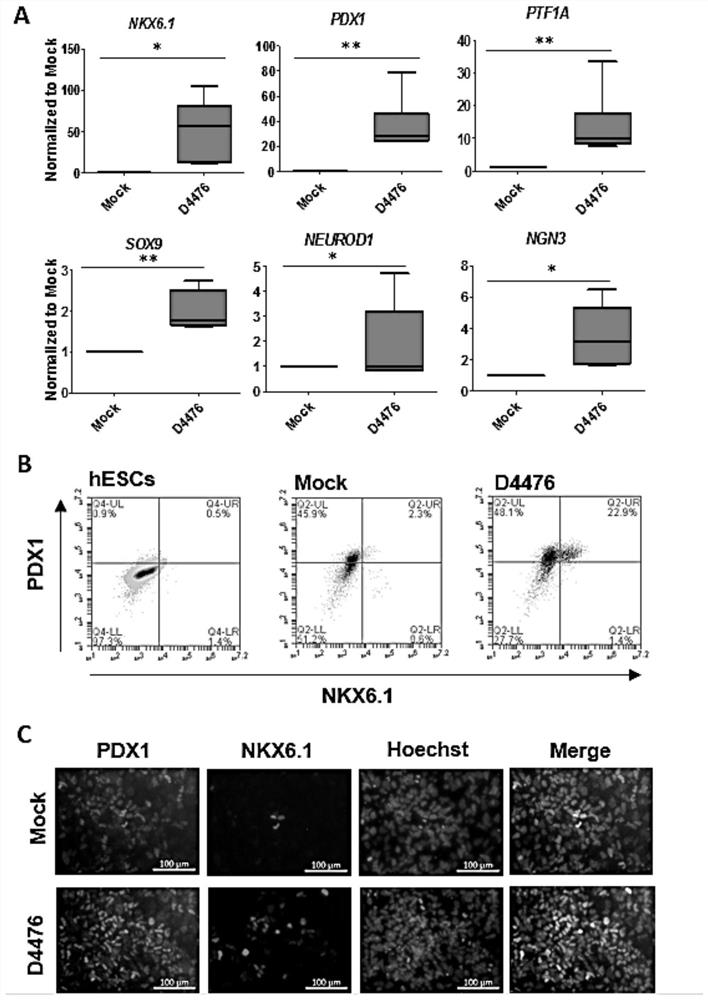
[0024] Casein kinase 1 inhibitors, referred to as CK1 inhibitors for short, the inventors have found through research that CK1 inhibitors play a key role in the process of inducing posterior segment cells to differentiate into pancreatic progenitor cells. In the case of no serum addition (that is, the chemical composition is determined), it can effectively promote the differentiation of posterior segment cells into pancreatic progenitor cells.
[0025] In some embodiments, "using a differentiation-inducing agent to induce the differentiation of the hindgut cel...
Embodiment 1
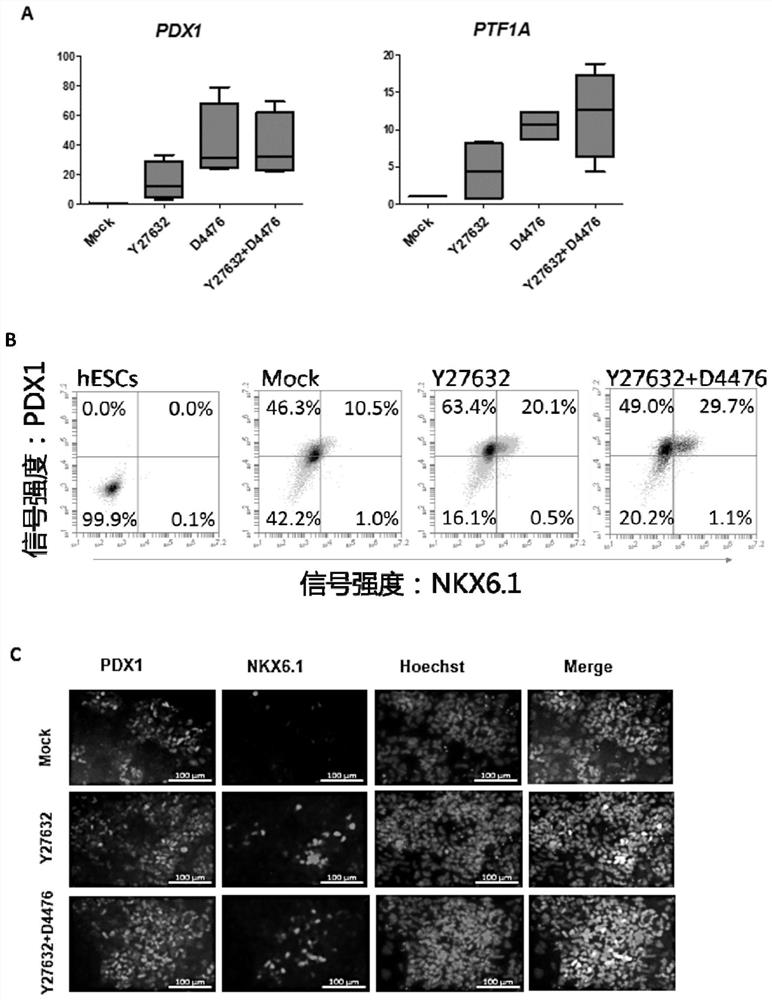
[0087] To verify the effect of different CK1 inhibitors in the preparation of pancreatic progenitor cells.
[0088] In this example, four CK1 inhibitors, D4476, LH 846, PF 4800567 and PF 5006739, were selected and treated on the 11th to 13th day of differentiation to detect their effects on the differentiation of pancreatic progenitor cells and induce human embryonic stem cells to differentiate into pancreatic The method for progenitor cells is as follows:
[0089] Human embryonic stem cells H1 were cultured in E8 medium, and fresh medium was changed every day, and subcultured when the cell density reached 70%-80%; first, wash twice with DPBS-EDTA, and incubate at room temperature for the third time for 5 minutes, and absorb DPBS -EDTA, add E8 medium containing 5 μM ROCK inhibitor, resuspend the cells, spread them in a 24-well plate pre-coated with Matrigel at a density of 1:3-1:6; change to E8 after the cells adhere to the wall for 1 day The medium continues to be cultured; ...
Embodiment 2
[0100] The embodiment of the present invention provides a method for preparing pancreatic progenitor cells, which includes the following steps:
[0101] Human embryonic stem cells H1 were cultured in E8 medium, and fresh medium was changed every day, and subcultured when the cell density reached 70%-80%; first, wash twice with DPBS-EDTA, and incubate at room temperature for the third time for 5 minutes, and absorb DPBS -EDTA, add E8 medium containing 5 μM ROCK inhibitor, resuspend the cells, and spread them into 24-well plates pre-coated with Matrigel at a density of 1:3-1:6. One day after the cells adhered to the wall, the E8 medium was changed to continue culturing. When the cells grew to 40%-50%, they began to differentiate. On the first day of differentiation, E5 differentiation medium containing CHIR99021 with a final concentration of 5 μM and Activin A with a final concentration of 100 ng / ml was added (E8 medium removed TGFβ, FGF2 and insulin , and add Chemically Define...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com