Two-stage homogenization treatment process for H13 die steel
A homogenization treatment and two-stage homogenization technology, applied in the field of materials, can solve the problems of coarse grains and high process costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] A two-stage homogenization treatment process for H13 die steel, the specific operation steps include:
[0022] (1) H13 hot work die steel is prepared by a certain smelting method, the composition is (mass percentage): C 0.41%, Si 1.11%, Mn 0.45%, Cr 5.45%, Mo 1.74%, V 1.15%, unavoidable impurities Content <0.1%, the balance is Fe;
[0023] (2) Put the mold steel into the soaking furnace, firstly perform the first-level homogenization treatment of the cast ingot at 800°C / 3h, and water-cool to room temperature after the heat preservation is completed;
[0024] (3) Place the mold steel after primary homogenization treatment in a soaking furnace, perform secondary homogenization treatment at 1200°C / 1h, and water cool to room temperature after heat preservation.
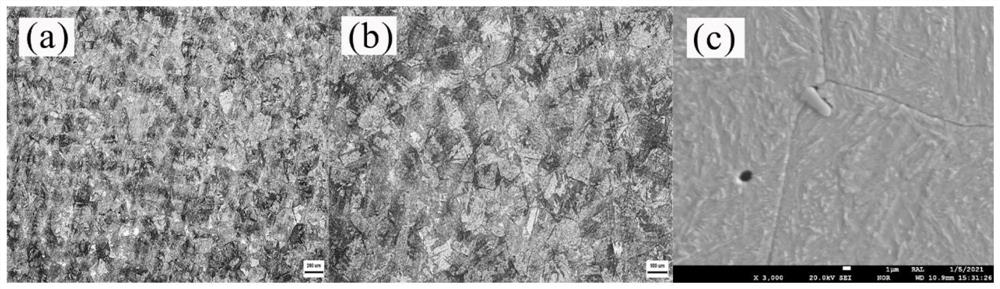
[0025] The microstructure of the H13 die steel sample after two-stage homogenization treatment is as follows: figure 1 shown. figure 1 (a) shows the dendrite segregation morphology. It can be seen that the dendr...
Embodiment 2
[0027] A two-stage homogenization treatment process for H13 die steel, the specific operation steps include:
[0028] (1) H13 hot work die steel is prepared by a certain smelting method, the composition is (mass percentage): C 0.37%, Si 1.01%, Mn 0.35%, Cr 5.15%, Mo 1.47%, V 1.01%, unavoidable impurities Content <0.1%, the balance is Fe;
[0029] (2) Put the die steel into the soaking furnace, and firstly perform the first-level homogenization treatment of the cast ingot at 800°C / 2h, and then water-cool to room temperature after the heat preservation is completed;
[0030] (3) Place the mold steel after primary homogenization treatment in a soaking furnace, perform secondary homogenization treatment at 1200°C / 2h, and water cool to room temperature after heat preservation.
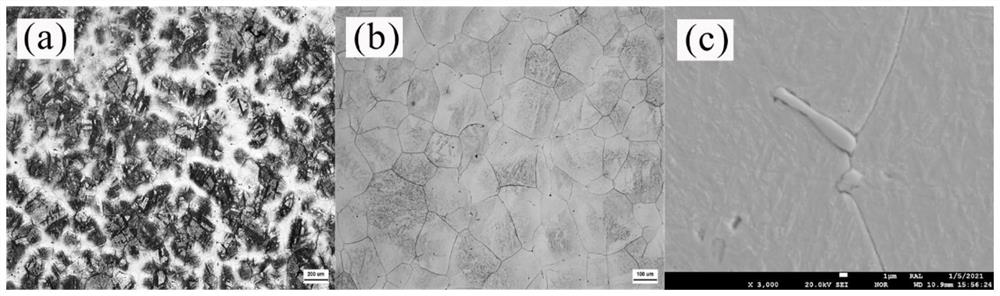
[0031] The microstructure of the H13 die steel sample after two-stage homogenization treatment is as follows: figure 2 shown. figure 2 (a) shows the dendrite segregation morphology. It can be seen that...
Embodiment 3
[0033] A two-stage homogenization treatment process for H13 die steel, the specific operation steps include:
[0034] (1) H13 hot work die steel is prepared by a certain smelting method, the composition is (mass percentage): C 0.33%, Si0.89%, Mn 0.26%, Cr 4.82%, Mo 1.28%, V 0.83%, unavoidable impurities Content <0.1%, the balance is Fe;
[0035] (2) Put the die steel into the soaking furnace, firstly perform the first-level homogenization treatment of the cast ingot at 800°C / 1h, and water-cool to room temperature after the heat preservation is completed;
[0036] (3) Place the mold steel after primary homogenization treatment in a soaking furnace, perform secondary homogenization treatment at 1200°C / 3h, and water cool to room temperature after heat preservation.
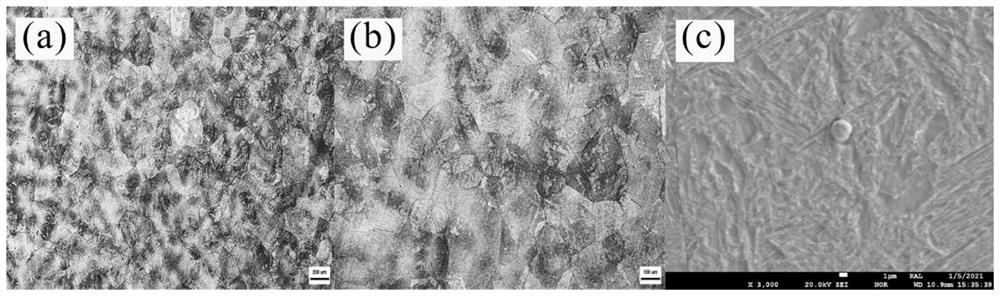
[0037] The microstructure of the H13 die steel sample after two-stage homogenization treatment is as follows: image 3 shown. image 3 (a) shows the dendrite segregation morphology. It can be seen that the dendrit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| microhardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com